34 What Is Async In Javascript
Hey gang, in this Asynchronous JavaScript tutorial, I'll introduce you to what Async JS actually is, and how it benefits us as JavaScript developers. Asynchr... What is Async and Await in JavaScript? It has to something to do with fetch and.then function, which returns promises in Asynchronous and allow other functions to run properly before the promises...
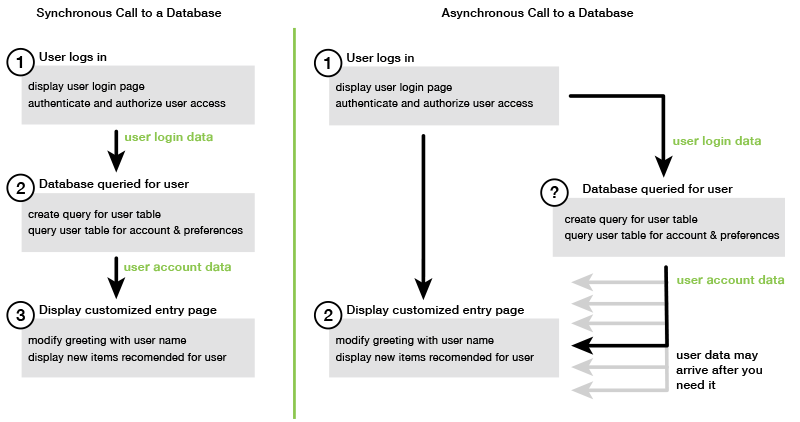 Managing Asychronous Calls Aws Sdk For Javascript
Managing Asychronous Calls Aws Sdk For Javascript
Asynchronous JavaScript. The examples used in the previous chapter, was very simplified. The purpose of the examples was to demonstrate the syntax of callback functions: Example. function myDisplayer(some) { document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = some;}

What is async in javascript. Hey gang, in this JavaScript tutorial series we'll dive into async js - from the very beginning. Rather than just start using fetch, async & await from the s... Javascript is synchronous "by default". Meaning, the next line of code cannot run until the current one has finished. The next function cannot run until the current one has completed. But blocks of code run in parallel when it comes to asynchronous; Asynchronous functions run independently. What is Asynchronous JavaScript? If you want to build projects efficiently, then this concept is for you. The theory of async JavaScript helps you break down big complex projects into smaller tasks.
Async is short for "asynchronous". It's easier to understand async if you first understand what "synchronous", the opposite, means. In programming, we can simplify the definition of synchronous code as "a bunch of statements in sequence"; so each statement in your code is executed one after the other. var done = this.async () is a pattern used in Grunt to help perform asynchronous functions within a Task. You need to invoke done () or done (returnValues) to tell Grunt the task is complete (after your chain of asynchronous tasks). 16/3/2021 · The word “async” before a function means one simple thing: a function always returns a promise. Other values are wrapped in a resolved promise automatically. For instance, this function returns a resolved promise with the result of 1; let’s test it: async function f() { return 1; } f().then( alert);
ECMAScript 2017 introduced the JavaScript keywords async and await. The following table defines the first browser version with full support for both: Chrome 55. Edge 15. Firefox 52. Safari 11. Opera 42. async. The async attribute is somewhat like defer.It also makes the script non-blocking. But it has important differences in the behavior. The async attribute means that a script is completely independent:. The browser doesn't block on async scripts (like defer).; Other scripts don't wait for async scripts, and async scripts don't wait for them. ... An asynchronous model allows multiple things to happen at the same time. When you start an action, your program continues to run. When the action finishes, the program is informed and gets access to the result (for example, the data read from disk).
We all know that JavaScript is the synchronous and single-threaded programming language. That is to say, only one task can perform at any point in time. But on the contrary, JavaScript also provides the ability to make it behave like an asynchronous language with the help of promises mechanisms.Async That's where asynchronous JavaScript comes into play. Using asynchronous JavaScript (such as callbacks, promises, and async/await), you can perform long network requests without blocking the main thread. While it's not necessary that you learn all these concepts to be an awesome JavaScript developer, it's helpful to know :) In asynchronous programming, the execution time of T2 is now unrelated to T1. In this sense, the tasks are NOT occurring at the same time (in a continuous time interval). Asynchronous programming...
