22 Javascript And Operator Example
What exactly is the JavaScript in operator? The JavaScript in operator is used to check if a specified property exists in an object or in its inherited properties (in other words, its prototype chain). The in operator returns true if the specified property exists. Anatomy of a simple JavaScript object. Jul 21, 2021 - ES6 has added spread property to object literals in javascript. The spread operator (…) with objects is used to create copies of existing objects with new or updated values or to make a copy of an object with more properties. Let’s take at an example of how to use the spread operator on ...
 Which Equals Operator Vs Should Be Used In
Which Equals Operator Vs Should Be Used In
It converts the value to a boolean value and then negates it. See the following example to show you, how to use the ! operator: 1. The logical not ! operator works based on the following rules: If a is undefined, the result is true. If a is null, the result is true. If a is a number other than 0, the result is false.

Javascript and operator example. What are Arithmetic Operators in Javascript? As the name suggests, you use arithmetic operators to perform mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and many other operations. For example, if you want to perform addition between two numeric values. In this case, you'll use the (+) operator in JavaScript. The logical AND (&&) operator (logical conjunction) for a set of operands is true if and only if all of its operands are true. It is typically used with Boolean (logical) values. When it is, it returns a Boolean value. However, the && operator actually returns the value of one of the specified operands, so if this operator is used with non-Boolean values, it will return a non-Boolean value. JavaScript logical operators covering description, example code, output of example, online practice editor and explanation by w3resource
Nov 08, 2011 - Why does the "in" operator in Javascript return true when testing if "0" exists in array, even when the array doesn't appear to contain "0"? For example, this returns true, and makes sense: var x... JavaScript operator are symbol that operates the operands. JavaScript includes various categories of operators: Arithmetic, Comparison and logical operators etc. Jul 04, 2020 - This chapter documents all the JavaScript language operators, expressions and keywords.
JavaScript will try to run all the statements in order, and will default to the else block if none of them are successful. In case of many else ifstatements, the switch statement can be preferred for readability. Conditional operator '?'¶ The "conditional" or "question mark" operator lets us in a shorter and simpler way assign a ... Javascript Operators JavaScript includes operators same as other languages. An operator performs some operation on single or multiple operands (data value) and produces a result. For example, in 1 + 2, the + sign is an operator and 1 is left side operand and 2 is right side operand. JavaScript - Operators, Let us take a simple expression 4 + 5 is equal to 9. Here 4 and 5 are called operands and ‘+’ is called the operator. JavaScript supports the followin
The logical operators are important in JavaScript because they allow you to compare variables and do something based on the result of that comparison. For example, if the result of the comparison is true, you perform a block of code; if it's false, you perform another block of code. JavaScript provides three logical operators: The operation or any action that is performed between two operands is called the operator. Example: var add=10+20; Here, + is the arithmetic operator and = is the assignment operator whereas 10 and 20 are operands For example, the addition (+) symbol is an operator that tells JavaScript engine to add two variables or values, while the equal-to (==), greater-than (>) or less-than (<) symbols are the operators that tells JavaScript engine to compare two variables or values, and so on.
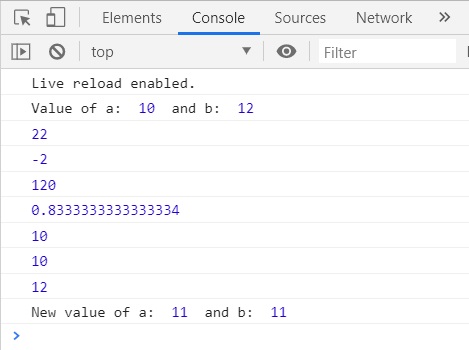
Given that x = 6 and y = 3, the table below explains the logical operators: ... Bit operators work on 32 bits numbers. Any numeric operand in the operation is converted into a 32 bit number. The result is converted back to a JavaScript number. The examples above uses 4 bits unsigned examples. In JavaScript, you can assign the data values (or the operands) to variables and apply an operator to get a result, or you can simply use numbers along with an operator and get the result. For example, Well organized and easy to understand Web building tutorials with lots of examples of how to use HTML, CSS, JavaScript, SQL, Python, PHP, Bootstrap, Java, XML and more.
