20 Javascript Global Variable Naming
Understanding variable scope in JavaScript is one of the keys to building a solid foundation in the language. ... As this simple example shows, the variable name is global. It's defined in the ... In JavaScript, variables have two primary scopes i.e. Private Scope and Global Scope. Let us understand the JavaScript variable scopes with some examples. Understanding JavaScript Global Scope Variables. In the below example, we declare a variable called x outside of any JavaScript function and when you do so, it becomes a global scope variable.
 How To Create And Use Powershell Global Variable Spguides
How To Create And Use Powershell Global Variable Spguides
One popular pattern for namespacing in JavaScript is opting for a single global variable as our primary object of reference. A skeleton implementation of this where we return an object with functions and properties can be found below: var myApplication = (function () { function() { //... }, return{ //...

Javascript global variable naming. The names of variables, called identifiers, conform to certain rules. A JavaScript identifier must start with a letter, underscore (_), or dollar sign ($). Subsequent characters can also be digits (0 - 9). Let’s see the simple example of global variable in JavaScript. <script>var value=50;//global variablefunction a(){alert(value);}function b(){alert(value);}</script>. Test it Now. Declaring JavaScript global variable within function. The reason I sometimes use php name-conventions with javascript variables: When doing input validation, I want to run the exact same algorithms both client-side, and server-side. I really want the two side of code to look as similar as possible, to simplify maintenance. Using dollar signs in variable names makes this easier.
In a web page, global variables belong to the window object. Global variables can be used (and changed) by all scripts in the page (and in the window). In the first example, a is a local variable. A local variable can only be used inside the function where it is defined. It is hidden from other functions and other scripting code. Global and ... JavaScript variables have only two scopes. Global Variables − A global variable has global scope which means it can be defined anywhere in your JavaScript code. Local Variables − A local variable will be visible only within a function where it is defined. Function parameters are always local to that function. Get global variable dynamically by name string in JavaScript? Javascript Web Development Object Oriented Programming. Display in alert by using alert (window ()). Following is the syntax −. alert (window ['yourVariableName' + 'yourVariableName' + otherVariableName]);
Naming Variables Variable names are known as identifiers in JavaScript. We discussed several of the rules of naming identifiers in Understanding Syntax and Code Structure in JavaScript, summarized here: Variable names can consist only of letters (a-z), numbers (0-9), dollar sign symbols ($), and underscores (_) Global Variable. A global variable is one that can be accessed, whether it is retrieving the value of, or assigning a value to it, anywhere in an application. Global variables are used for variables that will need to be accessed throughout an application, like totals, file paths, etc. As a rule of thumb, it is best to avoid using too many ... All JavaScript variables must be identified with unique names. These unique names are called identifiers. Identifiers can be short names (like x and y) or more descriptive names (age, sum, totalVolume). The general rules for constructing names for variables (unique identifiers) are:
I've noticed that everyone is advising global var creation this will lead to variables leak to global namespace. When you dynamically creating classnames or just variables it's easy to keep em local: this['className'] = 123; or . this['varName'] = 123; Name-spacing would look like this: vars = {}; vars['varName'] = 123; vars.varName // 123 If you are wanting a variable that is declared in the global context, it is attached to the window object. ex: window ["variableName"]. All variables are a hash table value within their scope. Variables declared Globally (outside any function) have Global Scope. Global variables can be accessed from anywhere in a JavaScript program. Variables declared with var, let and const are quite similar when declared outside a block. They all have Global Scope:
Variable declarations should always be made using var to not declare them as global variables. This avoids conflicts from using a variable name across different functions as well as conflicts with global variables declared by 3rd party plugins. Good Example. function sum(x, y) { var result = x + y; return result; } Bad Example The scoping within JavaScript is strange too. If a developer forgets to add a var declaration for a particular local variable within a function then the variable is added to the global scope, with the potential of nasty unforeseen side effects. Caplin's JavaScript Naming Convention Naming Conventions. Always use the same naming convention for all your code. For example: Variable and function names written as camelCase; Global variables written in UPPERCASE (We don't, but it's quite common); Constants (like PI) written in UPPERCASE; Should you use hyp-hens, camelCase, or under_scores in variable names?. This is a question programmers often discuss.
