24 What Is A Function Called In Javascript
JavaScript Define & Call Functions with Example What is Function in JavaScript? Functions are very important and useful in any programming language as they make the code reusable A function is a block of code which will be executed only if it is called. Functions are defined, or declared, with the function keyword. Below is the syntax for a function in JavaScript. function nameOfFunction() { } The declaration begins with the function keyword, followed by the name of the function.
 How To Get The Scope From Where A Function Was Called
How To Get The Scope From Where A Function Was Called
The JavaScript call () Method. The call () method is a predefined JavaScript method. It can be used to invoke (call) a method with an owner object as an argument (parameter). With call (), an object can use a method belonging to another object. This example calls the …

What is a function called in javascript. A JavaScript function is defined with the function keyword, followed by a name, followed by parentheses (). Function names can contain letters, digits, underscores, and dollar signs (same rules as variables). The parentheses may include parameter names separated by commas: (parameter1, parameter2,...) Here are the two functions - add (a, b, callback) and disp (). Here add () is called with the disp () function i.e. passed in as the third argument to the add function along with two numbers. As a result, the add () is invoked with 1, 2 and the disp () which is the callback. 21/6/2021 · We declare functions listing their parameters, then call them passing arguments. In the example above, one might say: "the function showMessage is declared with two parameters, then called with two arguments: from and "Hello"". Default values. If a function is called, but an argument is not provided, then the corresponding value becomes undefined.
Calling Functions: After defining a function, the next step is to call them to make use of the function. We can call a function by using the function name separated by the value of parameters enclosed between parenthesis and a semicolon at the end. Below syntax shows how to call functions in JavaScript: functionName( Value1, Value2, ..); Description The call () allows for a function/method belonging to one object to be assigned and called for a different object. call () provides a new value of this to the function/method. With call (), you can write a method once and then inherit it in another object, without having to rewrite the method for the new object. When it is used like that, the rest operator enables the developer to create functions that can take an indefinite number of arguments, also called functions of variable arity or variadic functions. Here's the simplest example of such a function. Let's assume you want to create a function that calculates the sum of all its arguments.
A Function Expression is created when the execution reaches it and is usable only from that moment. Once the execution flow passes to the right side of the assignment let sum = function… - here we go, the function is created and can be used (assigned, called, etc. ) from now on. Function Declarations are different. Whenever a function is called in JavaScript, regardless of how it is called, two implicit arguments are passed to it. Those 2 implicit arguments are this, the context in which the function will execute and the arguments parameter. The arguments parameter is an array-like structure containing any passed arguments. Its "array-like" but it is ... A callback function is a function that is passed as an argument to another function, to be "called back" at a later time. A function that accepts other functions as arguments is called a higher-order function, which contains the logic for when the callback function gets executed. It's the combination of these two that allow us to extend ...
Javascript: call(), apply() and bind() Omer Goldberg. ... Executes the function it was called upon right away. The call() method does not make a copy of the function it is being called on. Call by Value Vs Call by Reference in JavaScript. Call by Value: Suppose there is a variable named ";a". Now, we store a primitive value (boolean, integer, float, etc) in the variable ";a". Let us store an integer value in ";a", Let a=5. Now the variable ";a" stores 5 and has an address location where that primitive value sits in ... JavaScript Callbacks A callback is a function passed as an argument to another function. Using a callback, you could call the calculator function (myCalculator) with a callback, and let the calculator function run the callback after the calculation is finished:
In regular functions the this keyword represented the object that called the function, which could be the window, the document, a button or whatever. With arrow functions the this keyword always represents the object that defined the arrow function. Let us take a look at two examples to understand the difference. JavaScript does not have any special constructor functions. All we can do is convert a function call into a constructor call using new operator as shown in the above section. When a constructor call is made, a new object is created and set as the function's this argument. Before we use a function, we need to define it. The most common way to define a function in JavaScript is by using the function keyword, followed by a unique function name, a list of parameters (that might be empty), and a statement block surrounded by curly braces.
