35 Javascript Return Value From Promise
// using a resolved promise, the 'then' block will be triggered instantly, // but its handlers will be triggered asynchronously as demonstrated by the console.logs const resolvedProm = Promise. resolve (33); let thenProm = resolvedProm. then (value => {console. log ("this gets called after the end of the main stack. the value received and returned is: "+ value); return value;}); // instantly ... A Promise is a built-in javascript object that, when created, gets passed a callback function, which returns a resolve () or reject () function. There are two main properties of the Promise object,...
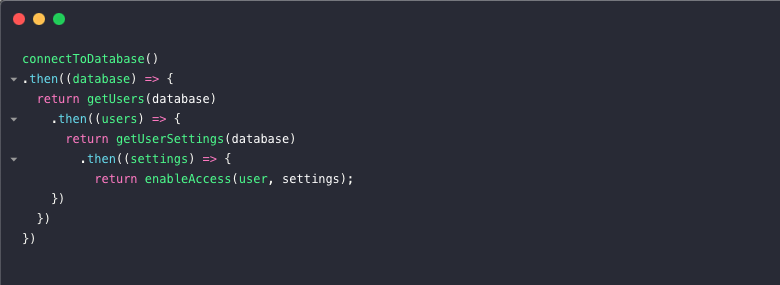 Callback Hell Promises And Async Await
Callback Hell Promises And Async Await
Find out how to return the result of an asynchronous function, promise based or callback based, using JavaScript Published Sep 09, 2019 , Last Updated Apr 30, 2020 Say you have this problem: you are making an asynchronous call, and you need the result of that call to be returned from the original function.

Javascript return value from promise. Promises are one of the best things that happened to JavaScript in the past few years. When we invoke a function that returns a promise, we chain the then() method of the promise to run a function when the promise resolves. Here's an example using the Fetch API: Re: Return a boolean value from a promise. When your promise code calls resolve, it can pass the result for the promise, or a new promise that when resolved returns the value. So if to resolve, your code needs to maker another async call it can return a new promise. so in example 1, your resolve returns the value. JavaScript Promises and Async/Await: As Fast As Possible™ ... If there is a return statement in the handler function, it returns a fulfilled promise with that return value as the payload.
When you call an async function, JavaScript returns a new promise. No matter what you return from an async function, JavaScript always returns a promise, so make sure you await on async function calls! async function test { return 42; } test() instanceof Promise; // true Without Executing. JavaScript promises are "hot" in the sense that ... An async function simply implies that a promise will be returned and if a promise is not returned, JavaScript will automatically wrap it in a resolved promise with the return value in that function. That would look like writing return Promise.resolve ('hello'). You can write an async function simply by placing the async keyword in front of ... The return statement stops the execution of a function and returns a value from that function. Read our JavaScript Tutorial to learn all you need to know about functions. Start with the introduction chapter about JavaScript Functions and JavaScript Scope.
Promises are, as their name implies, a promise that you will have a return value, though it might not be immediate. In this example, I am instantiating a new promise in a variable. If some operation is true, it resolves, otherwise it rejects. Promise.resolve () method in JS returns a Promise object that is resolved with a given value. Any of the three things can happened: If the value is a promise then promise is returned. If the value has a "then" attached to the promise, then the returned promise will follow that "then" to till the final state. Promise Object Properties. A JavaScript Promise object can be: Pending; Fulfilled; Rejected; The Promise object supports two properties: state and result. While a Promise object is "pending" (working), the result is undefined. When a Promise object is "fulfilled", the result is a value. When a Promise object is "rejected", the result is an ...
