21 What Is Module Exports Javascript
The module.exports in Node.js is used to export any literal, function or object as a module. It is used to include JavaScript file into node.js applications. The module is similar to variable that is used to represent the current module and exports is an object that is exposed as a module. Because of this, ECMAScript 2015 supports the use of JavaScript modules. A module is a bundle of code that acts as an interface to provide functionality for other modules to use, as well as being able to rely on the functionality of other modules. A module exports to provide code and imports to use other code.
 Javascript Modules Cheat Sheet And Comparison Joshua S Docs
Javascript Modules Cheat Sheet And Comparison Joshua S Docs
The ES Module (ESM) format. As of ES6 (ES2015), JavaScript supports a native module format. It uses an export keyword to export a module's public API and an import keyword to import it. The...

What is module exports javascript. In practice, there are mainly two kinds of modules. Modules that contain a library, pack of functions, like say.js above. Modules that declare a single entity, e.g. a module user.js exports only class User. Mostly, the second approach is preferred, so that every "thing" resides in its own module. The module is a plain JavaScript Object representing the current module. It is local to each module and also it is private. It has exports property which is a plain JavaScript variable, set to module.exports. At the end of the file, Node.js return module.exports to the required function. So you see that this returns a Module which is an object that has properties like id, exports, parent, etc. Well, let me show you how to add properties and functions to exports objects of that Module Object in Node.js. If we do execute module.exports.title and assign some value to it, then it adds the title to the module. exports object.
exports A reference to the module.exports that is shorter to type. See the section about the exports shortcut for details on when to use exports and when to use module.exports. 출처: Node.js v10.6.0... Node Module Exports Explained - With JavaScript Export Function Examples One of the most powerful things about software development is the ability to reuse and build upon the foundations of other people. This code sharing has helped software progress at an amazing rate. export The export statement is used when creating JavaScript modules to export live bindings to functions, objects, or primitive values from the module so they can be used by other programs with the import statement. The value of an imported binding is subject to change in the module that exports it.
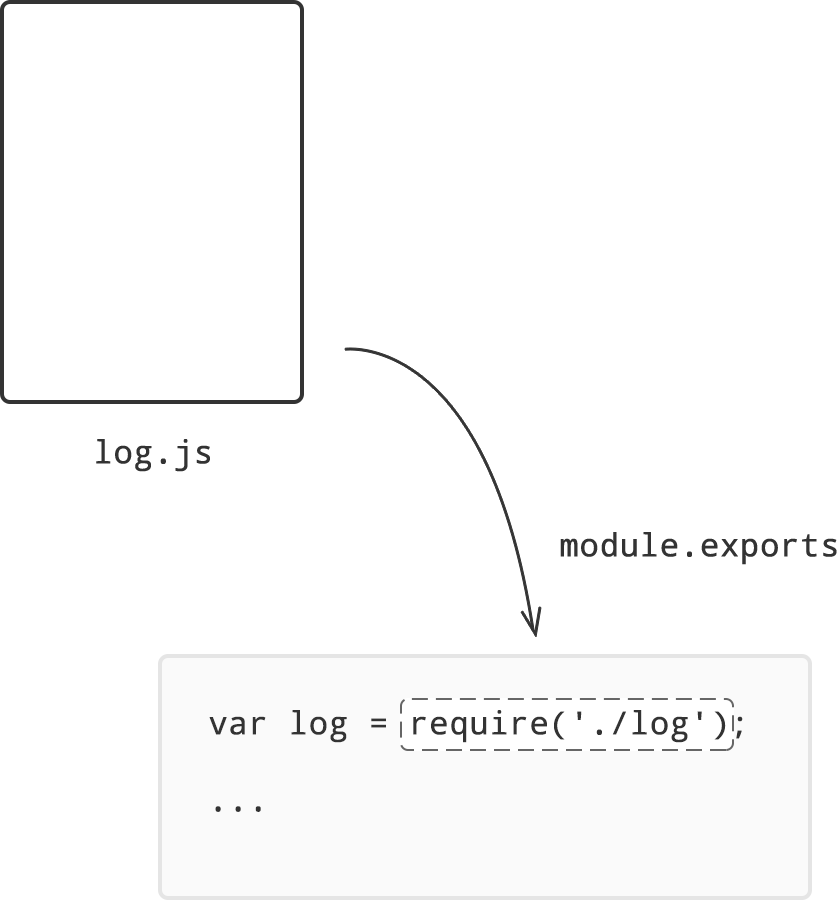
As our application grows bigger, we want to split it into multiple files, so called "modules". A module may contain a class or a library of functions for a specific purpose. For a long time, JavaScript existed without a language-level module syntax. That wasn't a problem, because initially scripts were small and simple, so there was no need. A module is a discrete program, contained in a single file in Node.js. Modules are therefore tied to files, with one module per file. Modules are available in other programming languages. Node.JS uses the CommonJS system of modules, but there are other module types used in the JavaScript ecosystem. Exports vs module.exports . The module is a plain Javascript object with an exports property. module refers to the object representing the current module. This holds the metadata about the module such as filename of the current module and export object. Log the value of the module and module.exports in the date.js file and execute the date.js ...
