33 Javascript Module Exports Example
So you see that this returns a Module which is an object that has properties like id, exports, parent, etc. Well, let me show you how to add properties and functions to exports objects of that Module Object in Node.js. If we do execute module.exports.title and assign some value to it, then it adds the title to the module. exports object. Mar 06, 2020 - I’ll start out going through an ES5 example in Node that uses ‘require’ statements and then show the same thing using ES6 ‘import’ statements. ... Using ES5 syntax in Node means that the sharing of code between files is done with the ‘require’ and ‘module.exports’ statements. A ‘module’ in Javascript ...
 Node Js Require Function And Relationship Between Module Exports And Exports
Node Js Require Function And Relationship Between Module Exports And Exports
To export code from a file, we assign values to the file's module.exports object. Each JavaScript file in Node has a module.exports object in its global scope that represents that specific file ...
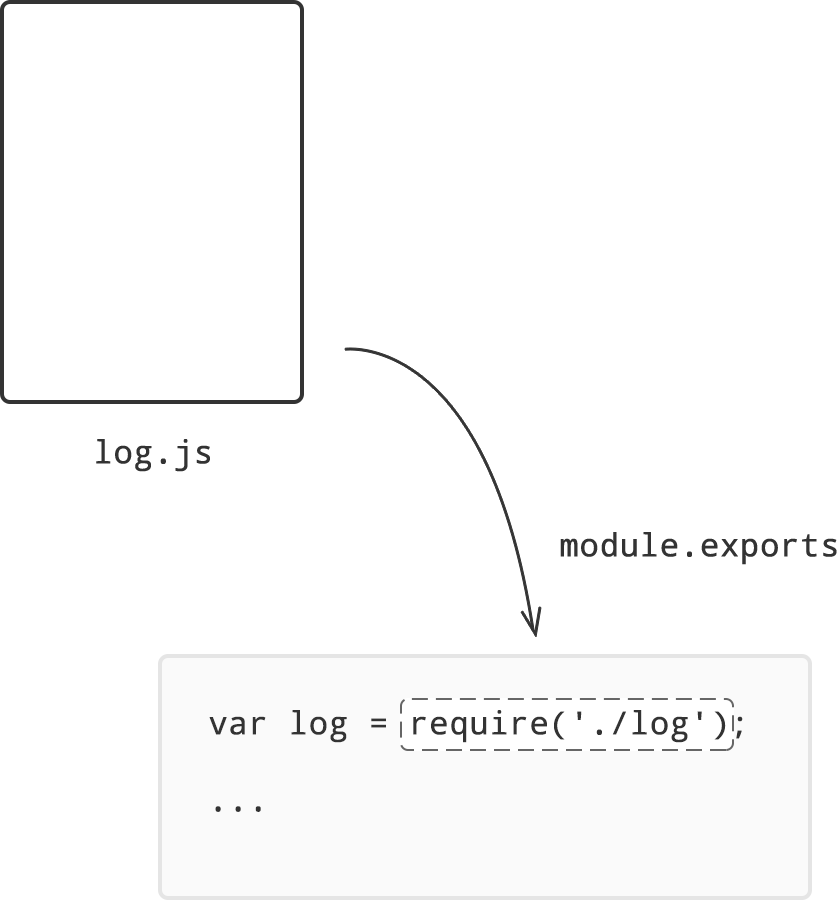
Javascript module exports example. You can use a simplified syntax to import the default export. import circleArea from './circle'; console.log (circleArea (4)); Note that a default export is implicitly equivalent to a named export with the name default, and the imported binding ( circleArea above) is simply an alias. The previous module can be written like. Default exports are marked with the keyword default; and there can only be one default export per module. default exports are imported using a different import form. default exports are really handy. For instance, a library like jQuery might have a default export of jQuery or $, which we'd probably also import under the name $ or jQuery. Exporting a library: There is a special object in JavaScript called module.exports. When some program include or import this module (program), this object will be exposed. Therefore, all those functions that need to be exposed or need to be available so that it can used in some other file, defined in module.exports.