Promises are important building blocks for asynchronous operations in JavaScript. You may think that promises are not so easy to understand, learn, and work with. And trust me, you are not alone! Promises are challenging for many web developers, even after spending years working with them. In this article, I Code language: JavaScript (javascript) The iterable argument is a list of the promises passed into the Promise.all () as an iterable object. If all the input promises resolve, the Promise.all () static method returns a new Promise that resolves to an array of resolved values from the input promises, in an iterator order. 8/7/2019 · Assuming that you have a basic understanding about JavaScript Promises, I’ll start by creating a method which returns a Promise, so that you can see how to return data from promise. function getPromise() { return new Promise(function(resolve,reject) { setTimeout(function() { resolve( {'country' : 'INDIA'}); },2000) }) }
The first Promise chain starts in line A. connection is the asynchronously delivered result of open (). The second Promise chain is nested inside the .then () callback starting in line B. It starts in line C. Note the return in line C, which ensures that both chains are eventually merged correctly. The nesting gives all callbacks in the second ... There's no way to otherwise make a Promise "return" something back to synchronous code - once you start using them, you're stuck with them. That's true, but you can keep chaining as many promises as you like using then. new Promise (resolve => setTimeout ( () => resolve (6), 1000)) .then (res => res * 7) .then (newRes => console.log ... The whole thing works, because a call to promise.then returns a promise, so that we can call the next.then on it. When a handler returns a value, it becomes the result of that promise, so the next.then is called with it. A classic newbie error: technically we can also add many.then to a single promise. This is not chaining.
You get a promise of a result. This means you will get undefined as the return value of apiGetAll. So const api will always equal undefined. If you still want to use promises, that's fine. Introduction to the JavaScript promise chaining. The instance method of the Promise object such as then (), catch (), or finally () returns a separate promise object. Therefore, you can call the promise's instance method on the return Promise. The successively calling methods in this way is referred to as the promise chaining. How can I obtain a value from this promise instead of another promise? You are getting the value in the callback: makeGeoCodingRequest(address).then(function(geo) { console.log(geo) console.log(Q.isPromise(geo)); // false // do anything with the value here }) // if you need to do anything with the result of the callback computation: // you're getting back another promise for that!
The Promise.resolve () method returns a Promise object that is resolved with a given value. If the value is a promise, that promise is returned; if the value is a thenable (i.e. has a "then" method ), the returned promise will "follow" that thenable, adopting its eventual state; otherwise the returned promise will be fulfilled with the value. A Promise object is widely used in Javascript async programming. And it’s sometimes confusing for developers how to use it properly. In this blog post, I’ve attempted to describe a use case when a developer needs to use a returned value from a Promise object somewhere later in code. A promise is a way of returning values from asynchronous callback functions. To understand promise in simpler terms you can imagine it as a token being given in a government office to get some help on a certain problem. That token represents that you will be called in at some later time and your problem will be addressed.
The return value of the executor is ignored. Returning a value from an executor function is a possible error because the returned value cannot be used and it doesn't affect the promise in any way. As you can see, both of these async functions return a Promise; and that Promise object resolves to the vanilla String values.. But, we've already identified the first flaw in my mental model.Which is that the above two async functions are different in some way. When, in reality, these two async functions are exactly the same because, according to the Mozilla Developer Network (MDN), any non ... Explanation: The request module does not natively return promises. Hence we use the promise constructor to wrap the possible response received from the HTTP request into a native promise. This promise is then handled with.then () and.catch () method. The advantages of using this method are manifold.
In the moment when console.log () function starting to run, a Promise that should be returned from a fetch () request is in a pending status. That said we can access the returned value of a Promise object in another.then () callback: Async return values. Async functions always return a promise, whether you use await or not. That promise resolves with whatever the async function returns, or rejects with whatever the async function throws. So with: // wait ms milliseconds. function wait(ms) {. return new Promise(r => setTimeout(r, ms)); } The solution is surprisingly simple. Even if you're a little uncomfortable with the idea of promises in JavaScript, you will love how you can solve this issue using them. As pointed out by Erop and Robin in the comments, Nodejs version 8 and above now support turning callback functions into promises using the built-in util module.
