23 What Is A Promise In Javascript
17/8/2021 · A promise in JavaScript is asynchronous, meaning it takes time to resolve or finish. Just as the search for the applicant's resume takes time to complete. For that reason, the interviewer decides not to sit around doing nothing, so they begin interviewing the candidate based on the promise of a résumé delivery. JavaScript Promises. In JavaScript, a Promise is used for performing asynchronous operations. It represents a result that may be available now, or in the future or never. Promises are easy to manage when dealing with multiple asynchronous operations. Where to use Promises
 How To Write A Javascript Promise
How To Write A Javascript Promise
2/1/2019 · Promises are used to handle asynchronous operations in JavaScript. They are easy to manage when dealing with multiple asynchronous operations where callbacks can create callback hell leading to unmanageable code. Prior to promises events and callback functions were used but they had limited functionalities and created unmanageable code.

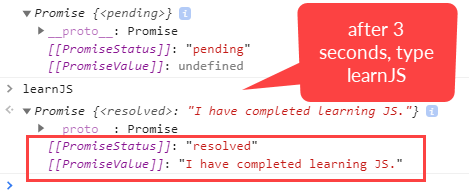
What is a promise in javascript. Promise.resolve (obj) == obj && BLUEBIRD.resolve (obj) == obj When this works it's because the algorithm explicitly demands that Promise.resolve must return the exact object passed in if and only if it is a promise created by this constructor. In JavaScript, a promise is a good way to handle asynchronous operations. It is used to find out if the asynchronous