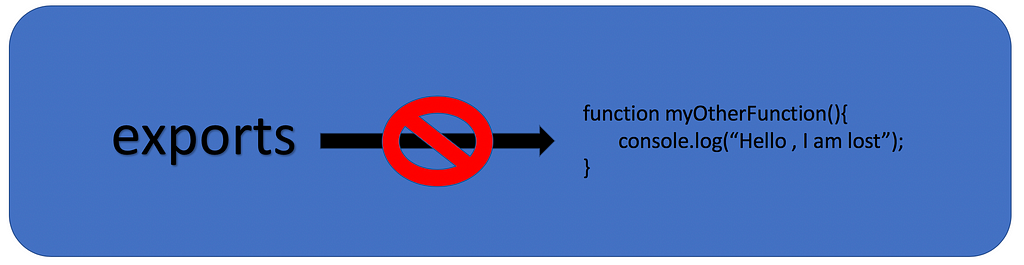
Basically node.js doesn't export the object that exports currently references, but exports the properties of what exports originally references. Although Node.js does export the object module.exports references, allowing we to call it like a function.; 2nd least important reason; They set both module.exports and exports to ensure exports isn't referencing the prior exported object. module.exports wins. What this means is that whatever object module.exports is assigned to is the object that is exported from your module. If you want to export a function from your module and you assign it to exports and not module.exports then this happens: Ruh roh! Your module will export an empty object, not the function that you probably ... Module exports are the instruction that tells Node.js which bits of code (functions, objects, strings, etc.) to "export" from a given file so other files are allowed to access the exported code. (Don't worry, we'll cover importing code in the next section.)
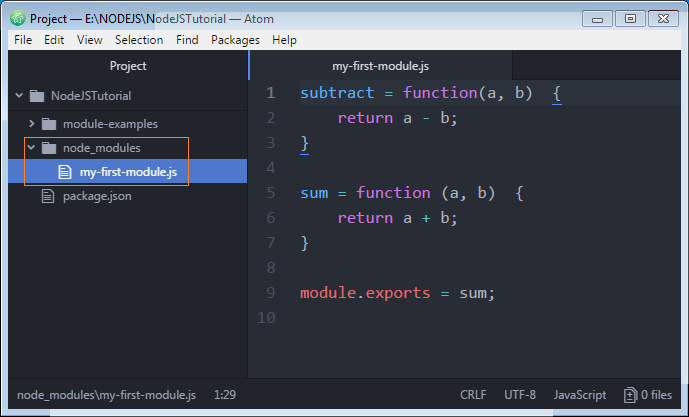
So, now they become official names for outsiders to be applied for imports. Export Default¶. In practice, there exist two types of modules.. Modules, containing a library, pack of functions ( for example, welcome.js). Modules, declaring a single entity ( for example, site.js exports only class Site). The second approach is preferred most of the time. module.exports is the object that's actually returned as the result of a require call. The exports variable is initially set to that same object (i.e. it's a shorthand "alias"), so in the module code you would usually write something like this: Module.exports It is the object reference that gets returned from the require () calls. It is automatically created by Node.js. It is just a reference to a plain JavaScript object.
A module groups related code into one single, separate unit of code. This can also be seen as moving related functions into a separate file by creating a module. Both the module.exports property and the exports object allow a module to choose what to share with the application. module.exports and exports First, exports is the […] The module.exports is a special object which is included in every JavaScript file in the Node.js application by default. The module is a variable that represents the current module, and exports is an object that will be exposed as a module. So, whatever you assign to module.exports will be exposed as a module. Because of this, ECMAScript 2015 supports the use of JavaScript modules. A module is a bundle of code that acts as an interface to provide functionality for other modules to use, as well as being able to rely on the functionality of other modules. A module exports to provide code and imports to use other code.
