35 Javascript Cross Domain Request
Cross domain requests (also known as Cross Origin Resource Sharing) can be made using JavaScript without trickery, as far as I can tell, in Firefox 3.5, Safari, Google Chrome and Internet Explorer 8. This is done with all browsers except IE8 using a standard XMLHttpRequest object. CORS is a mechanism that allows resources on a web page to be requested from another domain outside the domain the resource originated from. In particular, JavaScript's AJAX calls can use the XMLHttpRequest mechanism. Such "cross-domain" requests would otherwise be forbidden by web browsers, per the same origin security policy.
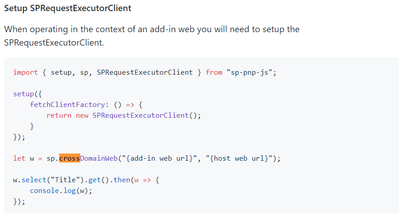
The cross-domain library is a client-side alternative in the form of a JavaScript file (SP.RequestExecutor.js) that is hosted on the SharePoint website that you can reference in your remote add-in. The cross-domain library lets you interact with more than one domain in your remote add-in page through a proxy.
Javascript cross domain request. [SOLVED] I can't get my cross-domain POST request to work. JavaScript. Marie000. October 28, 2020, 4:39pm #1. I am working on the voting app and trying to get the front-end and back-end to communicate with each other. I am building the front-end with Angular 2 with systemJS, which is using localhost:3000 ... Many websites have JavaScript functions that make network requests to a server, such as a REST API. The web pages and APIs are often in different domains. This introduces security issues in that any website can request data from an API. Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) provides a solution to these issues. 25/7/2013 · You can make cross domain requests using the XMLHttpRequest object. This is done using something called "Cross Origin Resource Sharing".
HTTP requests from Javascript are traditionally bound by the Same Origin Policy, which means that your ajax requests must have the same domain and port. The common ways to get around this are JSON-P, Proxying and message passing via <iframe>s. These all have their quirks, but the thing they generally have in common is legacy browser support. 13/3/2013 · It's because JavaScript only allows to request data from the same domain because of security consideration. In short, same domain strategy means a piece of code can read data from the same source, the same source here means the combination of the same domain, … JSONP stands for JSON with Padding. Requesting a file from another domain can cause problems, due to cross-domain policy. Requesting an external script from another domain does not have this problem. JSONP uses this advantage, and request files using the script tag instead of the XMLHttpRequest object.
The trick consists on loading an iframe with the URL you want to store the information with, and pass the "setItem" or "getItem" requests to that iframe with window.postMessage. The main difference is that the cross-domain storage is asyncronous, unlike the localStorage, so you'll need to adapt the behaviour to that. Cross-domain requests with jQuery. 12 Jan 2010. Chris Heilmann recently posted on how to use YQL to make cross-domain requests, which would usually be prohibited due to the same-domain-policy. I already knew about YQL, but I had no idea that it allowed retrieval of HTML from other sites, via JSON, returned as a single string! In order to realize cross domain requests, cross domain requests can be realized through script tags, and then JSON data is output on the server side and callback function is executed to solve cross domain data requests. 3. How to use jsonp? The following demo is actually a simple form of jsonp.