JavaScript Async Functions. Async and await are built on promises. The keyword "async" accompanies the function, indicating that it returns a promise. Within this function, the await keyword is applied to the promise being returned. The await keyword ensures that the function waits for the promise to resolve. Asynchronous JavaScript: Asynchronous code allows the program to be executed immediately where the synchronous code will block further execution of the remaining code until it finishes the current one. This may not look like a big problem but when you see it in a bigger picture you realize that it may lead to delaying the User Interface. Javascript will NOT wait for an async function like preheatOven to complete before it moves on to the tasks that follow like getFrozenPizza and openFrozenPizza. Javascript will await for an async function like ovenReady to complete and return data before moving on to the next task inside a parent async function.
Async/Await is the extension of promises which we get as a support in the language. You can refer Promises in Javascript to know more about it. Asynchronous Callbacks. The earliest and most straightforward solution to being stuck in the synchronous world is using asynchronous callbacks (think setTimeout()).. Let's use a database request as an example: asynchronous callbacks allow you to invoke a callback function which sends a database request (and any other nested callbacks) off to your app, where it waits for a response from the ... Asynchronous JavaScript - what is it? (Promises, callbacks, async/await) JavaScript code is executed synchronously. In other words, from top to bottom and one line at a time. First, the code will execute the function and know what to return when getText () is called.
Async/await helps you write synchronous-looking JavaScript code that works asynchronously. An async function returns a promise, if the functions returns a value, the promise is resolved with the value, but if the async function throws an error, the promise is rejected with that value. Let's create a simple async function below: JavaScript is a single-threaded programming language. This means it has one call stack and one memory heap. As expected, it executes code in order and must finish executing a piece of code before moving into the next. However, thanks to the V8 engine, JavaScript can be asynchronous which means we can execute multiple tasks in our code at one time. An async function is a function declared with the async keyword, and the await keyword is permitted within them. The async and await keywords enable asynchronous, promise-based behavior to be written in a cleaner style, avoiding the need to explicitly configure promise chains. Async functions may also be defined as expressions.
Basically, Async and Await are two keywords in JavaScript that are introduced recently. While the Async operates asynchronously via the event loop. Also, it returns a value. Further, it ensures that a Promise is returned. To contrast, if this page were to have an AJAX event (that's Asynchronous JavaScript and XML event) associated with some user action, this page would load some data from another source asynchronously - in parallel (theoretically) with any other actions going on. Example with Two Synchronous Events (A and B): First A does something. The async/await abstraction is the new and shiny for developers looking to be on the cutting edge of JavaScript development. It is only recently getting standard support in browsers but has been...
Async operations like promises are put into an event queue, which runs after the main thread has finished processing so that they do not block subsequent JavaScript code from running. The queued operations will complete as soon as possible then return their results to the JavaScript environment. The way "async" works is that it is attached to a function to make it an async function and then we can use the promise method that it returns accordingly with the use of "await". What "await" does is that, firstly, it is always going to be used inside an "async" function and secondly, it makes the code wait for the response to ...