operation is successfully completed or not. A promise may have one of three states. ... A promise starts in a pending state. That means the process is not complete. "I Promise a Result!" "Producing code" is code that can take some time "Consuming code" is code that must wait for the result A Promise is a JavaScript object that links producing code and consuming code
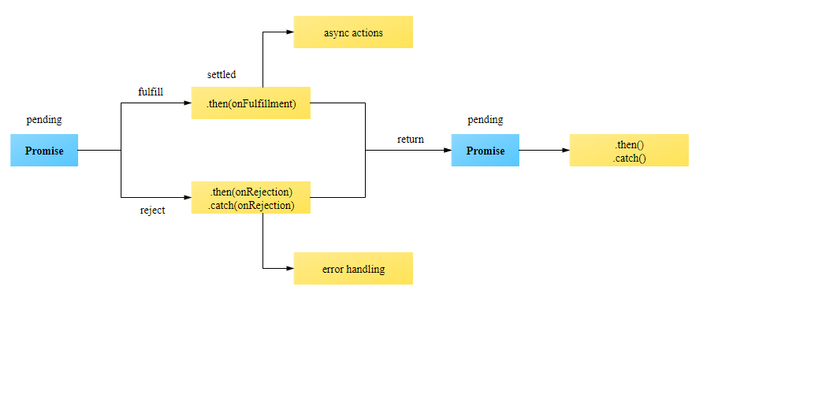
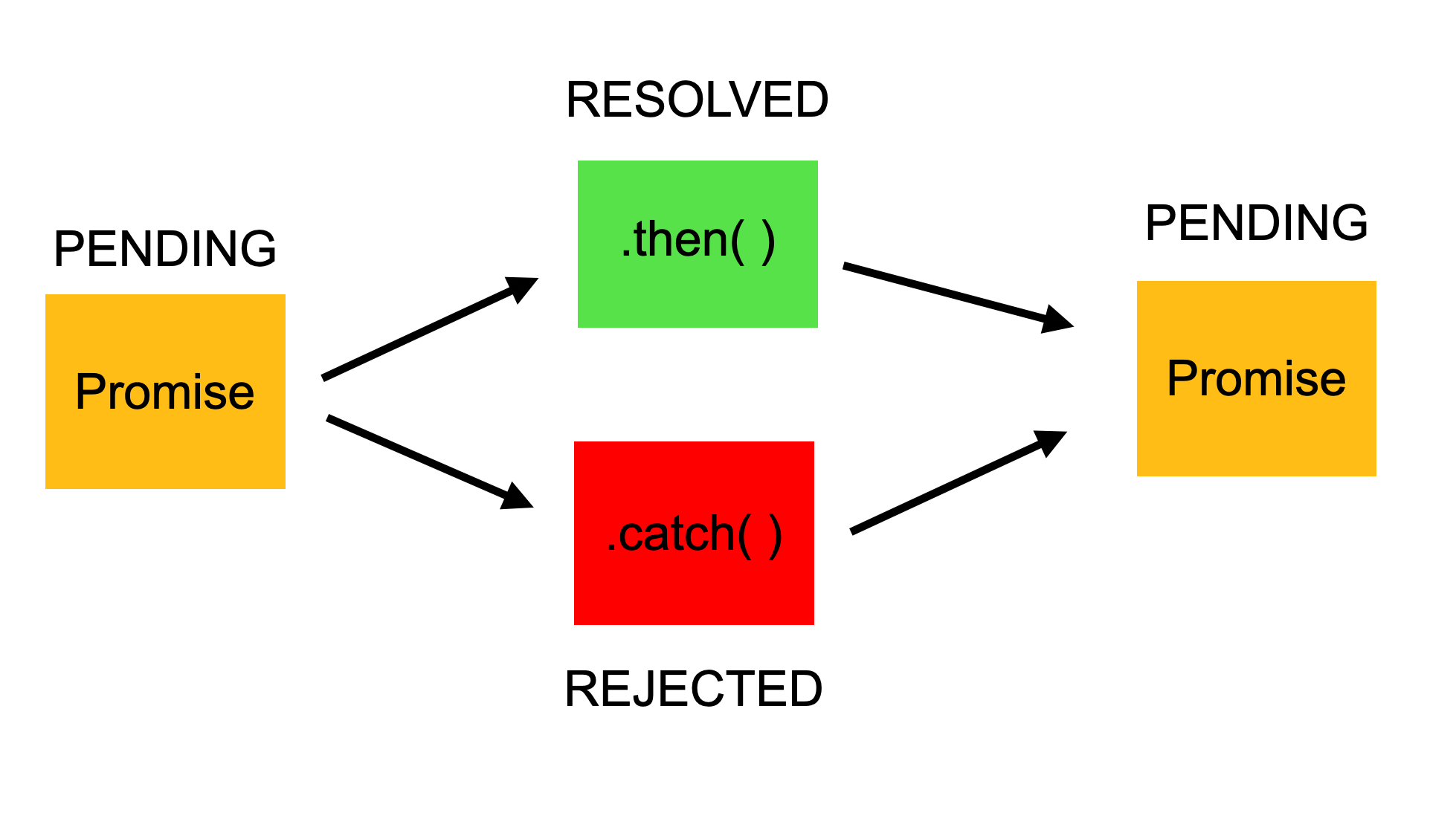
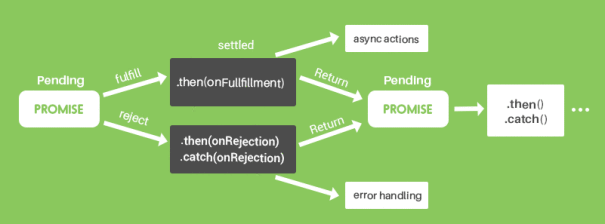
The promise is a placeholder holding the result of an asynchronous operation. If the operation completes successfully, then the promise fulfills with the operation value, but if the operation fails: the promise rejects with the reason of the failure. Promises can also create chains, which are useful in handling multiple dependent async operations. In JavaScript, a promise is just like a promise that you make in real life to show that you are committed to doing something. For example, I promise to get good marks in mathematics, and then this Promise has two outcomes, either it will be fulfilled (or resolved) or not fulfilled (or be rejected). 15/1/2020 · JavaScript Promises Explained What is a promise in JavaScript? JavaScript is single threaded, meaning that two bits of script cannot run at the same time; they have to run one after another. A Promise is an object that represents the eventual completion (or failure) of an asynchronous operation, and its resulting value.