Variable Names in JavaScript. Variable names are case-sensitive in JavaScript. So, the variable names msg, MSG, Msg, mSg are considered separate variables. Variable names can contain letters, digits, or the symbols $ and _. A variable name cannot start with a digit 0-9. A variable name cannot be a reserved keyword in JavaScript, e.g. var ... There are no special naming conventions for global JavaScript variables. A global JavaScript variable is declared at the top of a project/file. A global JavaScript variable is written in camelCase if it is mutable. A global JavaScript variable is written in UPPERCASE if it is immutable. The result of this definition is about the same. So, there are indeed reasons why class can be considered a syntactic sugar to define a constructor together with its prototype methods.. Still, there are important differences. First, a function created by class is labelled by a special internal property [[IsClassConstructor]]: true.So it's not entirely the same as creating it manually.
Then the variable a is accessed inside a function and the value changes to 3. Hence, the value of a changes after changing it inside the function. Note: It is a good practice to avoid using global variables because the value of a global variable can change in different areas in the program. It can introduce unknown results in the program. Good naming means easy reading. 5. Introduce intermediate variables. 6. Summary. 1. Prefer const, otherwise use let. I declare my JavaScript variables using const or let. The main difference between the two is that const variable requires an initial value, and its value can not be reassigned once initialized. So the global object will ultimately be searched for unqualified identifiers. You don't have to type globalThis.String, you can just type the unqualified String.The corollary, in non-strict mode, is that assignment to unqualified identifiers will, if there is no variable of the same name declared in the scope chain, assume you want to create a property with that name on the global object.
There is an alternative in JavaScript because all globally scoped variables are appended to the window object array. Hence, any variable created outside of a function or object, whether using the 'var' keyword or not, is appended to the global window namespace. That being the case, why not explicitly add them? Function.name. A Function object's read-only name property indicates the function's name as specified when it was created, or it may be either anonymous or '' (an empty string) for functions created anonymously. Note: In non-standard, pre-ES2015 implementations the configurable attribute was false as well. So my global variables would be named: var foo_lastnameGlobal; var bar_lastnameGlobal; I should point out (in case it isn't clear) this is just a personal convention, not a common or widely used one. It also helps me remember what my global variables are when I do use them.
Window object: JavaScript always has a global object defined. When the program creates global variables they're created as members of the global object. The window object is the global object in the browser. Any global variables or functions can be accessed with the window object. Global object. A global object is an object that always exists in the global scope. In JavaScript, there's always a global object defined. In a web browser, when scripts create global variables defined with the var keyword, they're created as members of the global object. (In Node.js this is not the case.) Global variables in JavaScript are variables declared outside of a function scope. Global objects should be organized in a global namespace (e.g., yourApp.*). SAP follows the OpenAjax concept for namespaces and reserves the sap namespace officially for SAP.
In javaScript global variables are variables that can be accessed from anywhere within a body of javaScript code, and are therefor at the global name space. In most environments global variables are also part of what is often called the global object, in client side javaScript this is typically the window object.