 Typescript Return Type Possibilities Of A Resolved Promise
Typescript Return Type Possibilities Of A Resolved Promise
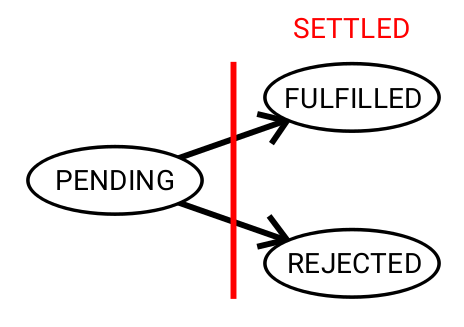 The Promise Then Function In Javascript Mastering Js
The Promise Then Function In Javascript Mastering Js
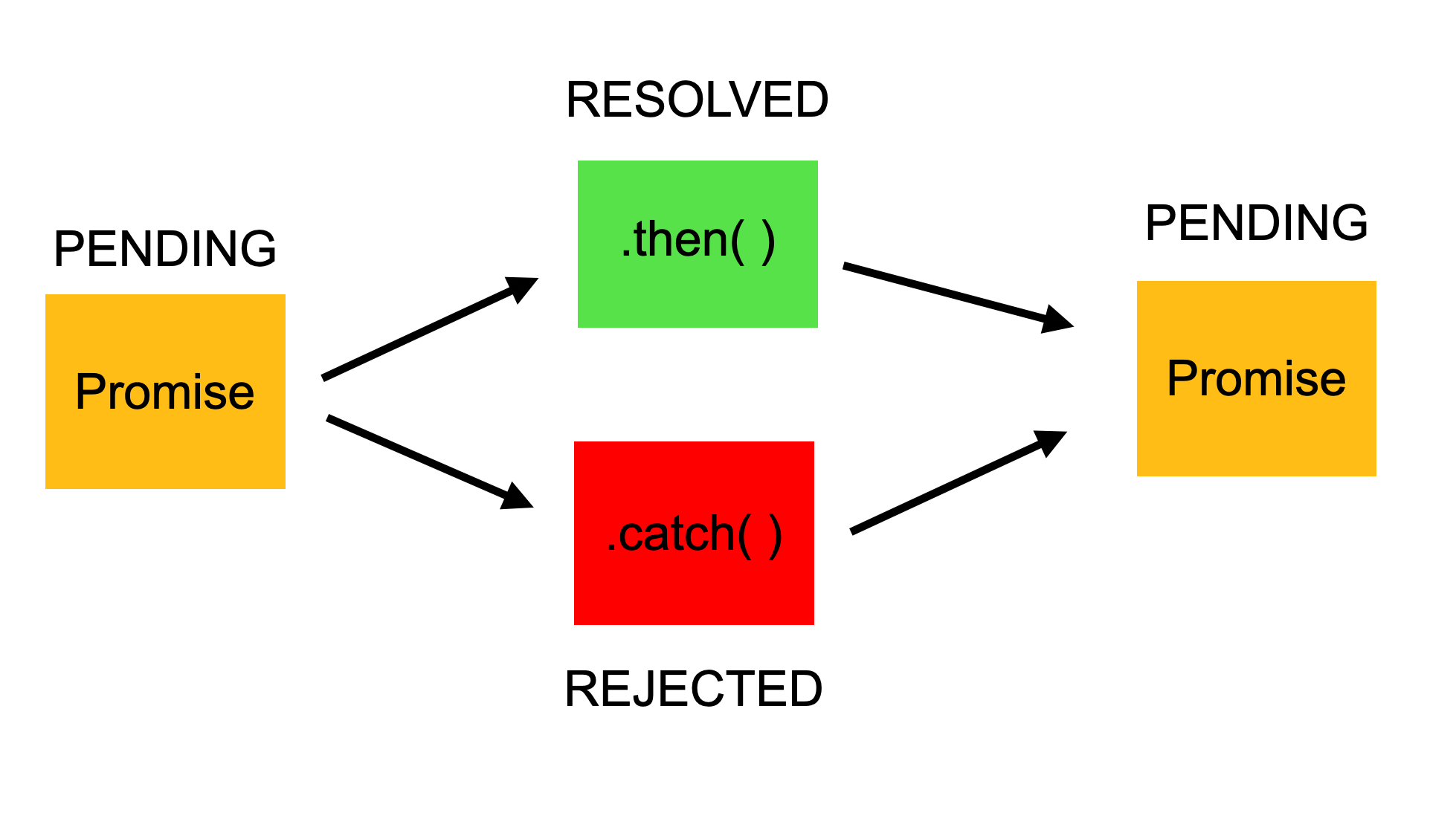 Javascript Promise Tutorial Resolve Reject And Chaining In
Javascript Promise Tutorial Resolve Reject And Chaining In
 Asynchronous Javascript Using Promises With Rest Apis In Node Js