When comparing a string with a number, JavaScript will convert the string to a number when doing the comparison. An empty string converts to 0. A non-numeric string converts to NaN which is always false. When comparing two strings, "2" will be greater than "12", because (alphabetically) 1 is less than 2. The "OR" operator is represented with two vertical line symbols: result = a || b; In classical programming, the logical OR is meant to manipulate boolean values only. If any of its arguments are true, it returns true, otherwise it returns false. In JavaScript, the operator is a little bit trickier and more powerful. 1 week ago - A bitwise operator treats their ... (zeros and ones), rather than as decimal, hexadecimal, or octal numbers. For example, the decimal number nine has a binary representation of 1001. Bitwise operators perform their operations on such binary representations, but they return standard JavaScript numerical ...
Bit operators work on 32 bits numbers. Any numeric operand in the operation is converted into a 32 bit number. The result is converted back to a JavaScript number. The examples above uses 4 bits unsigned examples. But JavaScript uses 32-bit signed numbers. Because of this, in JavaScript, ~ 5 will not return 10. It will return -6. Well organized and easy to understand Web building tutorials with lots of examples of how to use HTML, CSS, JavaScript, SQL, Python, PHP, Bootstrap, Java, XML and more. Note: In JavaScript, == is a comparison operator, whereas = is an assignment operator. If you mistakenly use = instead of == , you might get unwanted result. Example 2: Not Equal to Operator
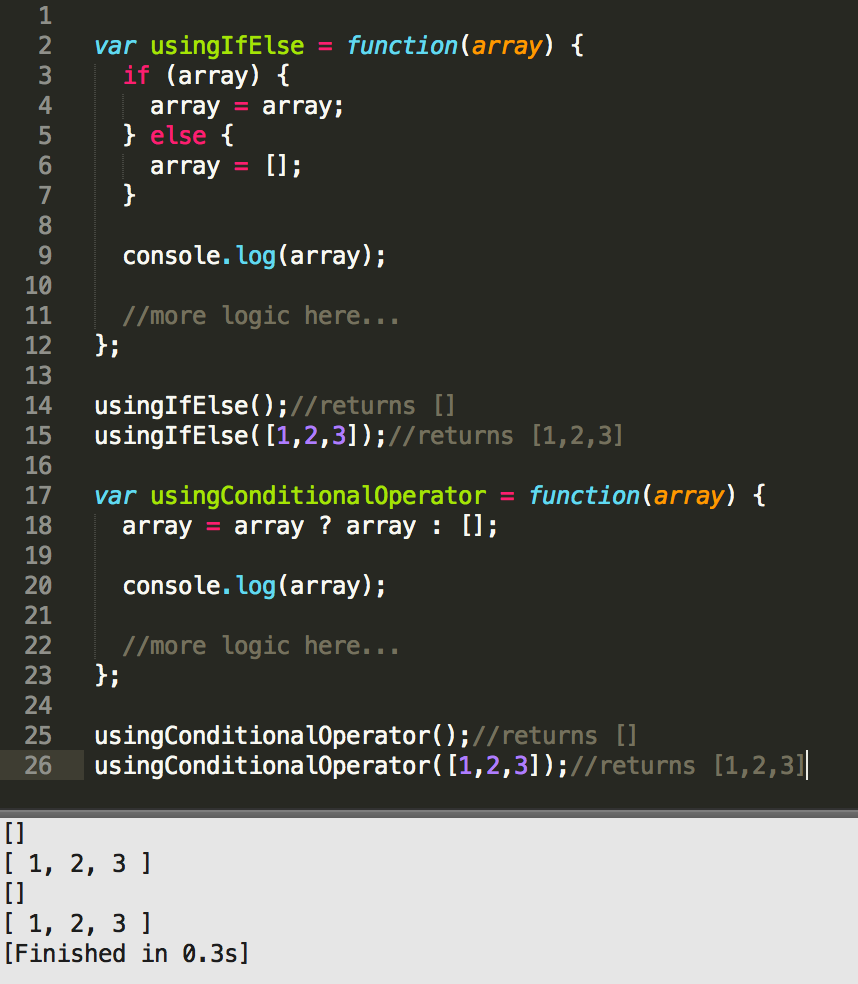
JavaScript Operators with Example JavaScript Arithmetic Operators. JavaScript arithmetic operator take operand (as a values or variable) and return the single value. We are use in our routine life arithmetic operators, addition(+), subtraction(-), multiplication (*), and division (/) and some other arithmetic operator are listed below. We have numeric variable: x = 10, y = 5 and result. What is an Operator? In JavaScript, an operator is a special symbol used to perform operations on operands (values and variables). For example, 2 + 3; // 5. Here + is an operator that performs addition, and 2 and 3 are operands. Ternary Operator. Does JavaScript include a special operator called ternary operator:? that assigns a value to a variable based on some condition. This is like a short form of the if-else condition. In other words, The conditional (ternary) operator is the only JavaScript operator that takes three operands. This operator is frequently used as a ...