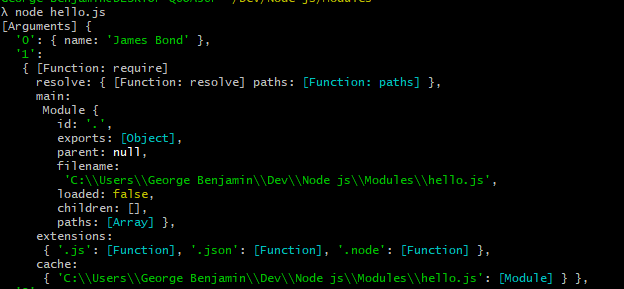
The import directive loads the module by path ./sayHi.js relative to the current file, and assigns exported function sayHi to the corresponding variable.. Let's run the example in-browser. As modules support special keywords and features, we must tell the browser that a script should be treated as a module, by using the attribute <script type="module">. You will see, for example, that the module.filename property is set to a file path that ends with the correct name of the file in which this module exists, which is module1.js. Here is an example output for the code above: $ node module1.js /Users/scott/projects/sandbox/javascript/module-test/module1.js. 27/12/2018 · Because the module’s object is simply an argument—an object, in this case—to our module that we can manipulate as we please. Below is an example of how that module object looks: { id: '.', exports: {}, parent: null, filename: '/test.js', loaded: false, children: [], paths: [ '/Users/lbichard/Desktop/node_modules', '/Users/lbichard/node_modules', ...
Sep 07, 2014 - Having both named exports and a default export in a module # The following pattern is surprisingly common in JavaScript: A library is a single function, but additional services are provided via properties of that function. Examples include jQuery and Underscore.js. The exports field in the package.json of a package allows to declare which module should be used when using module requests like import "package" or import "package/sub/path" . It replaces the default implementation that returns main field resp. index.js files for "package" and the file system lookup for "package/sub/path". Dec 09, 2019 - The export statement is used in Javascript modules to export functions, objects, or primitive values from one module so that they can be used in other programs (using the ‘import’ statement).
In the example above module.exports and exports are the same object. The cool part is that you don't see any of that in your CommonJS modules as the whole system takes care of that for you all you need to know is there is a module object with an exports property and an exports variable that points to the same thing the module.exports does ... The export statement is used when creating JavaScript modules to export live bindings to functions, objects, or primitive values from the module so they can be used by other programs with the import statement. The value of an imported binding is subject to change in the module that exports it. When a module updates the value of a binding that it exports, the update will be visible in its ... Default Exports. In the previous examples, you exported multiple named exports and imported them individually or as one object with each export as a method on the object. Modules can also contain a default export, using the default keyword. A default export will not be imported with curly brackets, but will be directly imported into a named ...
14/12/2015 · I cooked up an example. // Tiger.js function Tiger () { function roar (terrian) { console.log ('Hey i am in ' + terrian + ' and i am roaing'); }; return roar; } module.exports = Tiger; // animal.js import { Tiger } from './animals'; var animal = Tiger (); animal ("jungle"); Basically the import and export syntax is used everywhere where we write JavaScript and then transcompile and bundle it to "old-school" javascript. But the time when it can only be used in conjunction with compilers like Babel is over. Meanwhile Node.js also supports the so-called ES6 modules, and in the browser we can use them if we want to. This post presents 4 best practices on how to organize better your JavaScript modules. 1. Prefer named exports. When I started using JavaScript modules, I had used the default syntax to export the single piece that my module defines, either a class or a function. For example, here's a module greeter that exports the class Greeter as a default ...