Aug 23, 2019 - However, callbacks were limited ... promises were introduced to cater to these problems. According to MDN, “the Promise object represents the eventual completion (or failure) of an asynchronous operation and its resulting value.” ... A promise is created using a constructor ... Running checkIfItsDone() will specify functions to execute when the isItDoneYet promise resolves (in the then call) or rejects (in the catch call).. Chaining promises. A promise can be returned to another promise, creating a chain of promises. A great example of chaining promises is the Fetch API, which we can use to get a resource and queue a chain of promises to execute when the resource is ... Promises in JavaScript are an object representation of an asynchronous computation. You can think of a promise as a placeholder for a value that hasn't been computed yet. However, there's no way to get a promise's value from the promise directly - you need to call the then() ...
What is a Promise in JavaScript: Definition by MDN: A Promise is a proxy for a value not necessarily known when the promise is created. It allows you to associate handlers with an asynchronous action's eventual success value or failure reason. Mar 11, 2020 - Because the value will be returned by the promise in the future, the promise is very well-suited for handling asynchronous operations. It’ll be easier to understand the concept of JavaScript promises through an analogy. Promise constructor in JavaScript used to alert the end-user about application status like fulfilled, rejected, pending and settled. JavaScript promises mainly work with asynchronous applications. Recommended Articles. This is a guide to JavaScript Promise.
Sep 21, 2020 - You can help us out by using the "report an issue" button at the bottom of the tutorial. Javascript Promises are not difficult. However, lots of people find it a little bit hard to understand at the beginning. Therefore, I would like to write down the way I understand promises, in a dummy way. Promises in JavaScript represent processes that are already happening, which can be chained with callback functions. If you are looking to lazily evaluate an expression, consider the arrow function with no arguments: f = () => expression to create the lazily-evaluated expression, and f () to evaluate. Apr 17, 2018 - Many of us have already used promises in the form of libraries such as Q, when.js, RSVP.js, etc. Even jQuery has something called a Deferred object, which is similar to a promise. But now we have native support for promises in JavaScript, which is really exciting.
2 weeks ago - This is also the same for promises in JavaScript. When we define a promise in JavaScript, it will be resolved when the time comes, or it will get rejected. ... First of all, a Promise is an object. There are 3 states of the Promise object: A Promise represents the eventual completion of an asynchronous operation. Promises provide a straightforward alternative for composing and managing asynchronous code, without having to write too many callbacks, or spend extra time figuring out what the program should do. A Promise in JavaScript is a object representing a value which may be available in the future. For example, when asking the JavaScript runtime to make a request to Twitter, it might give you a Promise of the HTTP response instead of giving you the response immediately. We can use this promise object to get the response later.
As Madhuhc and other people describes, promises is a cleaner way of doing asynchronous programming in JS. It allows you to write asynchronous code in synchronous style as more developers are familiar with it. And it is easily testable and maintainable. Let's go into details, a Promise in Javascript is an object and represent an Asynchronous operation, the new Javascript API's are being purely implemented using Promises. To create new Promise instances we need to use the Promise constructor: Mar 31, 2021 - A promise is a special JavaScript object that links the “producing code” and the “consuming code” together. In terms of our analogy: this is the “subscription list”. The “producing code” takes whatever time it needs to produce the promised result, and the “promise” makes ...
