24 Javascript Is Equal To String
Not the string "0". And the function returned true! Incorrectly thinking it was a new job. In other words: JavaScript thinks that the number zero is equal to empty string. You can try this out ... Not equal is an comparison operator which is used to check the value of two operands are equal or not. If the value of two operands are not equal it returns true. The symbolic representation of Not equal operator in JavaScript is !=.
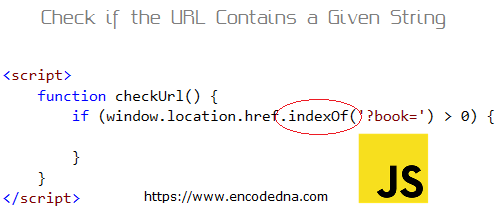 Check If The Url Bar Contains A Specified Or Given String In
Check If The Url Bar Contains A Specified Or Given String In
The javascript has both strict and type-converting comparisons, a strict comparison also we used in the javascript in strict is the keyword of the javascript i.e. === is the operator used for to compare the two operands are of the same data type and the contents of the data like string values are also the same matching scenarios most probably ...
Javascript is equal to string. So the battle really comes down to toString() and String() when you want to convert a value to a string. This one does a pretty good job. This one does a pretty good job. Except it will throw an ... .equals() In Java, string equals() method compares the two given strings based on the data/content of the string. If all the contents of both the strings are same then it returns true. If all characters are not matched then it returns false. Double equals (==) is a comparison operator, which transforms the operands having the same type before comparison. So, when you compare string with a number, JavaScript converts any string to a number. An empty string is always converts to zero. A string with no numeric value is converts to NaN (Not a Number), which returns false.
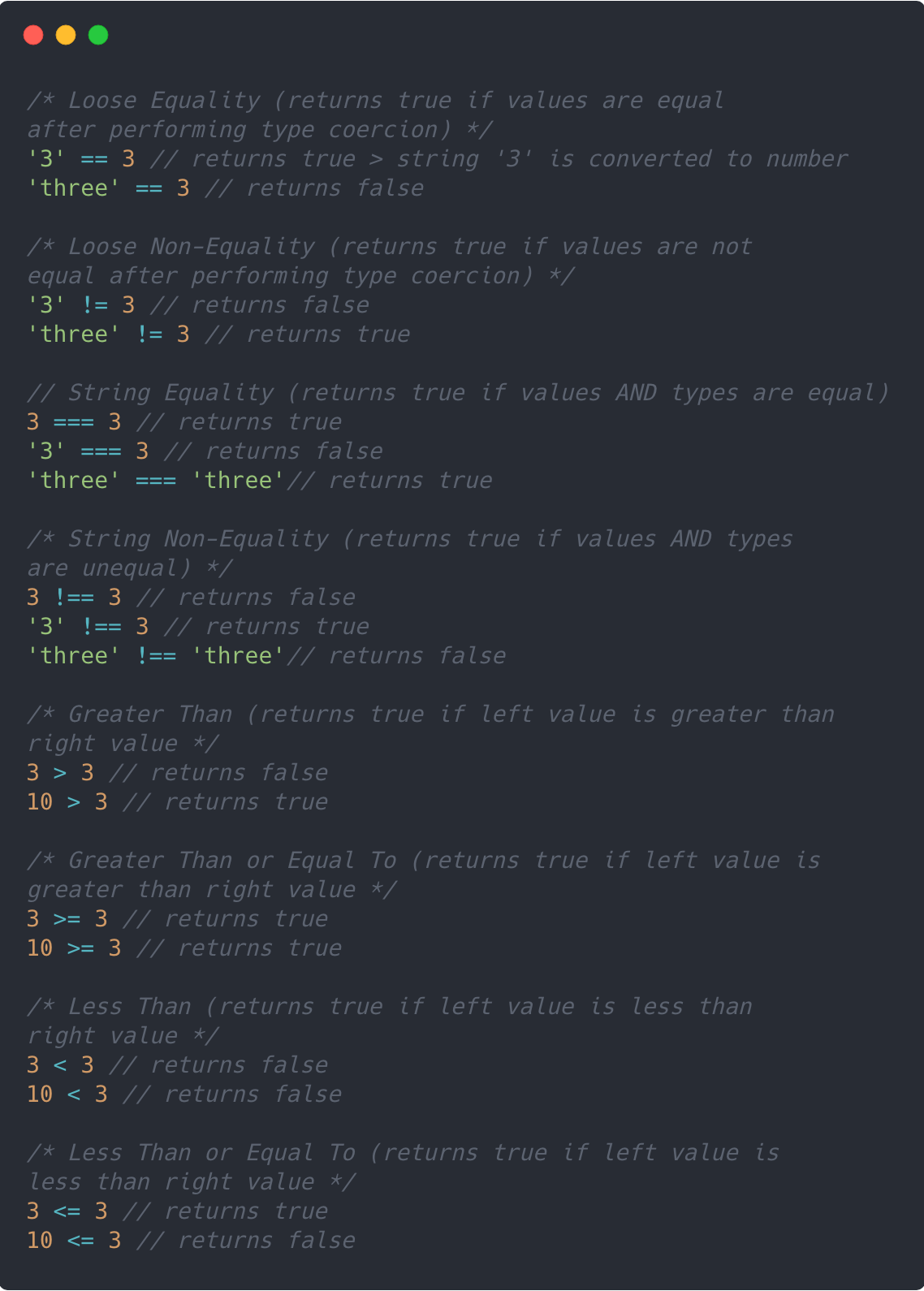
Triple Equals (===) The triple equals ( ===) is used for strict equality checking it means both operands should be same type and value then only it returns true otherwise it returns false. Example: 1 === "1". In the above example, we are comparing Number 1 with String "1" the value 1 is the same on both sides but the types of both operands are ... Generally, if the strings contain only ASCII characters, you use the === operator to check if they are equal. When the strings contain characters that include combining characters, you normalize them first before comparing them for equality. Was this tutorial helpful ? The comparison operators take simple values (numbers or string) as arguments and evaluate either true or false. Here is a list of comparison operators. Operator. Comparisons. Description. Equal (==) x == y. Returns true if the operands are equal. Strict equal (===)