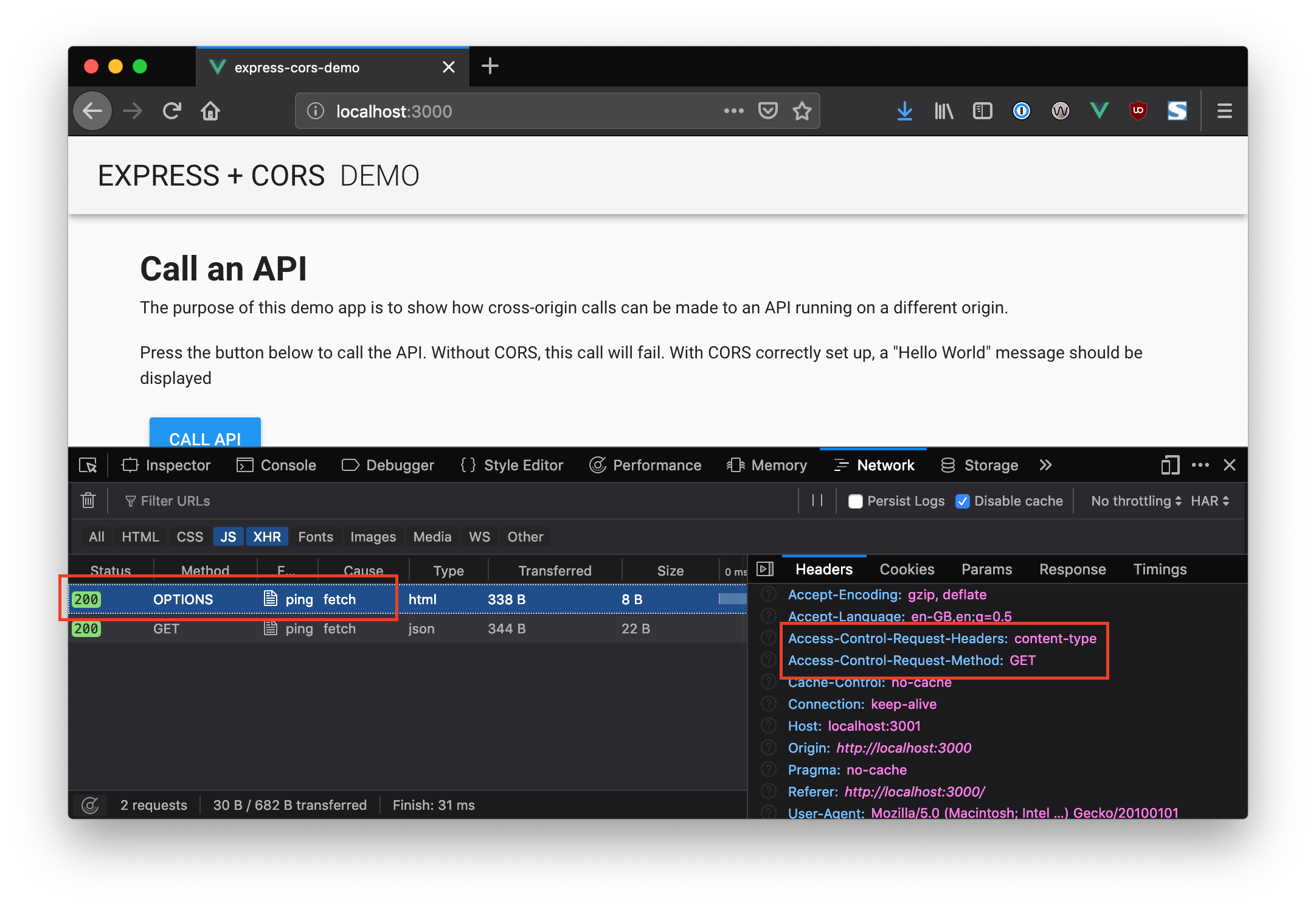
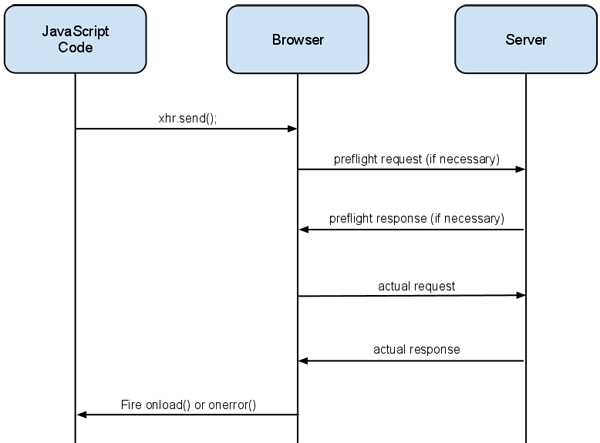
2/10/2016 · Cross domain ajax request. When you do a cross-origin request, the browser sends Origin header with the current domain value. Origin: http://zinoui . When the server receives the request, check whether the origin header is within the allowed list, and … The CORS specification introduces several new HTTP headers that enable cross-origin requests. If a browser supports CORS, it sets these headers automatically for cross-origin requests; you don't need to do anything special in your JavaScript code. Here is an example of a cross-origin request. Cross-domain polices prevent domains from reading information in some circumstances from other domains that don't explicitly allow it with CORS headers.But, that doesn't prohibit cross-origin requests from going out. The request in your example should be hitting be a "pre-flight" OPTIONS request: A probing request to see whether the "actual" request will succeed.