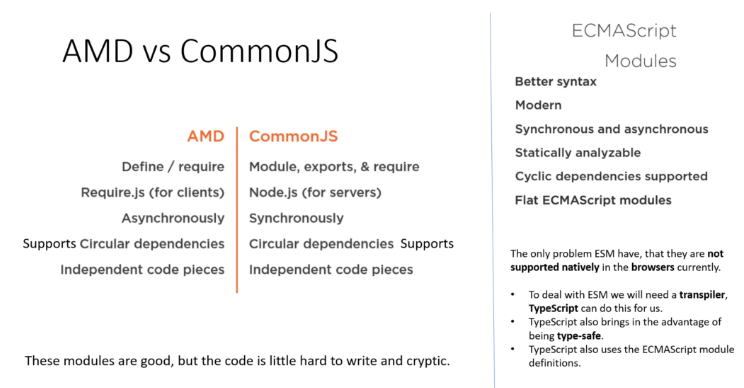
Current JavaScript module formats have a dynamic structure: What is imported and exported can change at runtime. One reason why ES6 introduced its own module format is to enable a static structure, which has several benefits. But before we go into those, let’s examine what the structure being ... You can export functions, var, let, const, and — as we'll see later — classes.They need to be top-level items; you can't use export inside a function, for example.. A more convenient way of exporting all the items you want to export is to use a single export statement at the end of your module file, followed by a comma-separated list of the features you want to export wrapped in curly braces. Jul 20, 2021 - The export statement is used when creating JavaScript modules to export live bindings to functions, objects, or primitive values from the module so they can be used by other programs with the import statement. The value of an imported binding is subject to change in the module that exports it.
The module.exports is a special object which is included in every JavaScript file in the Node.js application by default. The module is a variable that represents the current module, and exports is an object that will be exposed as a module. So, whatever you assign to module.exports will be exposed as a module. Aug 28, 2019 - All the expressions like import, export, module.exports, etc. are the result of not having a native, standard way of modularizing in early stages. We will explore some of them. ... It is better to take an example to discuss this further. Following is a simple HTML page with a simple JavaScript file ... Jun 07, 2019 - A CommonJS module is essentially a reusable piece of JavaScript which exports specific objects, making them available for other modules to require in their programs. If you’ve programmed in Node.js, you’ll be very familiar with this format. With CommonJS, each JavaScript file stores modules ...
Importing a module with a default member. You import the default member by giving it a name of your choice. In the following example Logger is the name given to the imported default member: import Logger from 'app.js'; And here's how you would import non-default members on top of the default one: import Logger, { Alligator, myNumbers } from ... Nov 26, 2019 - In this article, I’ll examine how to work with modules in Node.js, focusing on how to export and consume them. ... As JavaScript originally had no concept of modules, a variety of competing formats have emerged over time. Here’s a list of the main ones to be aware of: module.exports.method = function() {…} A simple module example. First, we need an example codebase. Let's start with a simple calculator: Usage: The module wrapper. Node.js internally wraps all require()-ed modules in a function wrapper: The module object. Variable "module" is an object representing the
1/1/2020 · JavaScript import an export Modules as alias. JavaScript allows us to rename an export, especially when we are importing it from another file. For instance, we give the tc alias to the toCelsius module. // app.js import {toCelsius as tc } from './data-module'; console. log (tc (77)) // Result => 25 24/9/2020 · JavaScript Module Edit TestModule.js // local usage, not exported function print(str) { console.log(str) } // enum const FruitType = Object.freeze({ CITRUS: 1, TROPICAL: 2, MELONS: 3 }) // class class Fruit { constructor(name, type) { this.name = name this.type = type } get fullName() { return `${this.name}, type=${this.type}` } print() { print(this.toString()) } } // function function tell(name) { print(`This is ${name}`) } // named export export … Actually running the first two examples yield different results then what's claimed. Whatever module.exports is set to once the module finishes running will always be what gets exported. The exports variable is just a local-variable alias to module.exports (it's as if let exports = module.exports is the first line of
Get code examples like"node js module export class". Write more code and save time using our ready-made code examples. When we want to export a single class/variable/function from one module to another module, we use module.exports way. Example: Create two file calculator.js and operation.js and export the Arithmetic class from calculator.js to operation.js using module.exports method. 23/1/2020 · Let’s consider another example, in which a module site.js exports a single main “default” thing along with several named ones: // site.js export default class Site { constructor(name) { this.name = name; } } export function welcome(site) { console.log(`Welcome to ${site}!`); }
Aug 26, 2011 - The module circle.js has exported ... additional properties on the special exports object. Variables local to the module will be private, because the module is wrapped in a function by Node.js (see module wrapper). In this example, the variable PI is private to circl... A module has either named exports or the default one. As there may be at most one default export per file, the exported entity may have no name. For instance, these are all perfectly valid default exports: export default class { constructor() {... Because of this, ECMAScript 2015 supports the use of JavaScript modules. A module is a bundle of code that acts as an interface to provide functionality for other modules to use, as well as being able to rely on the functionality of other modules. A module exports to provide code and imports to use other code. Modules are useful because they ...