Not equal value or Not equal type is an comparison operator which is used to check whether the two operands are having not equal value or not equal type. The symbolic representation of Not equal value or Not equal type is !==. In this any one should be different either value or type. Same value and different type gives result 'true'. If one of the operands is an object and the other is a number or a string, try to convert the object to a primitive using the object's valueOf() and toString() methods. If the operands have the same type, they are compared as follows: String: return true only if both operands have the same characters in the same order. Comparing two strings in JavaScript is easy: just use ===. But what if you want to treat uppercase and lowercase letters as equal, so Bill@Microsoft is equivalent to bill@microsoft ?
What is equal to (===) Operator in JavaScript? Triple equals(===) is a strict equality comparison operator in JavaScript, that returns false for the values which are not of a similar type. It performs type casting for equality. Uses of equal to (=) Operator in JavaScript. These are the following important uses of = in JavaScript: The example indicates that z is strictly equal to 4 (as it is assigned the numeric value of 4), but that it is not strictly equal to the string '4'. Because this operator is strict, you will need to keep in mind that you may need to convert user-entered data from one data type to another, for instance, when working with the identity operator. So the best way to check for equality is using the === operator because it checks value as well as type of both operands. If you want to check for equality between two objects then using String.prototype.valueOf is the correct way. new String ('javascript').valueOf () == new String ('javascript').valueOf () Share.
Comparing the length of JavaScript strings# If you need to find which of two strings is longer, then the operators "greater than" and "lower than" won't suit you well. They compare the characters of a string in alphanumeric order one by one and consider the length of the strings in the very end. Using the 'equals' method This is a frequently used, and preferred, option among experienced programmers. The equals method compares two strings and determines whether they contain similar characters. If all characters in the two strings are identical, then the operator gives a true or equal answer. When comparing strings with length greater than 1, JavaScript compares character by character. If both strings start with the same character, JavaScript compares the 2nd characters of each string. The end of a string is always < any character.