 Debugging Asynchronous Javascript With Chrome Devtools
Debugging Asynchronous Javascript With Chrome Devtools
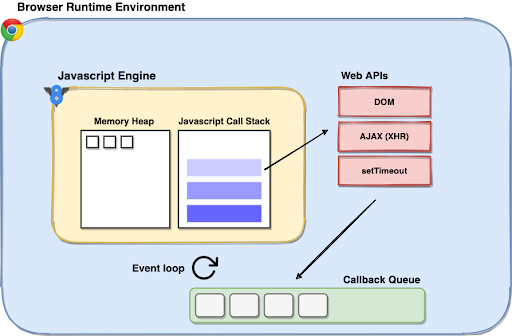
 Amazon Com Javascript Async Events Callbacks Promises And
Amazon Com Javascript Async Events Callbacks Promises And
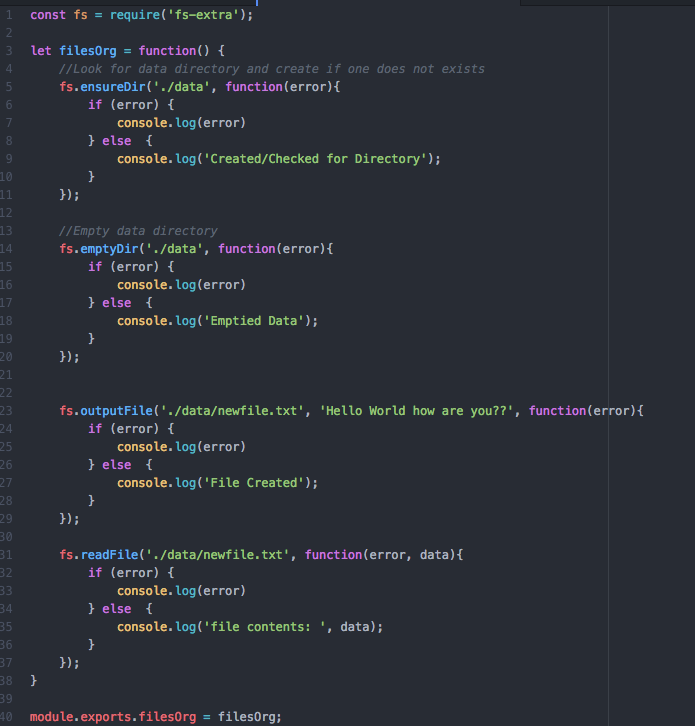 Cleaning Up Asynchronous Javascript With Async Await Keywords
Cleaning Up Asynchronous Javascript With Async Await Keywords
 Asynchronous Javascript Using Async Await Scotch Io
Asynchronous Javascript Using Async Await Scotch Io
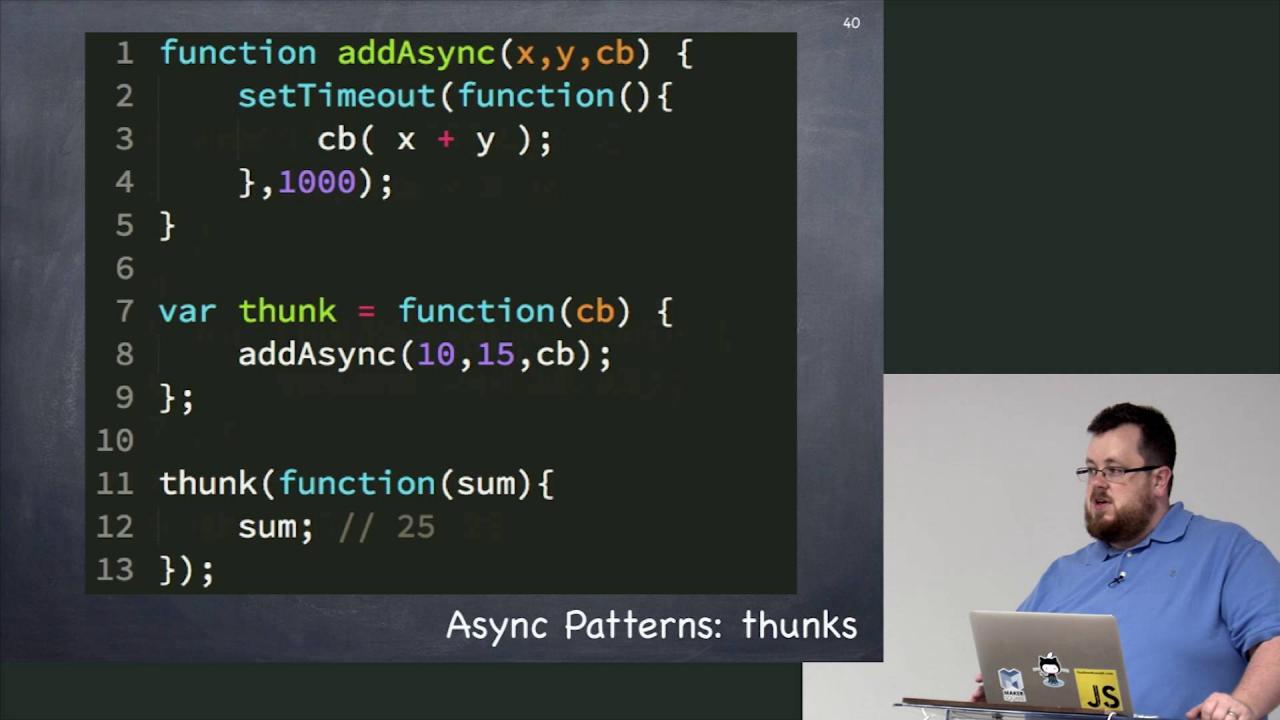 Learn Recap Rethinking Asynchronous Javascript
Learn Recap Rethinking Asynchronous Javascript
 How Does Async Await Simplify Javascript Programming
How Does Async Await Simplify Javascript Programming
 How To Use Async Await In Javascript By Ashay Mandwarya
How To Use Async Await In Javascript By Ashay Mandwarya