The above object basically describes an encapsulated module from a JS file with module.exports being the exported component of any types - object, function, string, and so on. Default exporting in a Node.js module is as simple as this: module.exports = function anExportedFunc () { return "yup simple as that"; }; There's another way of exporting ... A simple introduction to Node.JS modules by example. node start.js. In the above example, we have used an Import a single export from a module. If we have multiple export modules, then we can import various modules. Import Multiple Modules in Javascript. Now, we will create another module inside the data.js file.
ES6 modules are basically JavaScript File, so when you write any function in any JavaScript file those are not accessible outside the file by default, unless you export them! es6 module export. To export any variable or function outside the module you need to use export keyword, let's look at the example below.
 Node Js Npm Tutorial Create Publish Extend Amp Manage
Node Js Npm Tutorial Create Publish Extend Amp Manage

 Understanding Modules In Node Js The Hidden Parts By
Understanding Modules In Node Js The Hidden Parts By
 Javascript Module System Dzone Web Dev
Javascript Module System Dzone Web Dev
 Webstorm Unresolved Variable Or Type Sails Module
Webstorm Unresolved Variable Or Type Sails Module
 Modules Part 2 Writing Modules
Modules Part 2 Writing Modules
 Javascript Modules And How To Effectively Work With Export Import
Javascript Modules And How To Effectively Work With Export Import
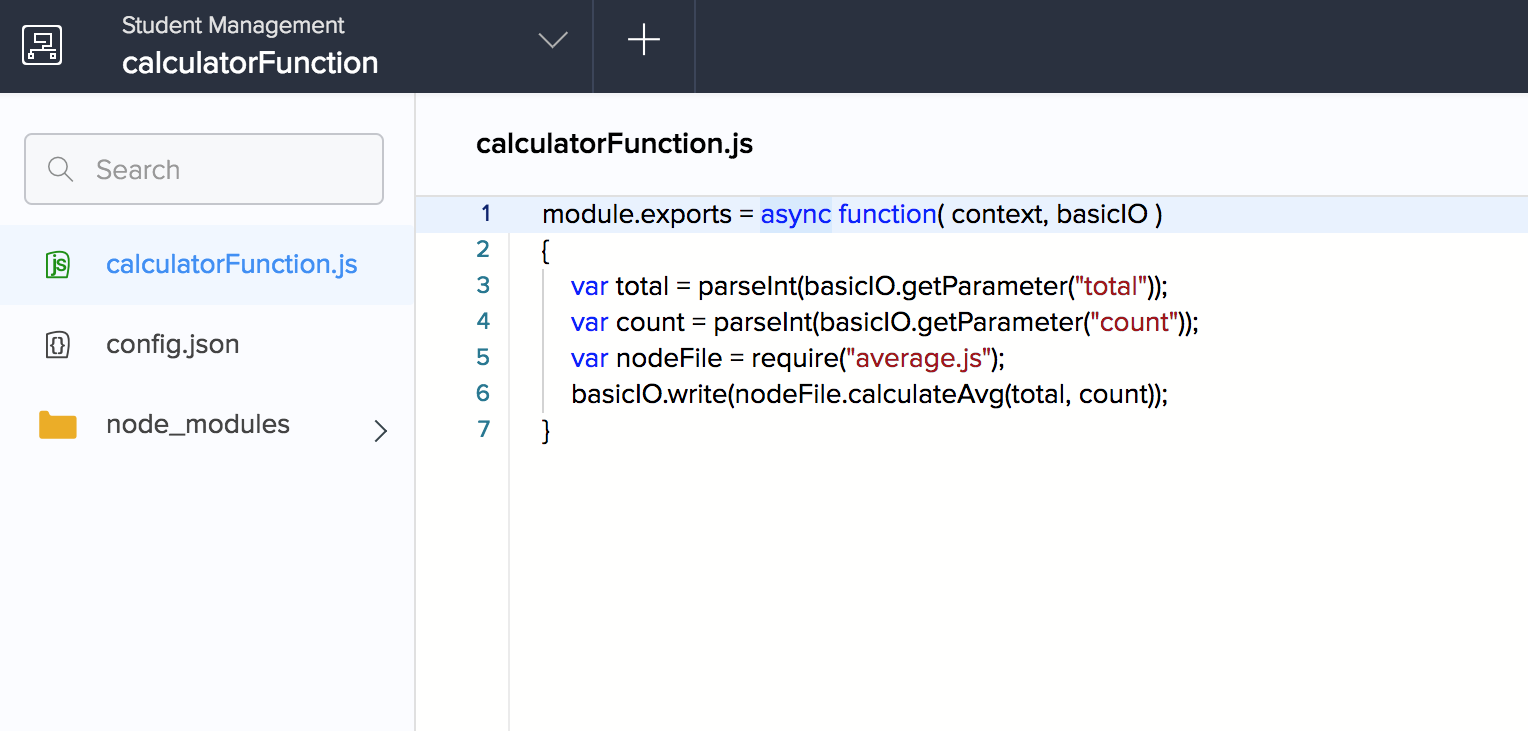
 Nodejs Tutorial Using Async Await With Module Exports
Nodejs Tutorial Using Async Await With Module Exports
 About Wayfair Custom Module Loading In A Node Js Environment
About Wayfair Custom Module Loading In A Node Js Environment
 How To Use Module Exports In Node Js
How To Use Module Exports In Node Js
 Understanding Modules Import And Export In Javascript
Understanding Modules Import And Export In Javascript
 How To Create Node Js Azure Functions Azure Lessons