1) You have a string in JavaScript, like var fruit = ''. 2) You need to know if that string is equal to one of multiple values, say "banana" or "lemon" (because the yellow fruits need special yellow fruit processing or something). Most people accomplish this by doing two string comparisons connected by a logical OR, which looks like this: To convert a string to an integer parseInt() function is used in javascript.parseInt() function returns Nan( not a number) when the string doesn't contain number.If a string with a number is sent then only that number will be returned as the output. This function won't accept spaces. If any particular number with spaces is sent then the part of the number that presents before space will be ... In JavaScript, the textual data is stored as strings. There is no separate type for a single character. The internal format for strings is always UTF-16, it is not tied to the page encoding.
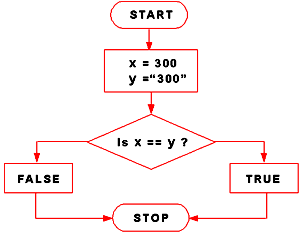
This definition of equality is enough for most use cases. When comparing the string "0" and the number 0 the result is false as expected. Sources such as D. Crockford and MDN both advise that only triple equals operator should be used when programming in JavaScript and double equals operator be ignored altogether. JavaScript variables are loosely/dynamically typed and the language doesn't care how a value is declared or changed: let x ; x = 1 ; // x is a number x = '1' ; // x is a string x = [ 1 ] ; // x ... The equals () method compares two strings, and returns true if the strings are equal, and false if not. Tip: Use the compareTo () method to compare two strings lexicographically.
When comparing a string with a number, JavaScript will convert the string to a number when doing the comparison. An empty string converts to 0. A non-numeric string converts to NaN which is always false. When comparing two strings, "2" will be greater than "12", because (alphabetically) 1 is less than 2. Strings must have the same characters in the same order. Booleans must be both true or both false. The most notable difference between this operator and the equality (==) operator is that if the operands are of different types, the == operator attempts to convert them to the same type before comparing. Otherwise, if both strings' first characters are the same, compare the second characters the same way. Repeat until the end of either string. If both strings end at the same length, then they are equal. Otherwise, the longer string is greater. In the first example above, the comparison 'Z' > 'A' gets to a result at the first step.
The difference between the String() method and the String method is that the latter does not do any base conversions. How to Convert a Number to a String in JavaScript¶ The template strings can put a number inside a String which is a valid way of parsing an Integer or Float data type: Remember when performing comparisons, the equality operator ( ==) will attempt to make the data types the same before proceeding. On the other hand, the identity operator ( ===) requires both data types to be the same, as a prerequisite. Let's understand with an example. See the code below : var valueOne = 3; var valueTwo = "3"; In JavaScript, there are four operators you can use for checking string equality. These operators are called the comparison operators. Strict equal (===): The Strict equal (also known as the triple equals operator) checks the value of the variable and its data type.