4 days ago - For example, Writing a=10 is fine. If we write 10=10, ‘a’ = 10 or ‘a’ = ‘a’, it will result in a reference error. ... Double equals (==) is a comparison operator, which transforms the operands having the same type before comparison. So, when you compare string with a number, JavaScript ... #Using Logical Operators with Non-Boolean Values. In JavaScript, the logical operators have different semantics than other C-like languages, though. They can operate on expressions of any type, not just booleans. Also, the logical operators do not always return a boolean value, as the specification points out in section 12.12: The logical OR (||) operator (logical disjunction) for a set of operands is true if and only if one or more of its operands is true. It is typically used with Boolean (logical) values. When it is, it returns a Boolean value. However, the || operator actually returns the value of one of the specified operands, so if this operator is used with non-Boolean values, it will return a non-Boolean value.
Before jumping into how the operators work, let's start with the basic concepts of truthy and falsy. 1. Falsy value. Because JavaScript is a loosely typed language, logical operations can be performed on any type. The expressions like 1 && 2, null || undefined, 'hello' && true are weird, but still valid in JavaScript. let [addition, multiplication] = sample(2, 5); console.log(addition) console.log(multiplication) Using Destructuring. And in the output, you can see we get the addition and multiplication of both numbers. What is the Spread Operator in JavaScript? Spread means spreading or expanding. And the spread operator in JavaScript is denoted by three dots. 3 weeks ago - For instance, in the multiplication of 5 * 2 there are two operands: the left operand is 5 and the right operand is 2. Sometimes, people call these “arguments” instead of “operands”. An operator is unary if it has a single operand. For example, the unary negation - reverses the sign ...
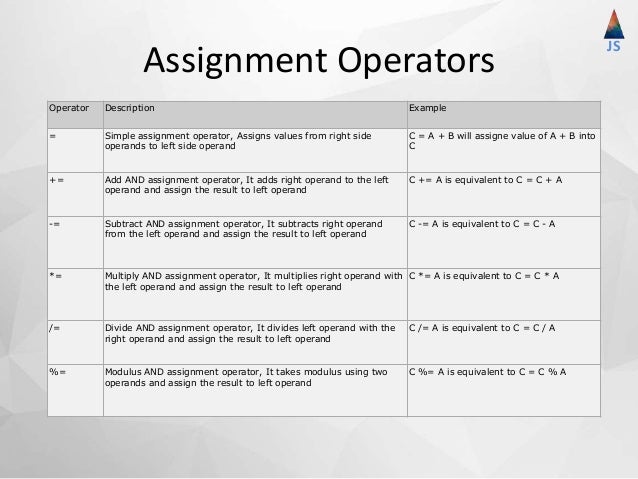
There are various Assignment Operators in JavaScript -. = (Assignment Operator) : Assigns right operand value to left operand. Example : If A = 10 and Y = A then Y = 10. += (Add and Assignment Operator) : Sums up left and right operand values and then assign the result to the left operand. Example : In operator used in enum data type for following use cases. Check string exists in Enum typescript or Javascript. In the below example, This operator used to chehck string and value presented in Enum data. false is return if there is no property or its value exists in Enum typescript For example, in the Equal operator we can write same value in different types gives the same result, like we declared var a = 5 and we are assigning a == 5 or a == "5" to the opertor gives the same result, but in Equal value and Equal type operator it is not possible. The symbolic representation of equal value and equal type is ===.