A Promise is an object representing the eventual completion or failure of an asynchronous operation. Since most people are consumers of already-created promises, this guide will explain consumption of returned promises before explaining how to create them. A Promise in JavaScript is an object that holds the future value of an asynchronous operation. For example, if we are requesting some data from a server, the promise promises us to get that data that we can use in the future. A promise object can have the following states: Aug 12, 2019 - What is a promise?A JavaScript promise is an object that represents the completion or failure of an asynchronous task and its resulting value.¹ The end. I’m kidding of course. So, what does that definition even mean? First of all, many things in JavaScript are objects. You can create
1 week ago - Async functions are stage 3 at the time of this writing, but I predict that they will soon become a very popular, very commonly used solution for asynchronous programming in JavaScript — which means that learning to appreciate promises is going to be even more important to JavaScript developers ... What is a Promise in JavaScript? A promise is an object which handles asynchronous requests. When the implementation is correct, it will always promise that you will get a single response (either... Introduction. Javascript Promises can be challenging to understand. Therefore, I would like to write down the way I understand promises. Understanding Promises. A Promise in short: "Imagine you are a kid.Your mom promises you that she'll get you a new phone next week.". You don't know if you will get that phone until next week. Your mom can really buy you a brand new phone, or she ...
Interactive API reference for the JavaScript Promise Object. A Promise is an object that represents an asynchronous operation that will eventually produce a value. Use the then() method to hook up a c Promises are objects represents the eventual completion/failure of an asynchronous operation and its resulting value. How do promises work in javascript? Promises can be created by the keyword new and its constructor. const APIgetPosts = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {. // call for an api to get the posts. Jan 18, 2021 - JavaScript promises started out in the DOM as "Futures", renamed to "Promises", and finally moved into JavaScript. Having them in JavaScript rather than the DOM is great because they'll be available in non-browser JS contexts such as Node.js (whether they make use of them in their core APIs ...
Promise.all takes an array of promises (it technically can be any iterable, but is usually an array) and returns a new promise. The new promise resolves when all listed promises are resolved, and the array of their results becomes its result. For instance, the Promise.all below settles after 3 seconds, and then its result is an array [1, 2, 3]: In JavaScript, a promise works the same way as a promise in real life. The JavaScript version of scenario can be written in the following way: // jeffBuysCake is a promise const promise = jeffBuysCake('black forest') (You'll learn how to construct jeffBuysCake later. For now, take it that its a promise). A promise in JavaScript is created using a constructor function. The constructor function takes a callback function as a parameter, which in turn takes 2 parameters: resolve and reject, which in turn take one argument which is a value that can be a string, number, boolean, array, or an object. Resolve () and reject () are static method inherent ...
ECMAScript 2015, also known as ES6, introduced the JavaScript Promise object. The following table defines the first browser version with full support for Promise objects: ... Get certified by completing a course today! Promises help you naturally handle errors, and write cleaner code by not having callback parameters, and without modifying the underlying architecture (i.e. you can implement them in pure JavaScript and use them to wrap existing asynchronous operations). ... The core idea behind promises is that ... A Promise in JavaScript just like a promise in real-world has 3 states. It can be 1) unresolved (pending), 2) resolved (fulfilled), or 3) rejected. For example: Unresolved or Pending — A Promise is pending if the result is not ready. That is, it's waiting for something to finish (for example, an async operation).