 Week 4 Workin It Out With Javascript By Zac Heisey Medium
Week 4 Workin It Out With Javascript By Zac Heisey Medium
Use Not Equal Operator To Compare A String And A Number In
 Which Equal Operator Should Be Used In Javascript Comparisons
Which Equal Operator Should Be Used In Javascript Comparisons
 Javascript Comparison Operators W3resource
Javascript Comparison Operators W3resource
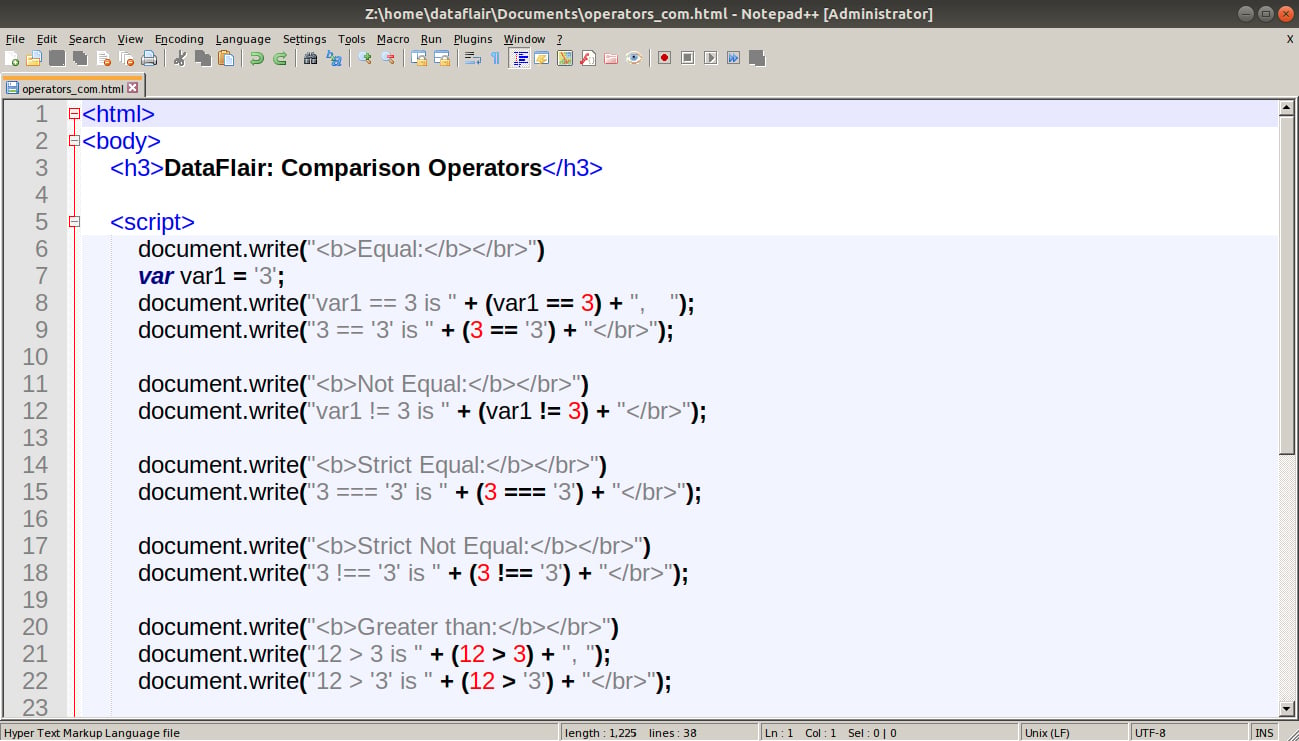 Javascript Operators Top 7 Types That You Can T Omit While
Javascript Operators Top 7 Types That You Can T Omit While
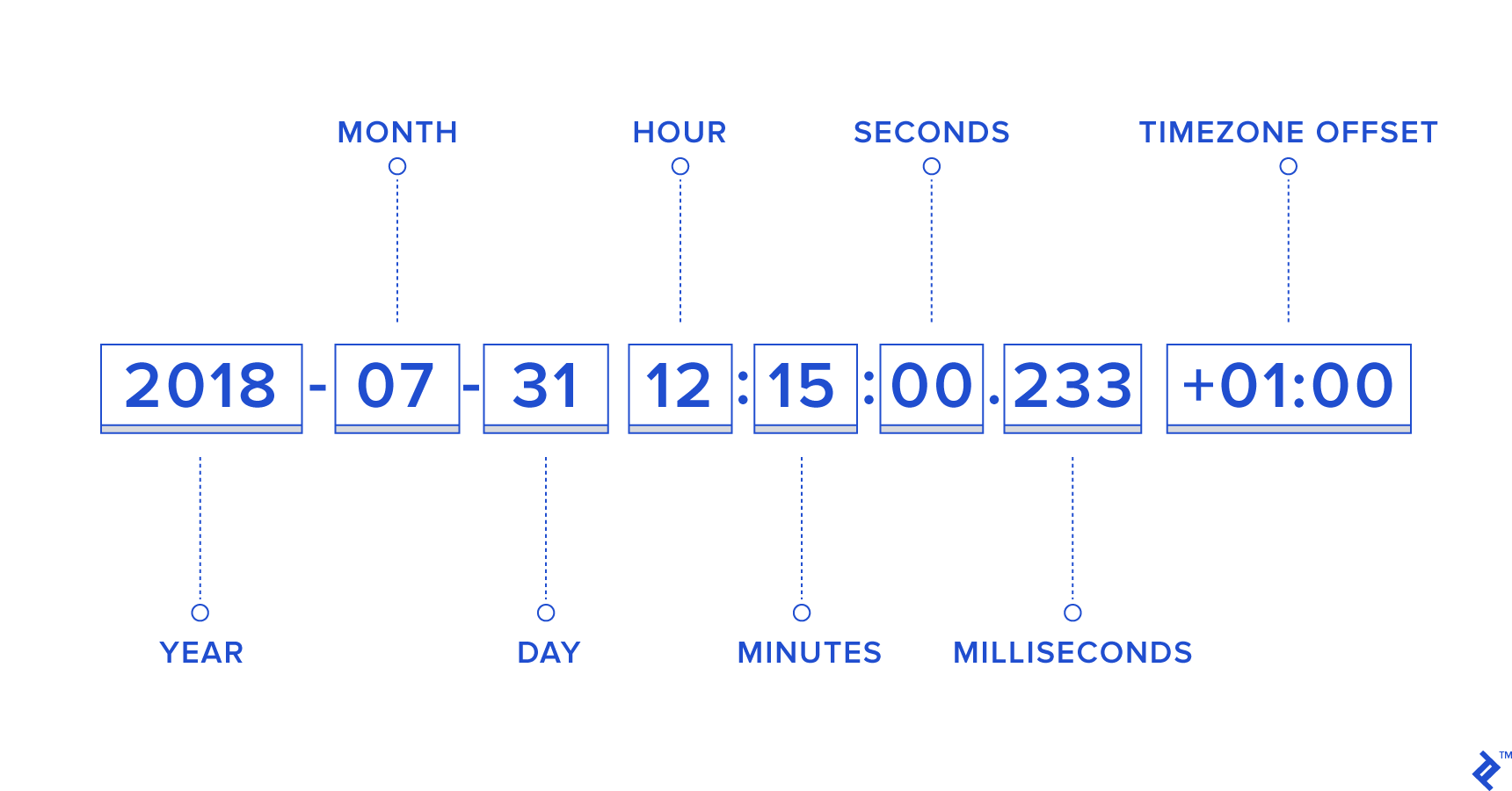 Demystifying Datetime Manipulation In Javascript Toptal