 Javascript Variable In Google Tag Manager Analytics Mania
Javascript Variable In Google Tag Manager Analytics Mania
 Using Variables Postman Learning Center
Using Variables Postman Learning Center
 Tools Qa What Are Javascript Variables And How To Define
Tools Qa What Are Javascript Variables And How To Define
 Python Variables How To Define Declare String Variable Types
Python Variables How To Define Declare String Variable Types
 Difference Between Local And Global Variable
Difference Between Local And Global Variable
 How To Change The Value Of A Global Variable Inside Of A
How To Change The Value Of A Global Variable Inside Of A
Internet Explorer Global Variable Blow Ups Rick Strahl S
 Javascript Correct Way To Define Global Variables
Javascript Correct Way To Define Global Variables
 What Is Global Variable Name In Javascript Variable Targeting
What Is Global Variable Name In Javascript Variable Targeting
A Horrifying Globalthis Polyfill In Universal Javascript
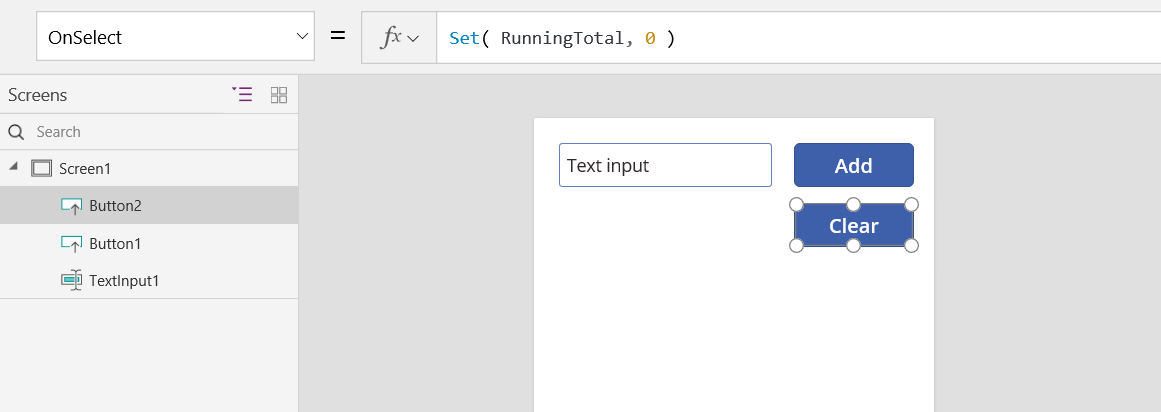 Understand Variables In Canvas Apps Power Apps Microsoft Docs
Understand Variables In Canvas Apps Power Apps Microsoft Docs
 Comprehending Variables Statement And Expression In
Comprehending Variables Statement And Expression In

 Global And Local Variables In Javascript Geeksforgeeks
Global And Local Variables In Javascript Geeksforgeeks
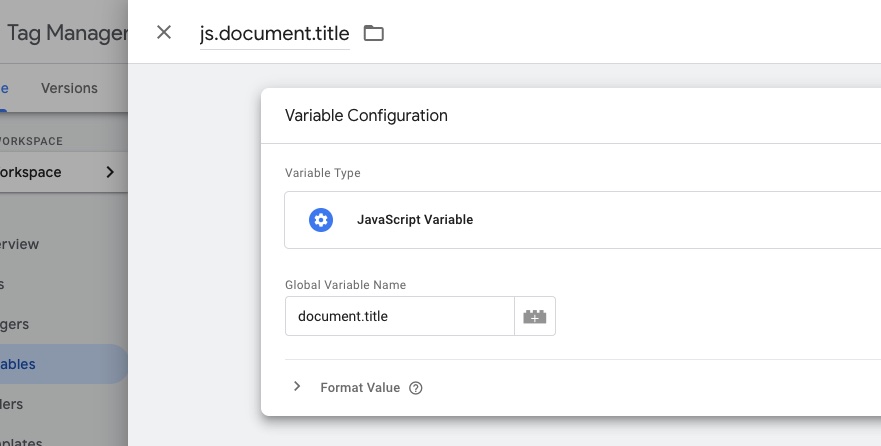 The Javascript Variable Type In Google Tag Manager Hume Dev
The Javascript Variable Type In Google Tag Manager Hume Dev
 Window Variable Javascript Declare Global Variables Inside
Window Variable Javascript Declare Global Variables Inside
 Global Variable Name Is Marked Deprecated Issue 114725
Global Variable Name Is Marked Deprecated Issue 114725

0 Response to "20 Javascript Global Variable Naming"
Post a Comment