Let's take the previous example of a basic addition calculation written in JavaScript. var x = 10; var y = 12; var z = x + y; Just like math, operators have a precedent. This means that some operators have a higher precedent than others, so when you use a simple calculation within an expression, the higher precedent operator will execute first. In this tutorial, you will learn about different operators available in JavaScript and how to use them with the help of examples. What is an Operator? In JavaScript, an operator is a special symbol used to perform operations on operands (values and variables).
 How To Use Javascript Unary Operators Digitalocean
How To Use Javascript Unary Operators Digitalocean
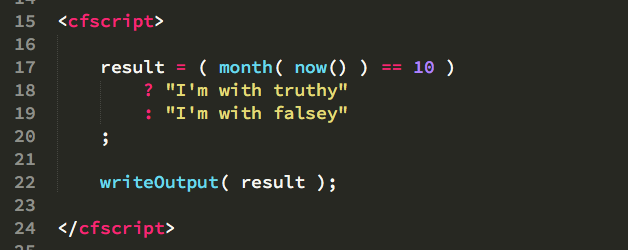 How I Format The Conditional Ternary Operator In Coldfusion
How I Format The Conditional Ternary Operator In Coldfusion
 Logical Operators In Javascript Logic Web Development
Logical Operators In Javascript Logic Web Development
Javascript Operators Types Of Operators In Javascript Edureka
 How The Question Mark Operator Works In Javascript
How The Question Mark Operator Works In Javascript
 Javascript Operators And Expressions
Javascript Operators And Expressions