In JavaScript, a function allows you to define a block of code, give it a name and then execute it as many times as you want. A JavaScript function can be defined using function keyword. It will be called when the document is ready. It is equivalent to: $(document).ready(function() { ... }); Document.ready indicates that the page is fully loaded on the client. WebParts are serverside controls and will be processed first in order to produce the html document sent to the client. An arrow function expression is a compact alternative to a traditional function expression, but is limited and can't be used in all situations.. Differences & Limitations: Does not have its own bindings to this or super, and should not be used as methods. Does not have new.target keyword.; Not suitable for call, apply and bind methods, which generally rely on establishing a scope.
In JavaScript, functions are first-class objects, because they can have properties and methods just like any other object. What distinguishes them from other objects is that functions can be called. In brief, they are Function objects. For more examples and explanations, see also the JavaScript guide about functions. JavaScript Functions. JavaScript functions are used to perform operations. We can call JavaScript function many times to reuse the code. Advantage of JavaScript function. There are mainly two advantages of JavaScript functions. Code reusability: We can call a function several times so it save coding. Less coding: It makes our program compact ... Define a Function. There are a few different ways to define a function in JavaScript: A Function Declaration defines a named function. To create a function declaration you use the function keyword followed by the name of the function.
To create a function in JavaScript we have to use the"function " keyword before writing the name of our function as you can see in given syntax: Syntax of creating function. Function functionname ( parameters list) {. Lines of code to be executed/set of instructions to be executed in order to perform a specific task. } A function definition (also called a function declaration, or function statement) consists of the function keyword, followed by: The name of the function. A list of parameters to the function, enclosed in parentheses and separated by commas. The JavaScript statements that define the function, enclosed in curly brackets, {...}. So, how to call a function in JavaScript? The call function can be invoked as either a function or a method. What is more, it can be performed by using function methods and constructors. We will now review all options one by one, so you could understand the differences and cases in which they should be used.