Demystifying Datetime Manipulation In Javascript Toptal
 Truthy And Falsy When All Is Not Equal In Javascript Sitepoint
Truthy And Falsy When All Is Not Equal In Javascript Sitepoint
 Vs In Javascript And Which Should Be Used When Codeahoy
Vs In Javascript And Which Should Be Used When Codeahoy
 Javascript Compare Strings Examples Tuts Make
Javascript Compare Strings Examples Tuts Make
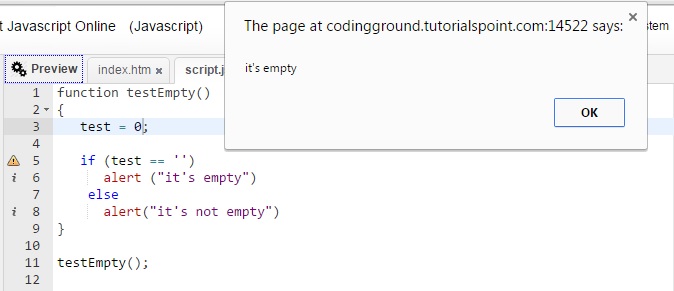 When Zero Is Equal To Empty String Yudy S Blog
When Zero Is Equal To Empty String Yudy S Blog
 Which Equals Operator Vs Should Be Used In
Which Equals Operator Vs Should Be Used In