What is a Module in Node.js? Consider modules to be the same as JavaScript libraries. A set of functions you want to include in your application. There is also a type of export called the default export — this is designed to make it easy to have a default function provided by a module, and also helps JavaScript modules to interoperate with existing CommonJS and AMD module systems (as explained nicely in ES6 In Depth: Modules by Jason Orendorff; search for "Default exports"). Exporting Module export - The export statement is used when creating JavaScript modules to export functions, objects, or primitive values from the module so they can be used by other programs with the import statement. There are two different types of export - named and default.
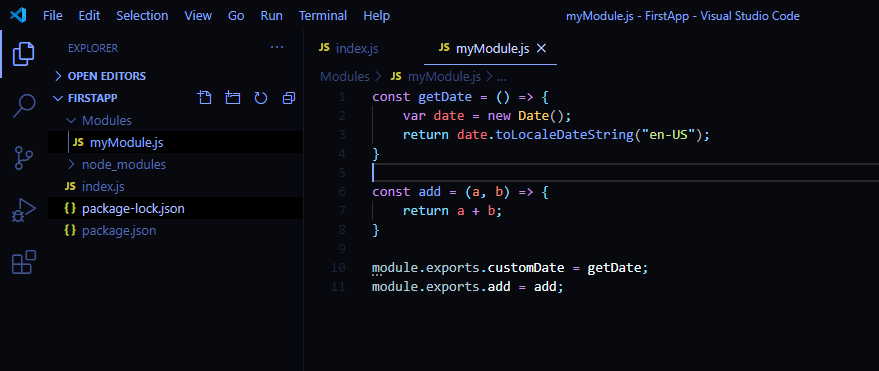
module.exports is an object that the current module returns when it is "required" in another program or module. Whenever we want something like values or functions to be available for another module to import and use, we attach that value or function with this module.exports. Example: Export a few properties from one module: In JavaScript, you can export modules in three different ways: by placing the export statement before the module: export const .. syntax; Or in a separate line: export { a, b, c} You can also specify a default export with export default .. And named export with export {xyz as abc} Then you can also import these modules as: Before a module's code is executed, Node.js will wrap it with the module wrapper. By doing so, we can achieve module scoped variables that don't leak out to the global object, and we also get access to module-specific variables like module and exports. The exports shortcut is assigned the value of module.exports.
Welcome to javascript course. This is a new javascript course designed, created and recorded fresh in 2020. This course will give you a fantastic start for y... Each JavaScript file in Node has a module.exports object in its global scope that represents that specific file. That object will hold any code that we want to export from the file. We can assign...
 Modules Part 2 Writing Modules
Modules Part 2 Writing Modules
 Node Js Creating And Using Modules Parallelcodes
Node Js Creating And Using Modules Parallelcodes
 Module Exports Javascript Function Inside Add Api Code Example
Module Exports Javascript Function Inside Add Api Code Example
 Understanding Module Exports And Exports In Node Js
Understanding Module Exports And Exports In Node Js
 Module Exports Vs Exports In Node Js Stack Overflow
Module Exports Vs Exports In Node Js Stack Overflow
 Node Js Module Exports And Require By Levi Chen Levi Chen
Node Js Module Exports And Require By Levi Chen Levi Chen
 Understanding Module Exports And Exports In Node Js
Understanding Module Exports And Exports In Node Js
 Mixing Module Exports With Exports Jake Trent
Mixing Module Exports With Exports Jake Trent
 What Is The Purpose Of Node Js Module Exports And How Do You
What Is The Purpose Of Node Js Module Exports And How Do You
 How To Optimize Module Encapsulation In Node Js Dev Community
How To Optimize Module Encapsulation In Node Js Dev Community
Learn And Understand Nodejs 027 Exports Vs Module Exports
 Understanding Module Exports Exports And Different Type Of
Understanding Module Exports Exports And Different Type Of
 How To Export Class In Node Js Code Example
How To Export Class In Node Js Code Example
 4 08 How Do Node Modules Really Work Module Exports And
4 08 How Do Node Modules Really Work Module Exports And
 3 Modularizing And Managing Javascript Modern Javascript
3 Modularizing And Managing Javascript Modern Javascript
Every Thing You Should Know About Javascript Export By
 How To Use Module Exports In Node Js
How To Use Module Exports In Node Js
 Unknown Facts About Exports And Module Exports In Node Js
Unknown Facts About Exports And Module Exports In Node Js
0 Response to "21 What Is Module Exports Javascript"
Post a Comment