 Asynchronous Javascript From Callback Hell To Async And
Asynchronous Javascript From Callback Hell To Async And
 Javascript Async Await Explained How Does It Work 2021
Javascript Async Await Explained How Does It Work 2021
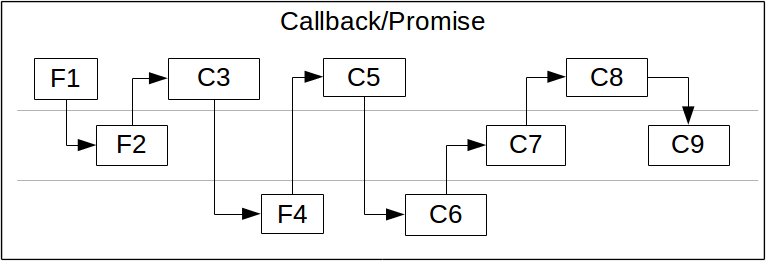 Javascript Async Amp Await Promises And Callbacks The Linux
Javascript Async Amp Await Promises And Callbacks The Linux
 Is Javascript Synchronous Or Asynchronous What The Hell Is A
Is Javascript Synchronous Or Asynchronous What The Hell Is A
 Should I Use Promises Or Async Await Hacker Noon
Should I Use Promises Or Async Await Hacker Noon
 Don T Make That Function Async Dev Community
Don T Make That Function Async Dev Community
 How To Use Async Await In Javascript
How To Use Async Await In Javascript
 Understanding Async Await In Javascript By Gemma Stiles
Understanding Async Await In Javascript By Gemma Stiles
 Javascript Async Patterns Quick Guide