Hour 3 Using Javascript In The Mongodb Shell
Ternary Operator And Javascript Keywords Issue 173 Atom
 Ternary Operator Multiple Conditions Javascript Example Code
Ternary Operator Multiple Conditions Javascript Example Code
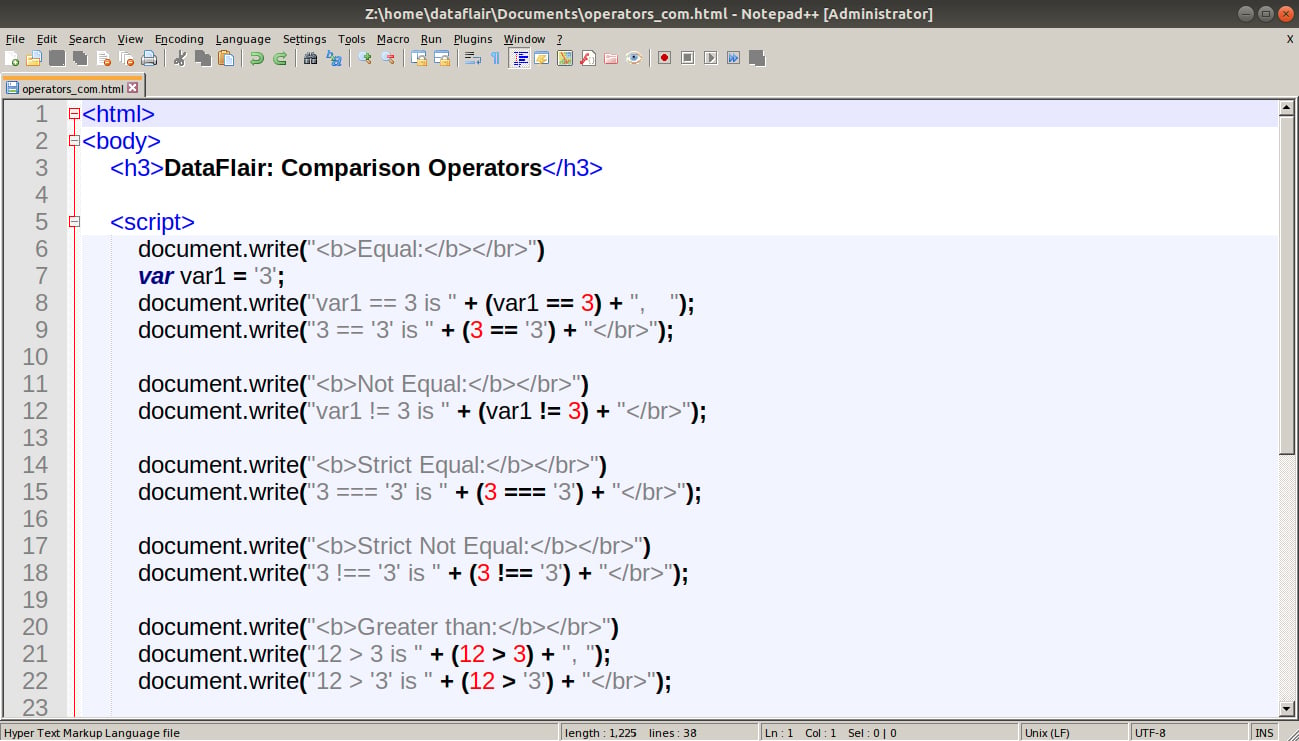 Javascript Operators Top 7 Types That You Can T Omit While
Javascript Operators Top 7 Types That You Can T Omit While
 Javascript Operators Types Of Javascript Operators
Javascript Operators Types Of Javascript Operators
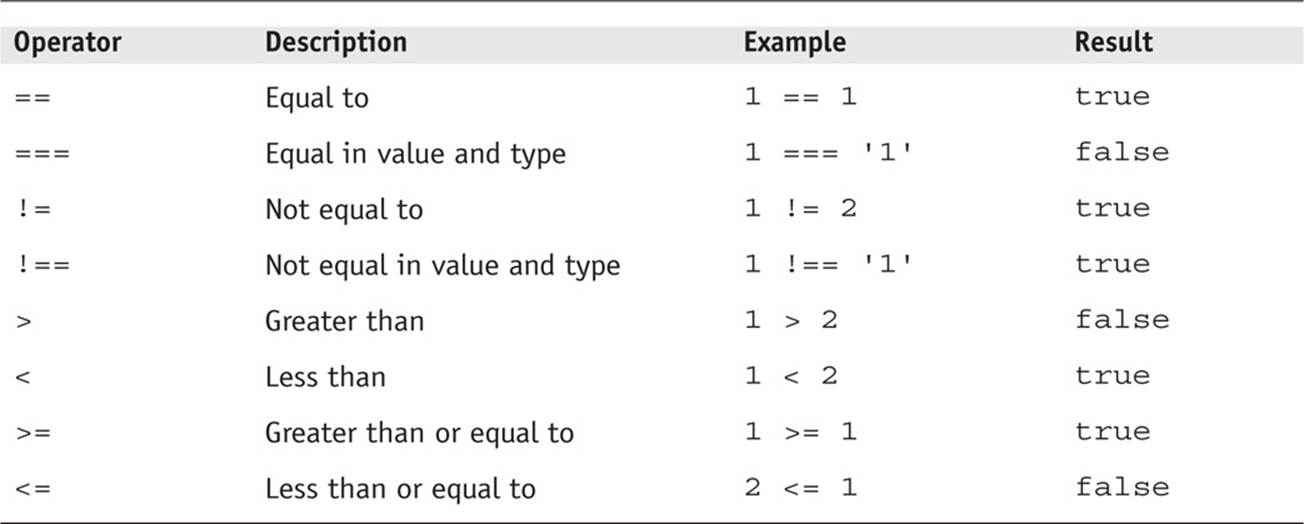 Applying Comparison And Logical Operators Javascript Basics
Applying Comparison And Logical Operators Javascript Basics
List Of Operators Used In Javascript Nios
 Javascript Operators With Examples Dot Net Tutorials
Javascript Operators With Examples Dot Net Tutorials
 Use Javascript Ternary Operator As An Alternative For If Else
Use Javascript Ternary Operator As An Alternative For If Else
 Javascript Ternary Operator A Best Way To Clean Coding Codez Up
Javascript Ternary Operator A Best Way To Clean Coding Codez Up
 Javascript Logical Operators Amp Amp By Cristian
Javascript Logical Operators Amp Amp By Cristian
Operator Precedence And Associativity In Javascript
0 Response to "22 Javascript And Operator Example"
Post a Comment