Asynchronous Javascript Using Promises With Rest Apis In Node Js
 Javascript Promise Tutorial How To Resolve Or Reject
Javascript Promise Tutorial How To Resolve Or Reject
 How To Rewrite A Callback Function In Promise Form And Async
How To Rewrite A Callback Function In Promise Form And Async
 Deeply Understanding Javascript Async And Await With Examples
Deeply Understanding Javascript Async And Await With Examples
 Javascript Fetch Api How To Save Output To Variable As An
Javascript Fetch Api How To Save Output To Variable As An
 What Is A Promise Javascript Promises For Beginners
What Is A Promise Javascript Promises For Beginners
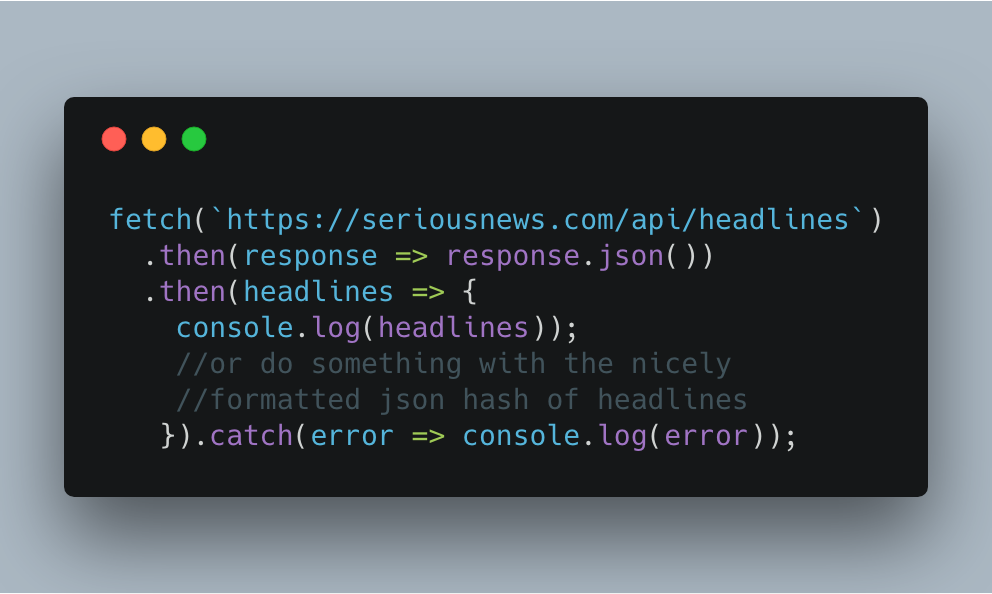 Promises In Javascript Explained Whimsically By Kevin Kim
Promises In Javascript Explained Whimsically By Kevin Kim
 Asynchronous Javascript Using Async Await Scotch Io
Asynchronous Javascript Using Async Await Scotch Io
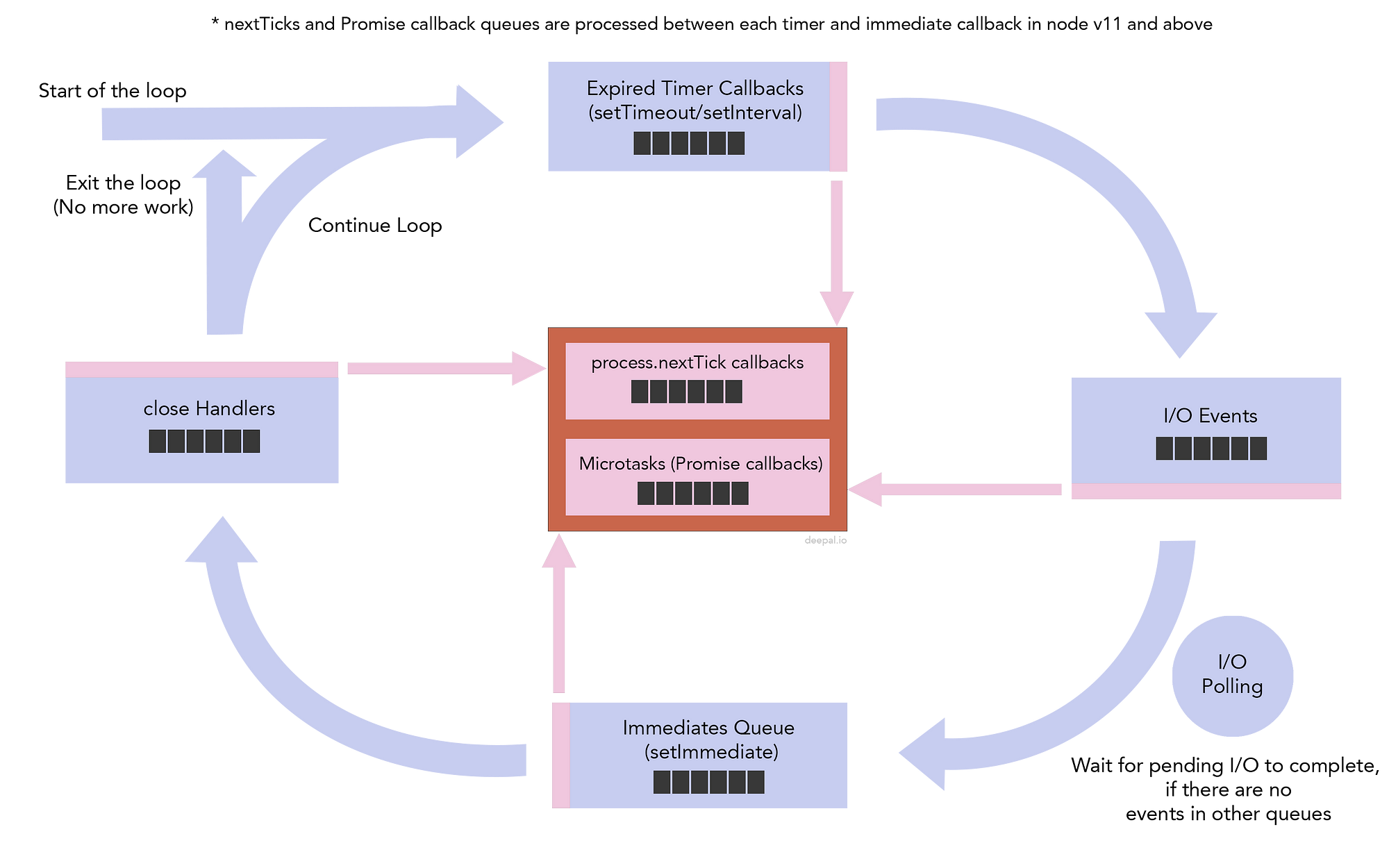 Promises Next Ticks And Immediates Nodejs Event Loop Part
Promises Next Ticks And Immediates Nodejs Event Loop Part