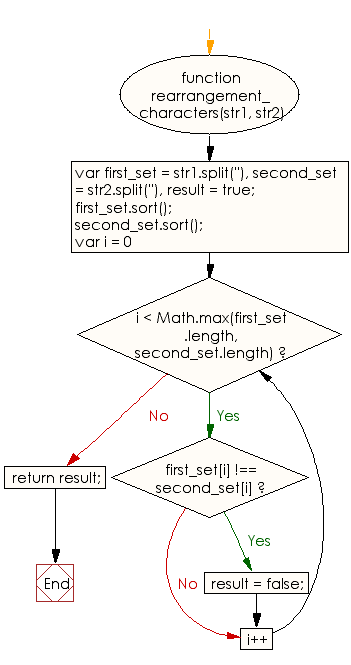 Javascript Basic Rearrange Characters Of A Given String In
Javascript Basic Rearrange Characters Of A Given String In
 Truthy And Falsy When All Is Not Equal In Javascript Sitepoint
Truthy And Falsy When All Is Not Equal In Javascript Sitepoint
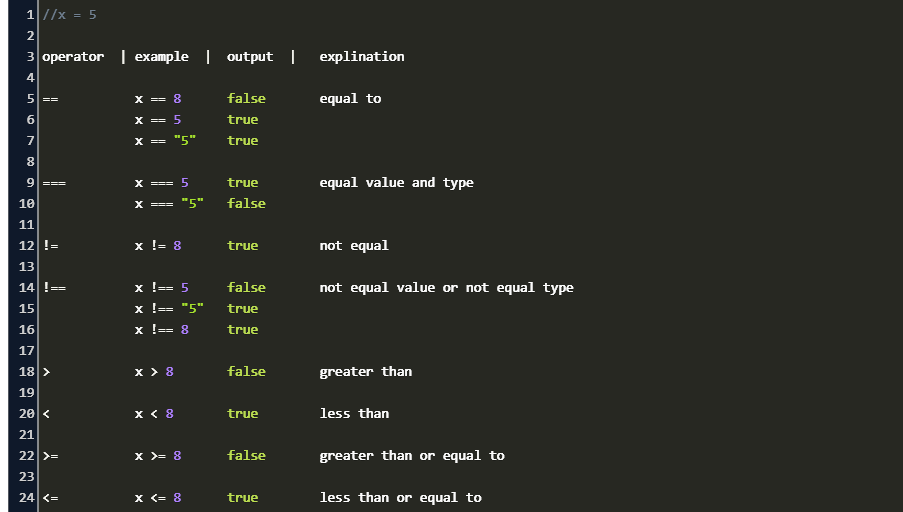 How To Compare String And Number In Javascript Code Example
How To Compare String And Number In Javascript Code Example
 Javascript Strings Find Out Different Methods Of String
Javascript Strings Find Out Different Methods Of String
 How To Check If A String Contains A Substring In Javascript
How To Check If A String Contains A Substring In Javascript