Javascript Async Patterns Quick Guide
 Javascript Promises Or Async Await Dev Community
Javascript Promises Or Async Await Dev Community
 Async Javascript From Pure Callbacks To Promises To Async
Async Javascript From Pure Callbacks To Promises To Async
 Async Javascript By Trevor Burnham
Async Javascript By Trevor Burnham
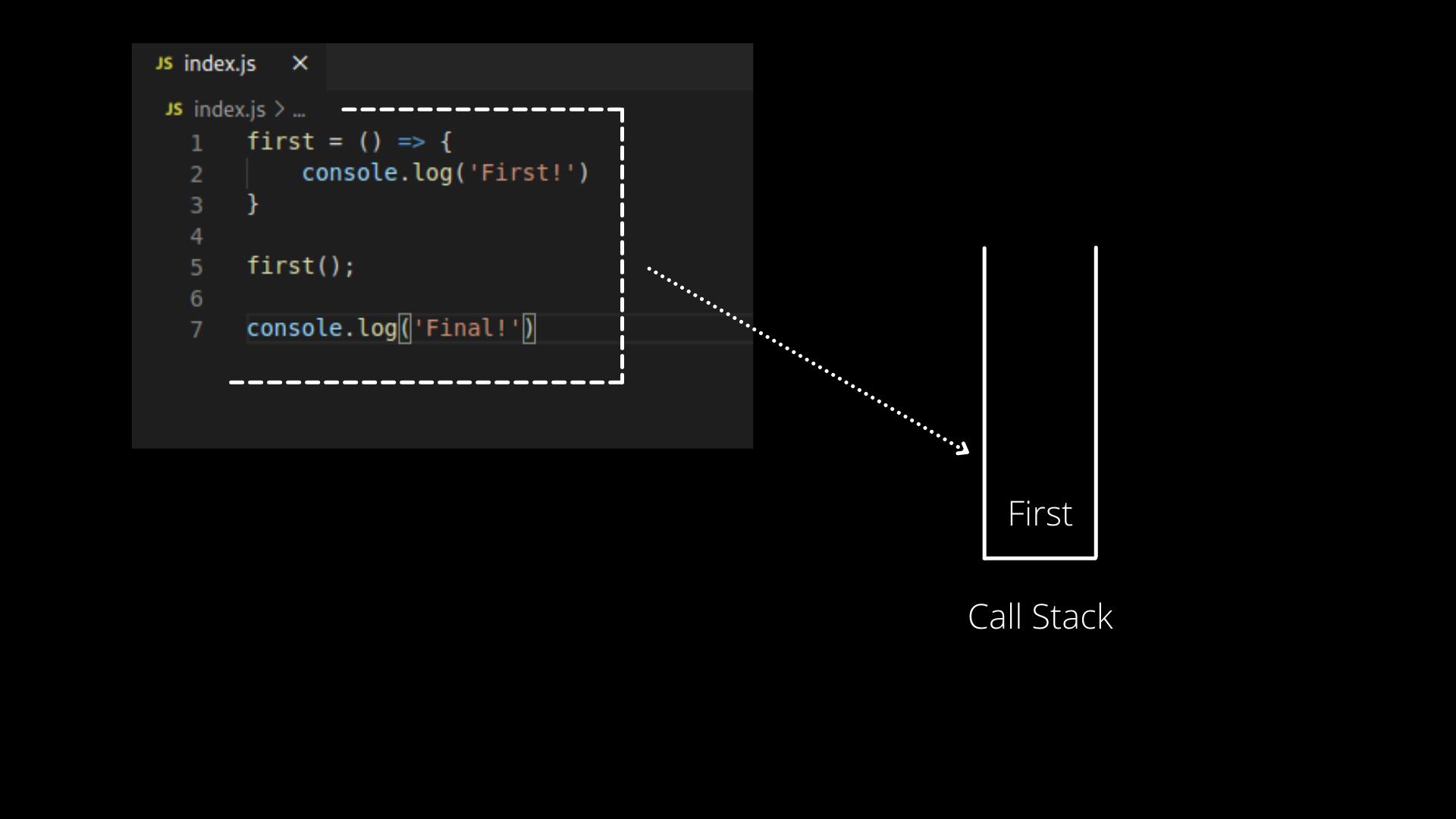 How To Use Async Await In Javascript With Example Js Code
How To Use Async Await In Javascript With Example Js Code
 Asynchronous Javascript Introducing Async And Await
Asynchronous Javascript Introducing Async And Await
 Callbacks Vs Promises Vs Async Awaits Understanding
Callbacks Vs Promises Vs Async Awaits Understanding
 Asynchronous Javascript Tutorial 1 What Is Async Javascript
Asynchronous Javascript Tutorial 1 What Is Async Javascript
 How Javascript Works Event Loop And The Rise Of Async
How Javascript Works Event Loop And The Rise Of Async