Callback Hell Is A Myth Www Thecodebarbarian Com
 Javascript Promises Dev Community
Javascript Promises Dev Community
 A Friendly Guide To Promise All Speed Up Your Async
A Friendly Guide To Promise All Speed Up Your Async
 Javascript Promise Resolve Example Promise Resolve
Javascript Promise Resolve Example Promise Resolve
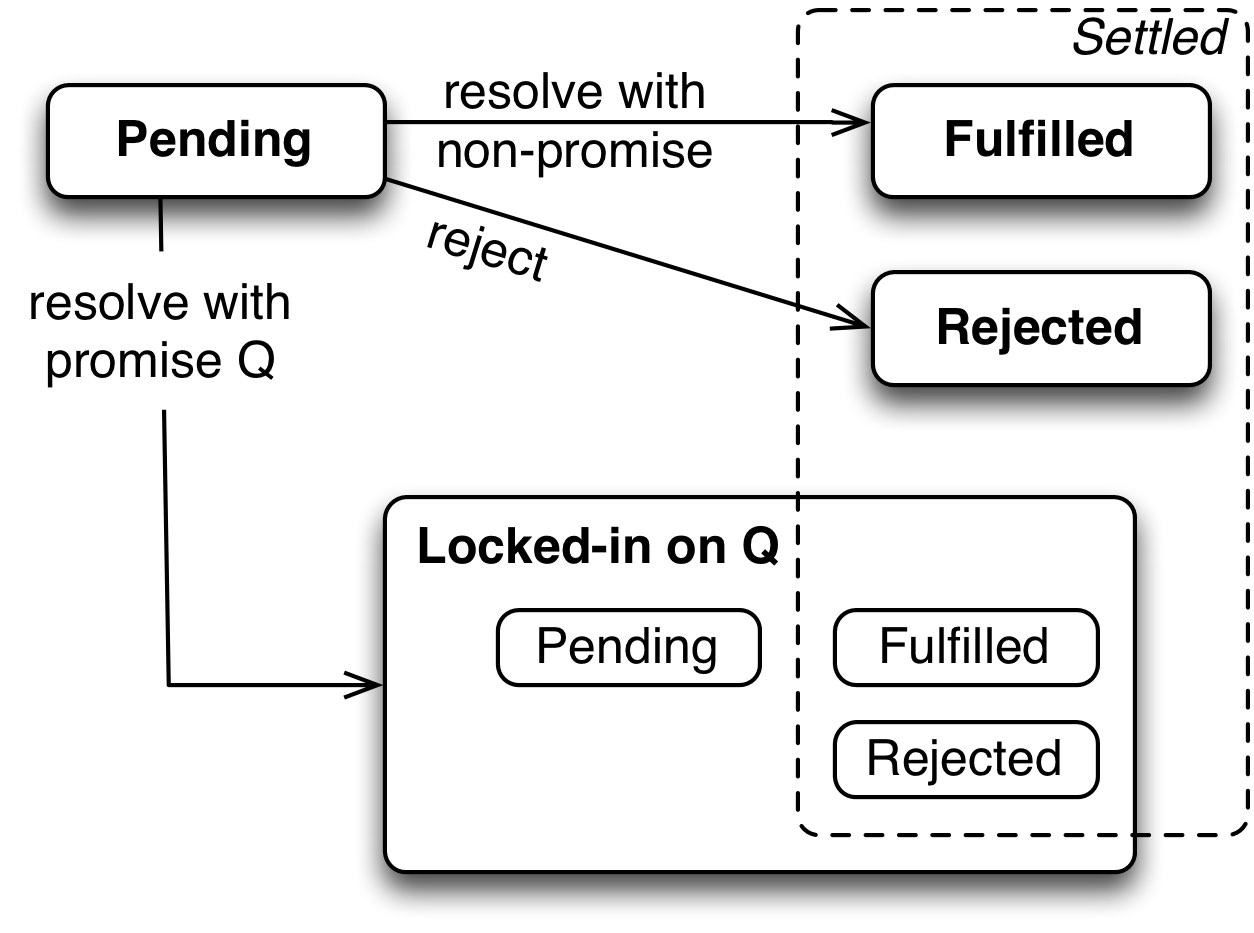 25 Promises For Asynchronous Programming
25 Promises For Asynchronous Programming
 Async And Await In Javascript The Extension To A Promise