How To Create Node Js Azure Functions Azure Lessons
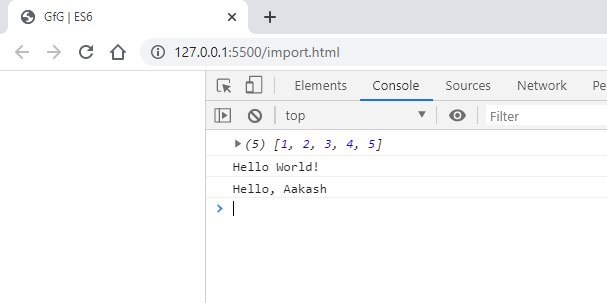 Es6 Import And Export Geeksforgeeks
Es6 Import And Export Geeksforgeeks
 Webstorm 2017 2 Eap 172 2827 Better Webpack Support Convert
Webstorm 2017 2 Eap 172 2827 Better Webpack Support Convert
Javascript Module Module Exports Amp Related Best Practices
 Javascript Reference Guide Js Module Ecosystem Logrocket Blog
Javascript Reference Guide Js Module Ecosystem Logrocket Blog
 Getting Started With Node Js Modules Require Exports
Getting Started With Node Js Modules Require Exports
 Nodejs Export And Import Modules Journaldev
Nodejs Export And Import Modules Journaldev
 What Is Node Js Module Module Exports Example Codez Up
What Is Node Js Module Module Exports Example Codez Up
 How To Export Multiple Variables In Node Js Code Example
How To Export Multiple Variables In Node Js Code Example
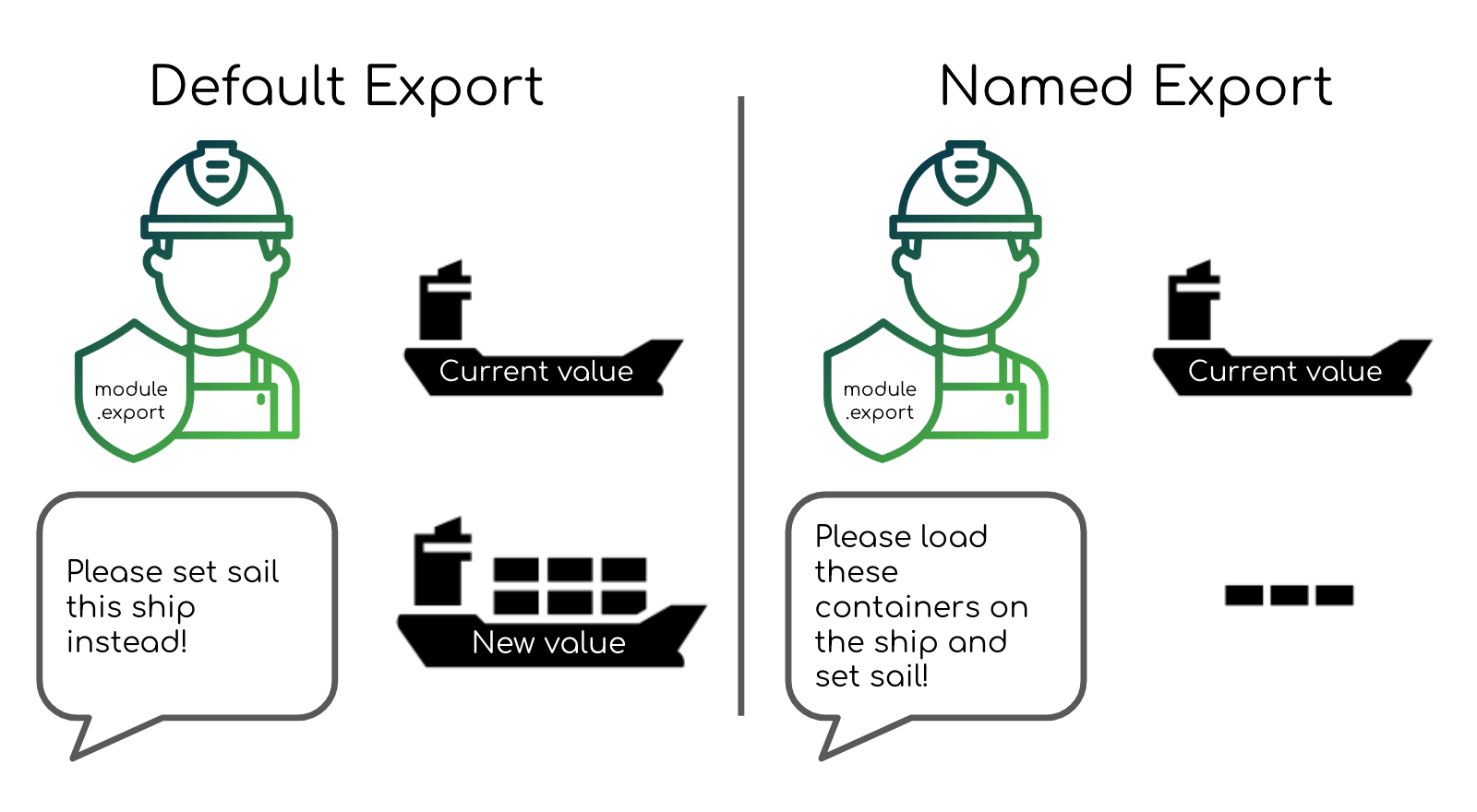 Node Module Exports Explained With Javascript Export
Node Module Exports Explained With Javascript Export