Browsers enforce "same-origin" access control unless the site explicitly allows cross origin requests (either via CORS or JSONP). So, if the site you are trying to access does not allow cross origin requests, then you cannot get the data directly from the site using only a browser. 9/1/2017 · Setting up a CORS policy. By default you are not allowed to make AJAX requests to another domain. Your browser applies the Same-origin policy as part of the web security model. To allow the browser to make a cross domain request from foo.app.moxio to sso.moxio we must set up a CORS policy on the target domain. Browsers allow consuming JavaScript (JavaScript function) that is present in a different domain but not data. Since the data is wrapped in a JavaScript function, this can be consumed by a web page that is present in a different domain. Steps to make ASP.NET Web API Service return JSONP formatted data and consume it from a cross-domain AJAX request
2/1/2021 · A cross-origin request initiated by JavaScript code by default does not bring any credentials (cookies or HTTP authentication). That’s uncommon for HTTP-requests. Usually, a request to http://site is accompanied by all cookies from that domain. Cross-origin requests made by JavaScript methods on the other hand are an exception. Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) is an HTTP-header based mechanism that allows a server to indicate any origins (domain, scheme, or port) other than its own from which a browser should permit loading of resources. CORS also relies on a mechanism by which browsers make a "preflight" request to the server hosting the cross-origin resource, in order to check that the server will permit the ... If you can get the other domain to return javascript that will do Cross-Domain Communication With Iframes (http://softwareas /cross-domain-communication-with-iframes) then you are in luck, and you can capture the response as well. Of course, if you want to use your server as a proxy, you can avoid all this.
Cross-Domain JavaScript Requests allow developers to work around security restrictions that would prevent an application from contacting Places (Search) API directly. For example, certain location information might not be retrievable without enabling this method. Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) is a standard that allows a server to relax the same-origin policy. This is used to explicitly allow some cross-origin requests while rejecting others. For example, if a site offers an embeddable service, it may be necessary to relax certain restrictions. Setting up such a CORS configuration isn't necessarily easy and may present some challenges. What is a Cross-Origin Request? If the script on your page is running from domain mydomain and would like to request a resource via an XmlHttpRequest or XDomainRequst from domain otherdomain , this is a cross-origin request. Historically, for security reasons these types of requests have been prohibited by browsers.
There's two issues with cross-domain requests: whether a request makes it to the server and whether a response is visible to the client script that issued the request. So-called "simple" requests (which use a "simple" method and include only "simple" headers) are guaranteed to make it to the server, but their visibility to the client script still depends on appropriate CORS headers. What this header says is that this is the only domain that is allowed to make this cross-origin request - essentially the two domains are the same domain. A request from any other domain will fail the Same-origin policy of CORS and the request will fail. Reference: MDN Access-Control-Allow-Origin. Header: Access-Control-Allow-Credentials Browser does not allow cross domain AJAX requests due to security issues. Cross-domain requests are allowed only if the server specifies same origin security policy. Read more about Cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) : Wiki To enable CORS, You need to specify below HTTP headers in the server.
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) is a protocol that enables scripts running on a browser client to interact with resources from a different origin. This is useful because, thanks to the same-origin policy followed by XMLHttpRequest and fetch, JavaScript can only make calls to URLs that live on the same origin as the location where the ... This post explains how to make a simple, cross-domain, cross-browser JSON call to a script on a different domain. For security reasons, browsers cannot make GET or POST calls to scripts on other domains using JavaScript - which is a good thing - but means us web developers have to jump through a couple of hoops whenever we need to make JavaScript based cross-domain requests. There are many ... It was straightfoward enough to set up the authentication with ADFS using WIF 4.5 for each of A and B following the MSDN "How To"; I had each of the applications separately working with the same ADFS instance, but the cross domain script request from A to B at step 5 for the script file generated an HTTP redirect sequence (302) that ...