Async And Await In Javascript The Extension To A Promise
 How To Rewrite A Callback Function In Promise Form And Async
How To Rewrite A Callback Function In Promise Form And Async
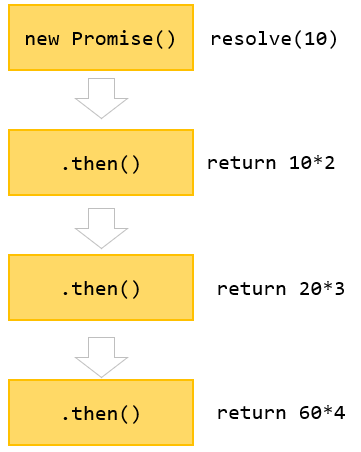 Promise Chaining In Javascript
Promise Chaining In Javascript
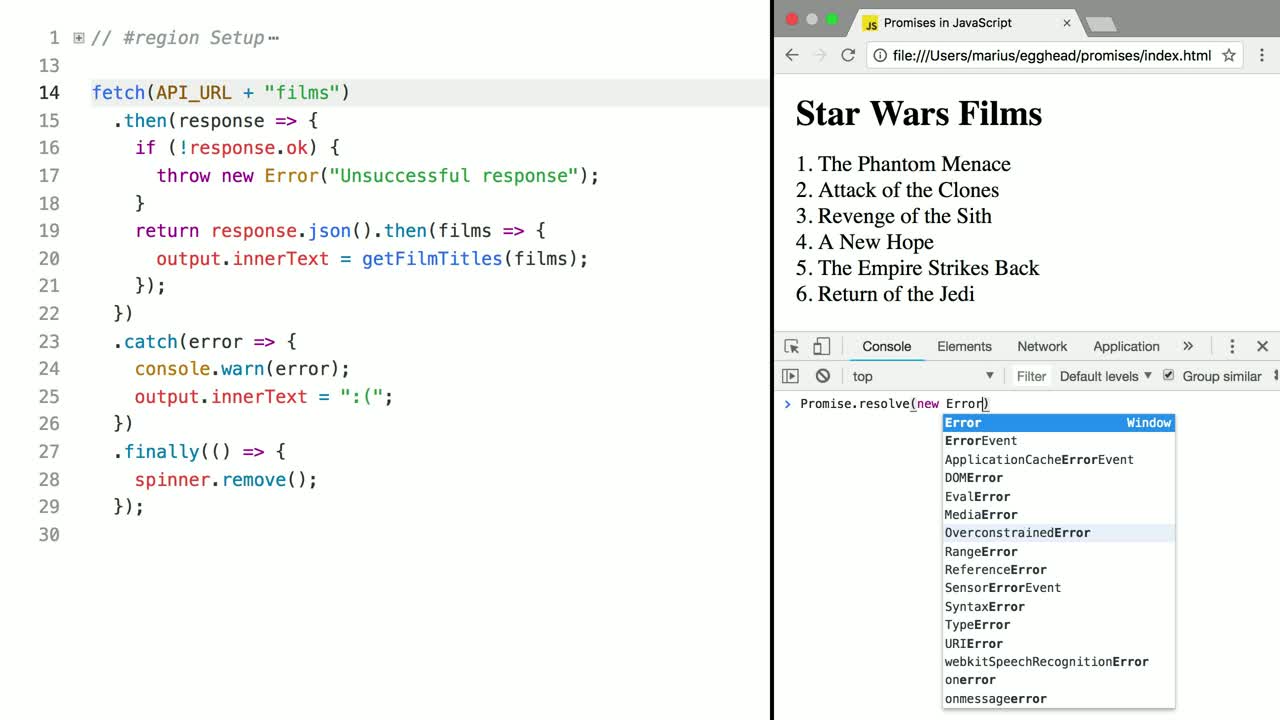 Javascript Promises In Depth Egghead Io
Javascript Promises In Depth Egghead Io
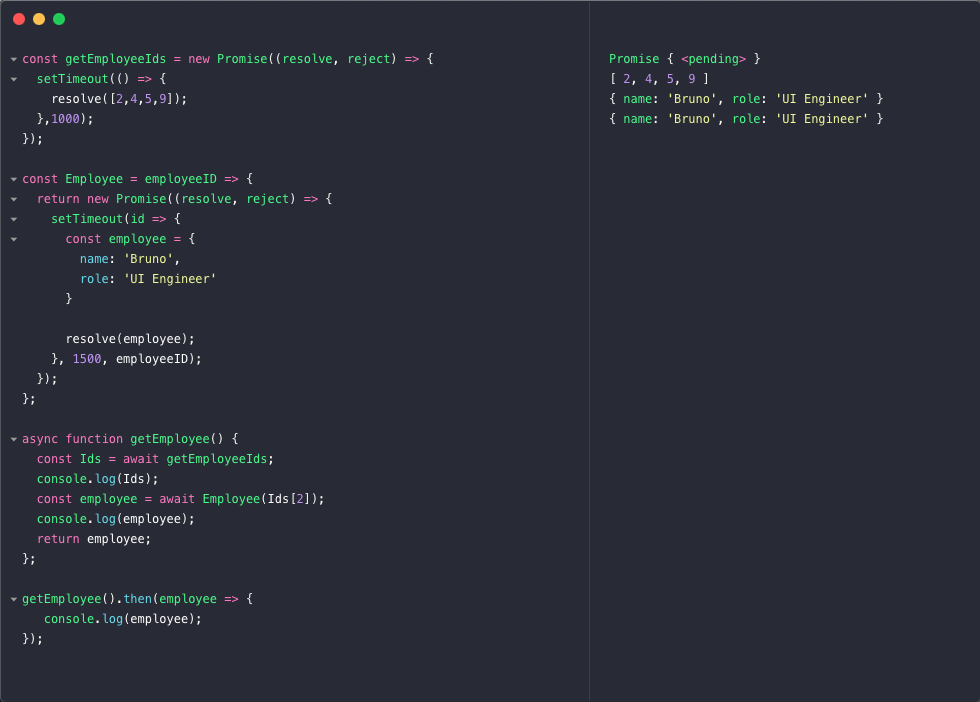 Callback Hell Promises And Async Await