This is called a JavaScript closure. It makes it possible for a function to have " private " variables. The counter is protected by the scope of the anonymous function, and can only be changed using the add function. A closure is a function having access to the parent scope, even after the parent function has closed. Description. When a return statement is used in a function body, the execution of the function is stopped. If specified, a given value is returned to the function caller. For example, the following function returns the square of its argument, x , where x is a number. If the value is omitted, undefined is returned instead.
 Implement Your Own Call Apply And Bind Method In
Implement Your Own Call Apply And Bind Method In
 Webview Javascript Function Call From Unity C Script No Use
Webview Javascript Function Call From Unity C Script No Use
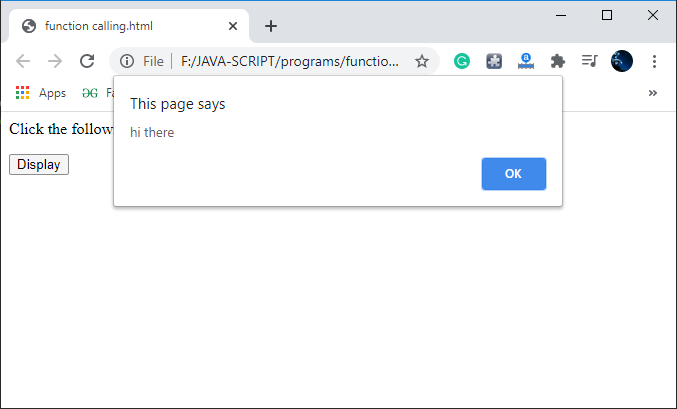 How To Call Javascript Function In Html Javatpoint
How To Call Javascript Function In Html Javatpoint
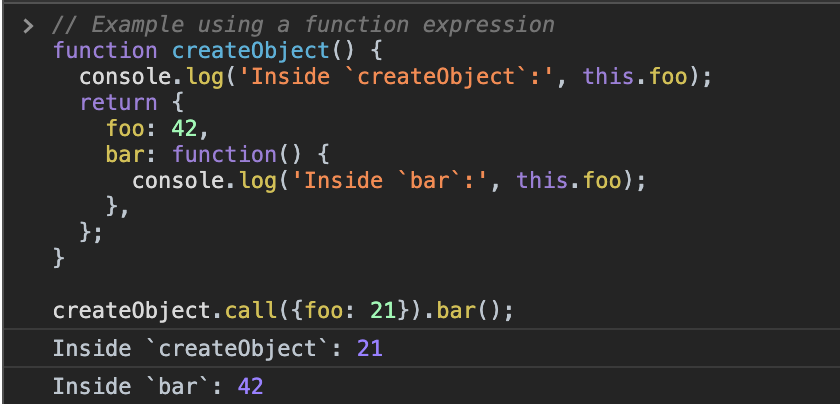 Arrow Functions Vs Regular Functions In Javascript Level Up
Arrow Functions Vs Regular Functions In Javascript Level Up

 How To Call A Function That Return Another Function In
How To Call A Function That Return Another Function In
 Javascript Function And Function Expressions With Examples
Javascript Function And Function Expressions With Examples
 Introduction To Javascript Functions Part 3 Prezentaciya
Introduction To Javascript Functions Part 3 Prezentaciya
 How To Chain Functions In Javascript Jamis Charles Digital
How To Chain Functions In Javascript Jamis Charles Digital