Promises for layman Promises in JavaScript are very similar to the promises you make in real life. So first let us look at promises in real life. The definition of a promise from the dictionary is as follows
 The Definitive Guide To The Javascript Promises
The Definitive Guide To The Javascript Promises
 Javascript Promises Explained Dev Community
Javascript Promises Explained Dev Community
 How To Check If A Javascript Promise Has Been Fulfilled
How To Check If A Javascript Promise Has Been Fulfilled
 Promises In Javascript Background Concept Hashnode
Promises In Javascript Background Concept Hashnode
 Javascript Promise Tutorial Resolve Reject And Chaining In
Javascript Promise Tutorial Resolve Reject And Chaining In
 Adding A Promise To Sequence If Condition Is Met Stack Overflow
Adding A Promise To Sequence If Condition Is Met Stack Overflow
 Javascript Promise And Promise Chaining Learn Javascript
Javascript Promise And Promise Chaining Learn Javascript
Javascript Promises Tutorial How To Use Them Ictshore Com
 What Is A Promise In Javascript Learn Tech Systems
What Is A Promise In Javascript Learn Tech Systems
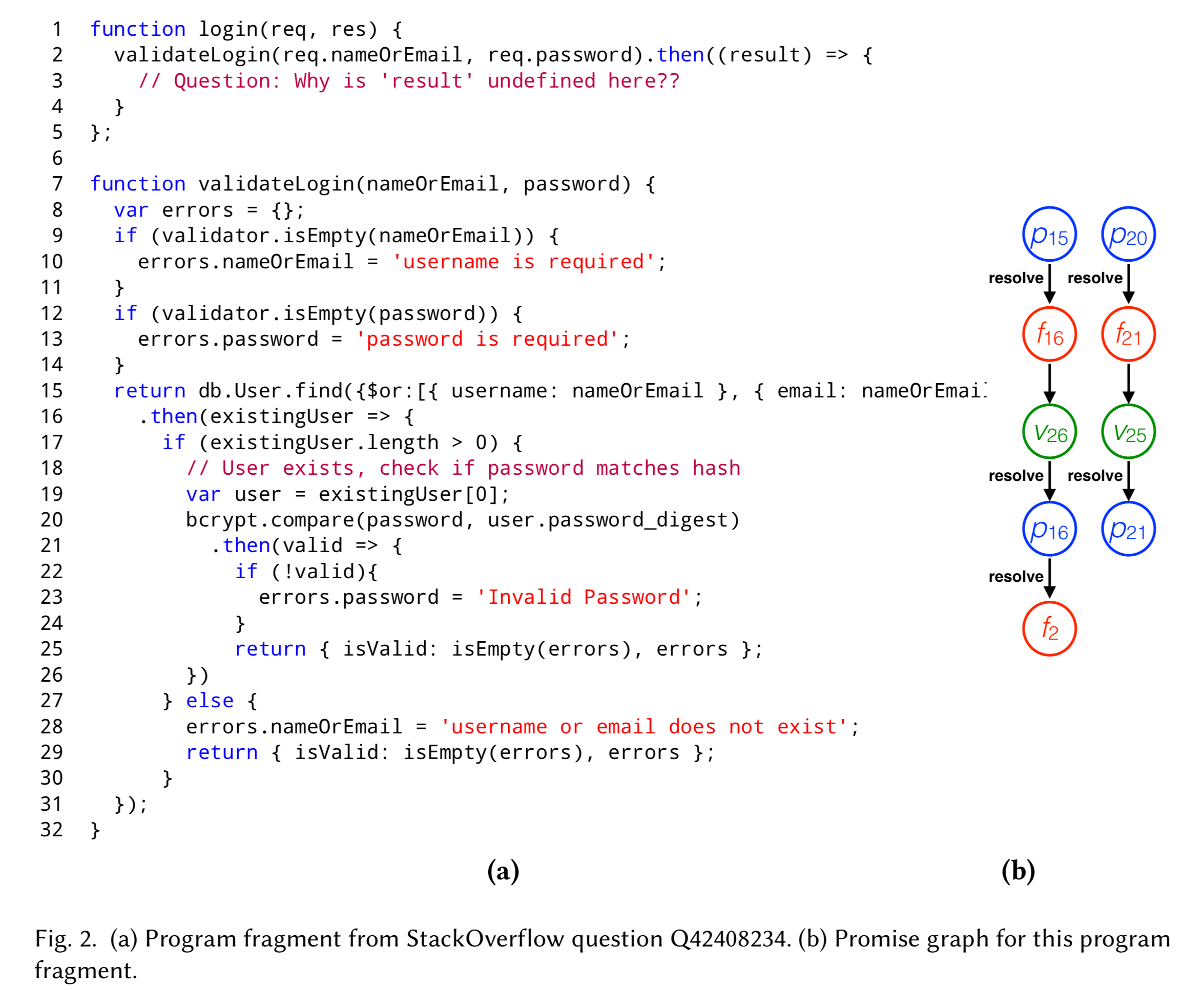 A Model For Reasoning About Javascript Promises The Morning
A Model For Reasoning About Javascript Promises The Morning