 Commonjs Javascript Everywhere
Commonjs Javascript Everywhere

Custom Javascript Targeting Optimize Resource Hub
 Javascript Algorithm Truncate A String By Erica N Level
Javascript Algorithm Truncate A String By Erica N Level
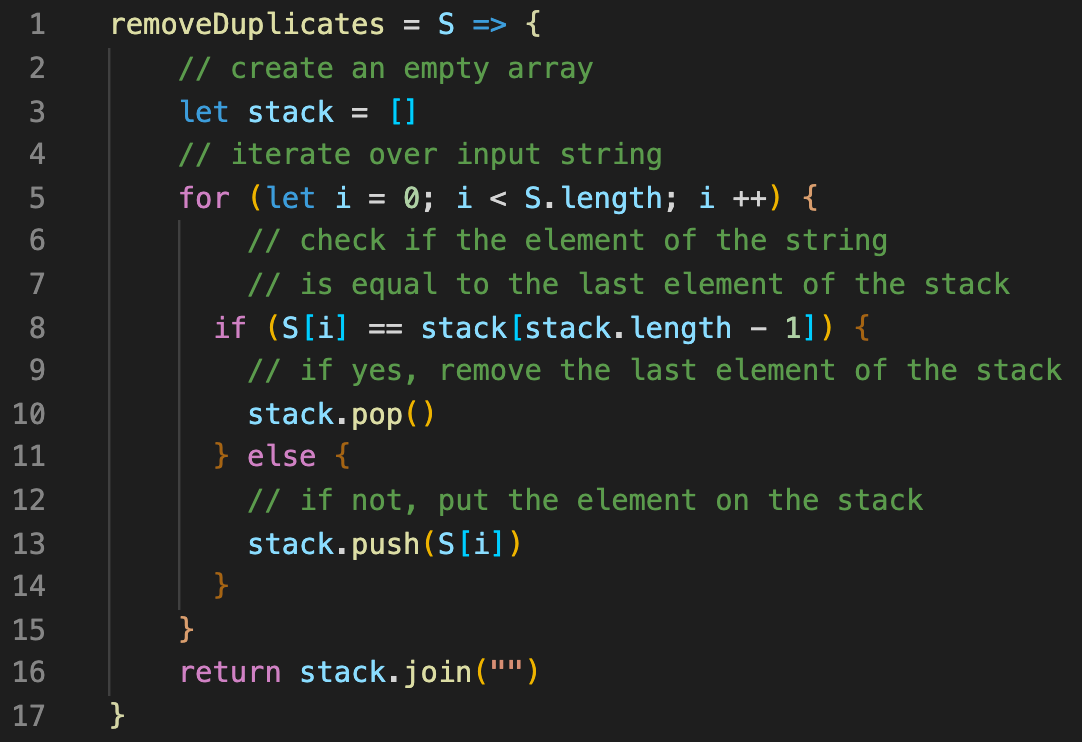 Remove Adjacent Duplicates Problem By Bahay Gulle Bilgi
Remove Adjacent Duplicates Problem By Bahay Gulle Bilgi
 How To Build An Html Calculator App From Scratch Using Javascript
How To Build An Html Calculator App From Scratch Using Javascript
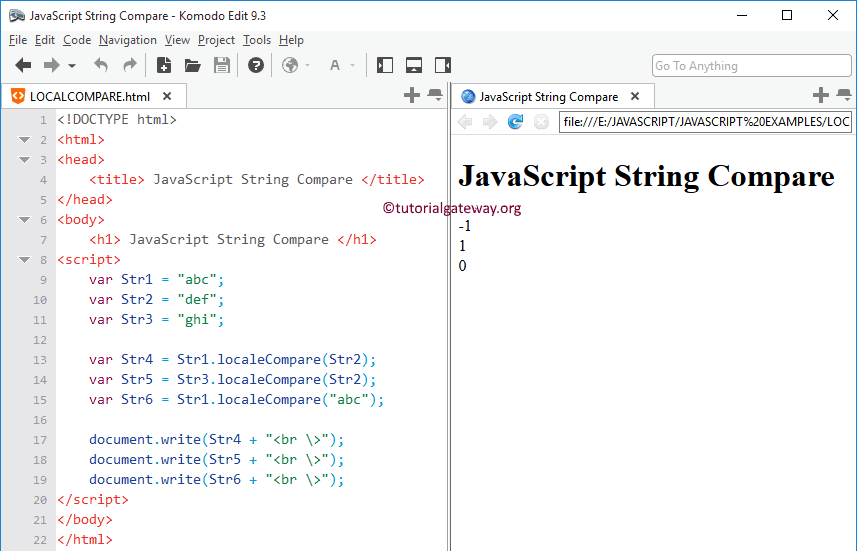
0 Response to "24 Javascript Is Equal To String"
Post a Comment