 Javascript Functions Understanding The Basics By Brandon
Javascript Functions Understanding The Basics By Brandon
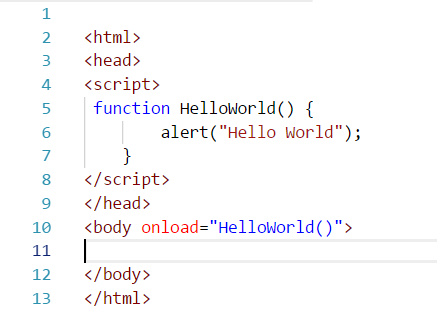 Debugging Javascript Functions Through Console Carl De Souza
Debugging Javascript Functions Through Console Carl De Souza
 Tutorial Mastering This In Javascript The New Stack
Tutorial Mastering This In Javascript The New Stack
 Javascript Call Constructor Variable In Static Method Code
Javascript Call Constructor Variable In Static Method Code
 Arrow Functions Vs Regular Functions In Javascript Level Up
Arrow Functions Vs Regular Functions In Javascript Level Up
 What Is The Call Stack In Javascript Geeksforgeeks
What Is The Call Stack In Javascript Geeksforgeeks
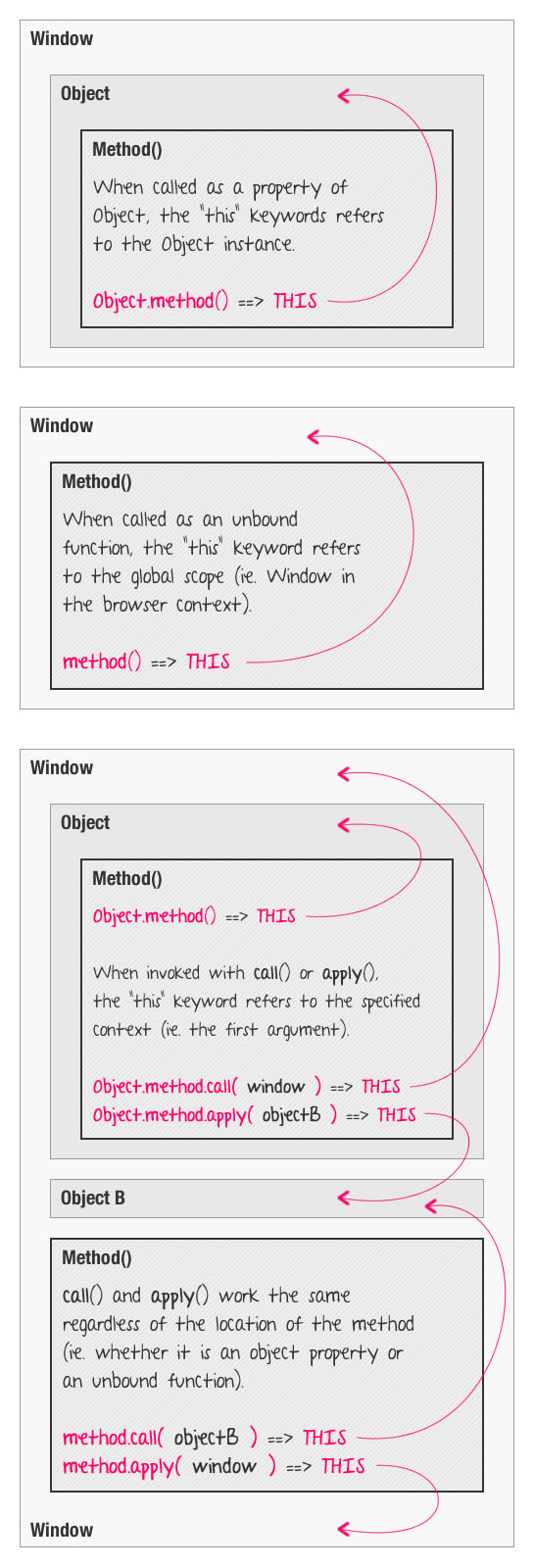 Changing The Execution Context Of Javascript Functions Using
Changing The Execution Context Of Javascript Functions Using
 What Is The Function Call In C Javatpoint
What Is The Function Call In C Javatpoint
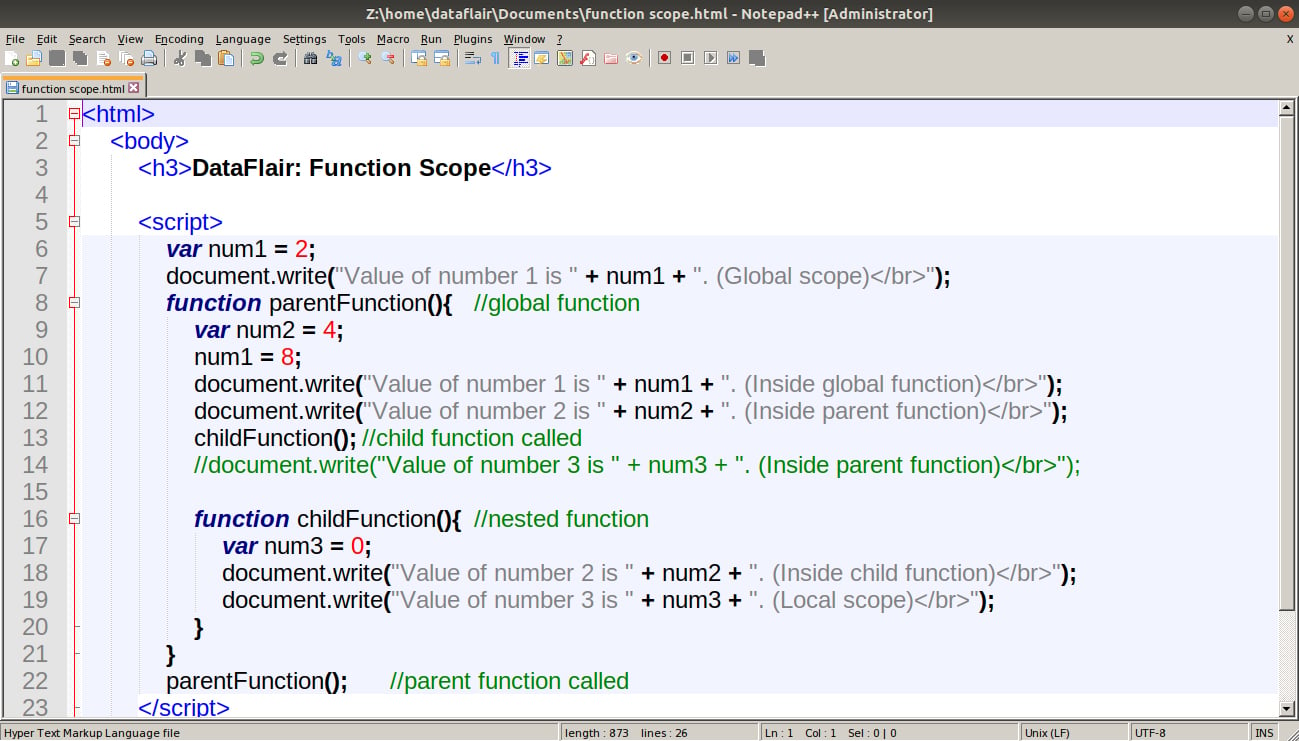 Javascript Functions Concept To Ease Your Web Development
Javascript Functions Concept To Ease Your Web Development
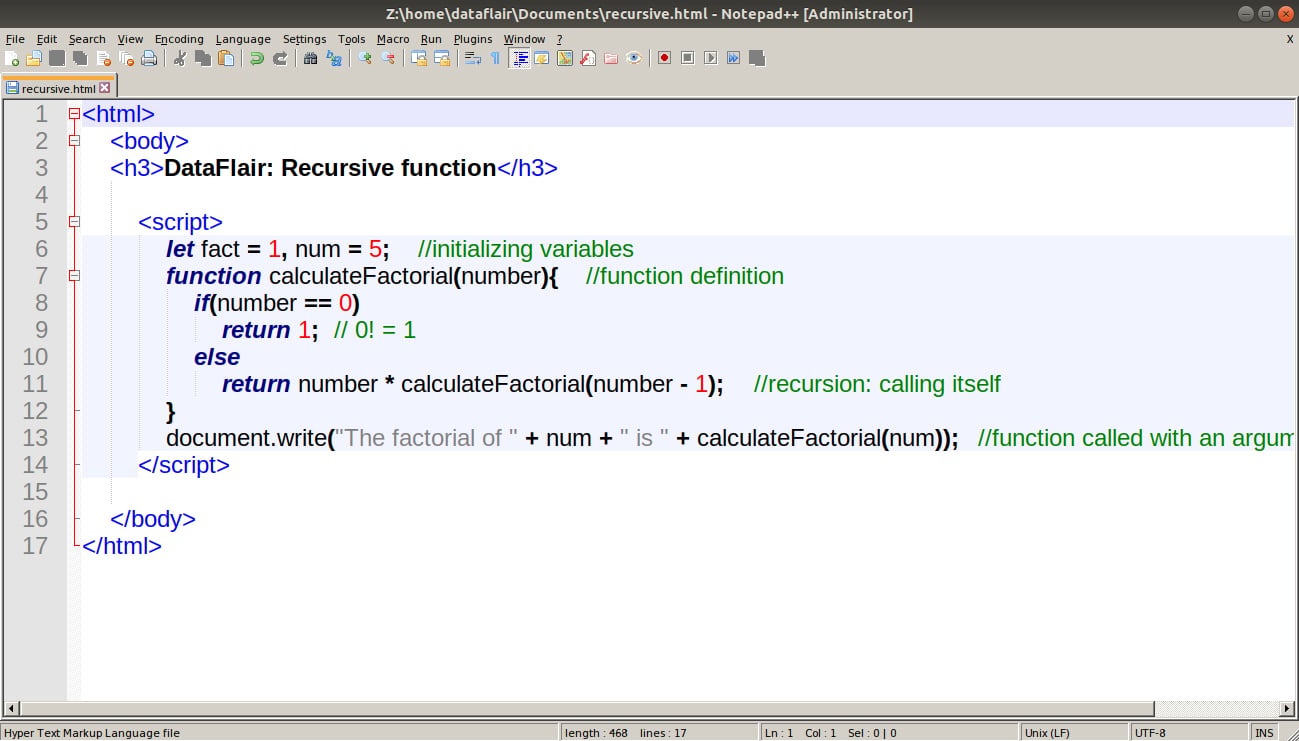 Javascript Functions Concept To Ease Your Web Development
Javascript Functions Concept To Ease Your Web Development
 Advanced Javascript Function Definition Style In Javascript
Advanced Javascript Function Definition Style In Javascript

0 Response to "24 What Is A Function Called In Javascript"
Post a Comment