 Tools Qa What Are Promises In Javascript And How To Use
Tools Qa What Are Promises In Javascript And How To Use
 Asynchronous Javascript Introduction To Javascript Promises
Asynchronous Javascript Introduction To Javascript Promises
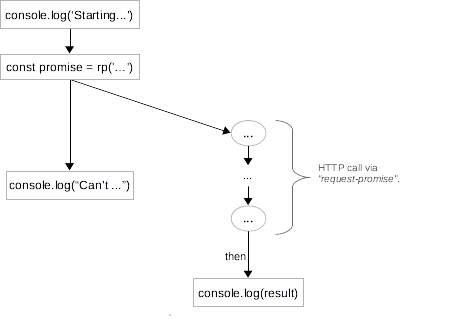 Await And Async Explained With Diagrams And Examples
Await And Async Explained With Diagrams And Examples
Creating Dynamic Promise Chains Cmichel
 What Are The Differences Between Deferred Promise And Future
What Are The Differences Between Deferred Promise And Future
 Javascript Promise With Examples Dot Net Tutorials
Javascript Promise With Examples Dot Net Tutorials
 Using Es6 Array Destructing With Promises Dev Community
Using Es6 Array Destructing With Promises Dev Community
 Introduction To The Javascript Promises Our Code World
Introduction To The Javascript Promises Our Code World
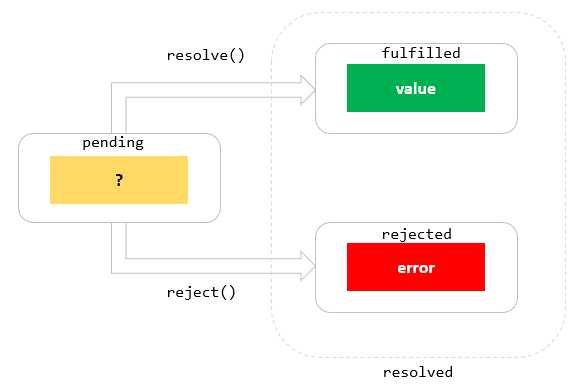 The Definitive Guide To The Javascript Promises
The Definitive Guide To The Javascript Promises
 Overview Of Promises In Javascript
Overview Of Promises In Javascript
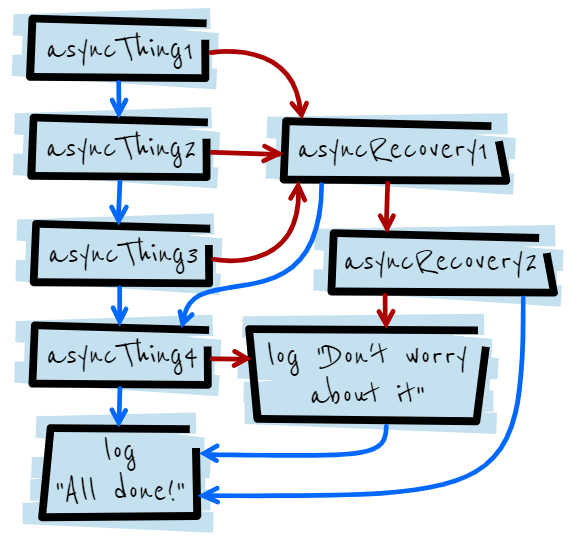 Exploring Javascript Promises In Depth Javascript In Plain
Exploring Javascript Promises In Depth Javascript In Plain
0 Response to "23 What Is A Promise In Javascript"
Post a Comment