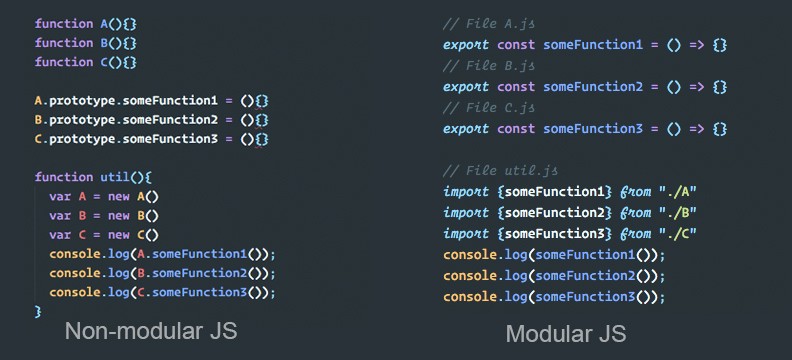 Learn The Basics Of The Javascript Module System And Build
Learn The Basics Of The Javascript Module System And Build
 Feature Request Make Es Module Exports Conform To An
Feature Request Make Es Module Exports Conform To An
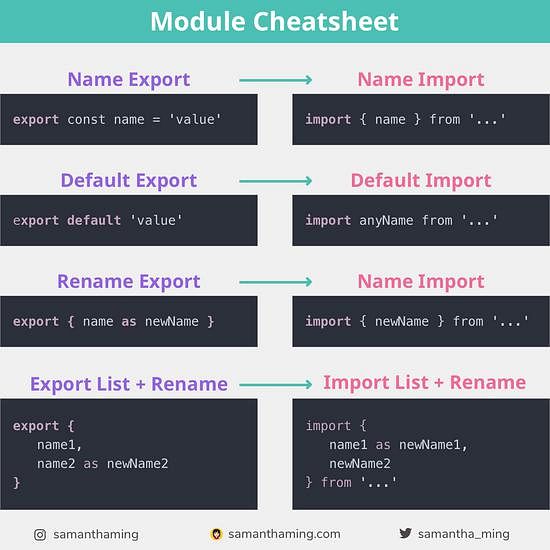 Module Cheatsheet Samanthaming Com
Module Cheatsheet Samanthaming Com
 Module Exports Vs Exports In Node Js Stack Overflow
Module Exports Vs Exports In Node Js Stack Overflow
 Javascript Module Cheatsheet By Samantha Ming
Javascript Module Cheatsheet By Samantha Ming
 Import And Export Statements In Javascript And How To Use Them
Import And Export Statements In Javascript And How To Use Them
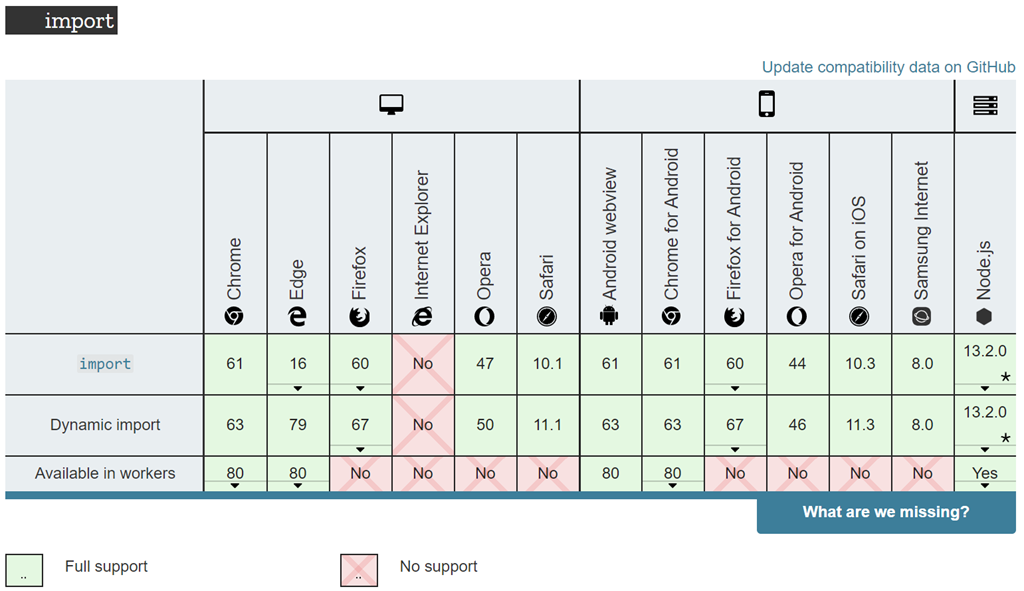 Dixin S Blog Understanding All Javascript Module Formats
Dixin S Blog Understanding All Javascript Module Formats
Github Sindresorhus Add Module Exports Webpack Plugin Add
Creating A True Singleton In Node Js With Es6 Symbols

0 Response to "33 Javascript Module Exports Example"
Post a Comment