Callback Hell Promises And Async Await
 Async Await In Node Js How To Master It Risingstack
Async Await In Node Js How To Master It Risingstack
 Promise Async Await Inconsistencies Issue Issue 5294
Promise Async Await Inconsistencies Issue Issue 5294
 A Simple Guide To Es6 Promises The Woods Are Lovely Dark
A Simple Guide To Es6 Promises The Woods Are Lovely Dark


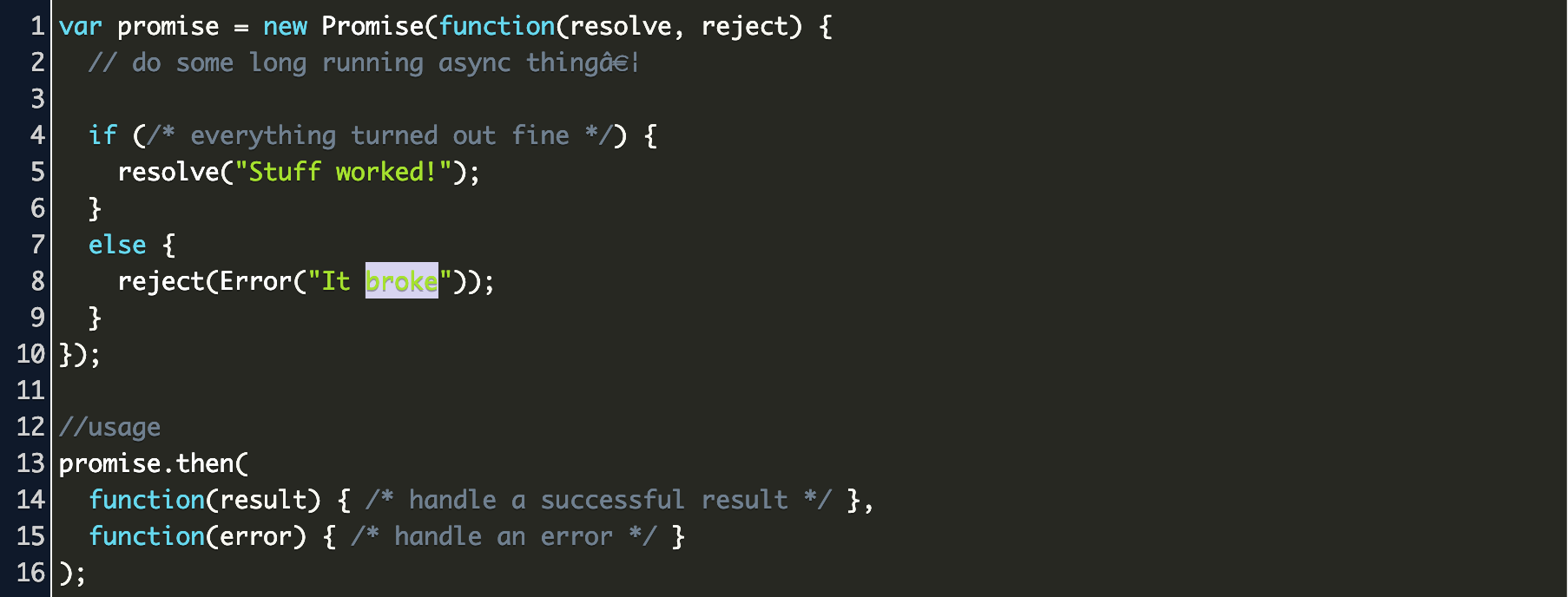
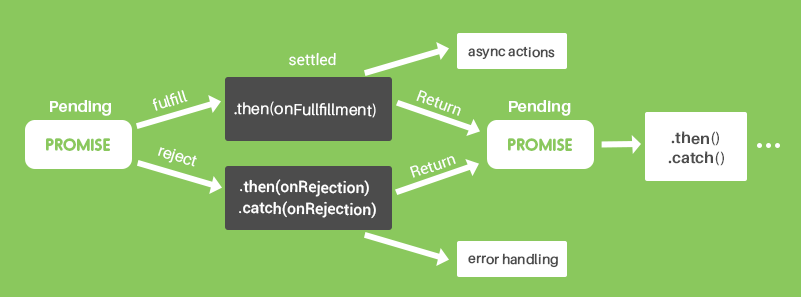

0 Response to "35 Javascript Return Value From Promise"
Post a Comment