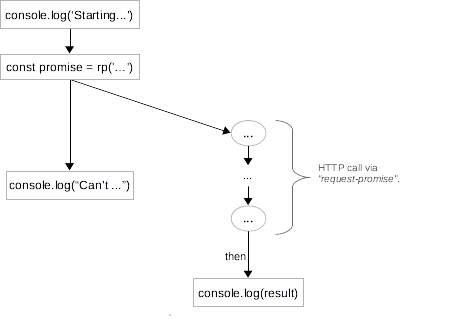 Await And Async Explained With Diagrams And Examples
Await And Async Explained With Diagrams And Examples
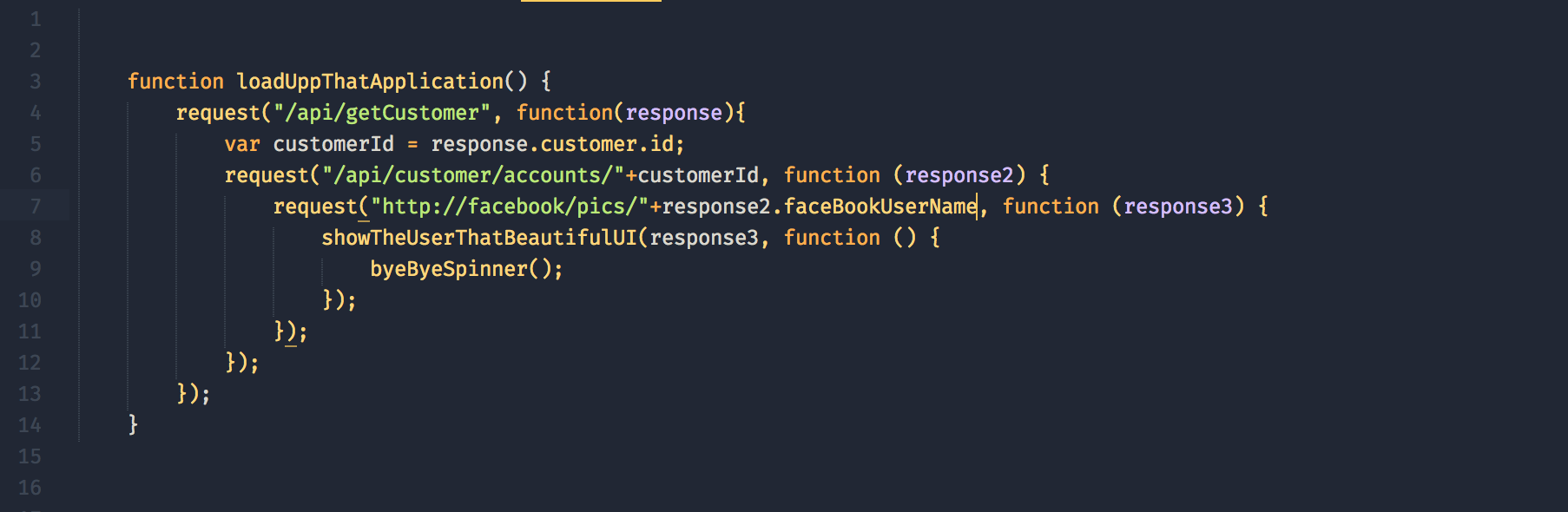 Javascript Es8 Introducing Async Await Functions By Ben
Javascript Es8 Introducing Async Await Functions By Ben
 Cleaner Code With Async Await Tutorial Khalil Stemmler
Cleaner Code With Async Await Tutorial Khalil Stemmler
Faster Async Functions And Promises V8
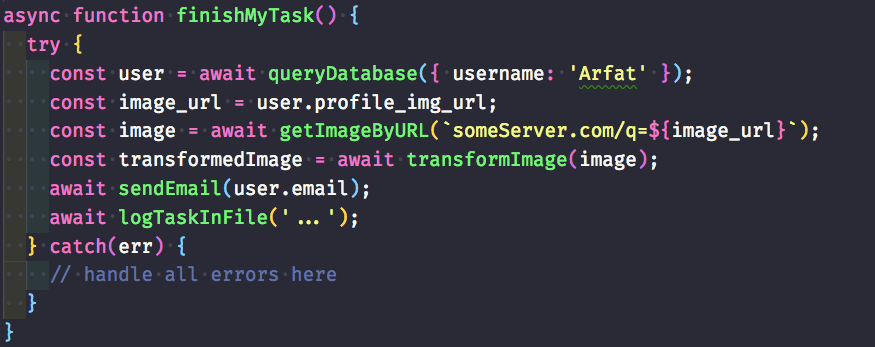 Deeply Understanding Javascript Async And Await With Examples
Deeply Understanding Javascript Async And Await With Examples
 How Is Javascript Asynchronous And Single Threaded
How Is Javascript Asynchronous And Single Threaded
How To Run Async Javascript Functions In Sequence Or Parallel
 Javascript Asynchronous Tutorial
Javascript Asynchronous Tutorial
0 Response to "34 What Is Async In Javascript"
Post a Comment