Working With And Around The Same Origin Policy Sitepoint
 Chapter 86 Framework For Cross Domain Ajax
Chapter 86 Framework For Cross Domain Ajax
Github Gfdev Javascript Jquery Transport Xdr Jquery Plugin
 Fix Cors Error Javascript Dev Community
Fix Cors Error Javascript Dev Community
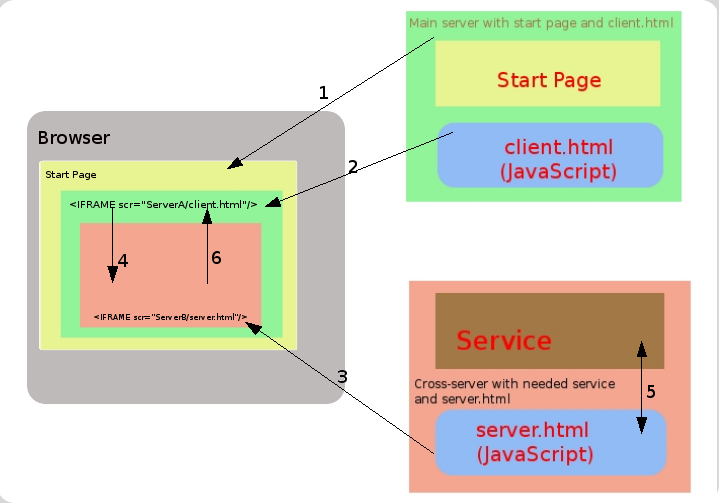 Chapter 86 Framework For Cross Domain Ajax
Chapter 86 Framework For Cross Domain Ajax
Sending Cross Domain Requests Exchanging Data Ajax Iphone
 Cross Domain Requests With Cors
Cross Domain Requests With Cors
 Cross Origin Resource Sharing And Why We Need Preflight
Cross Origin Resource Sharing And Why We Need Preflight
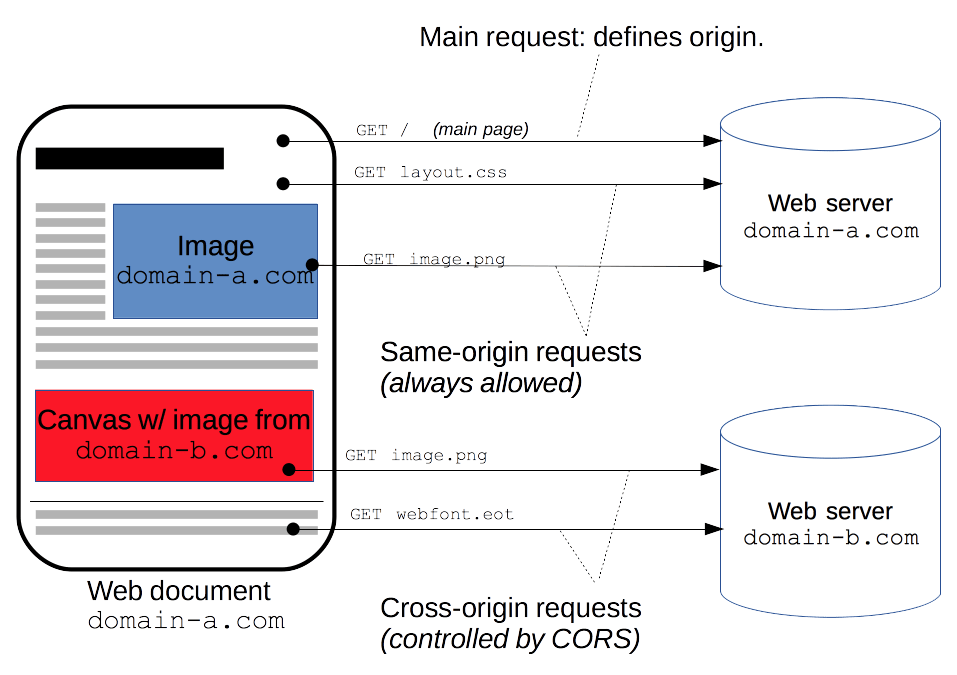 Cross Origin Resource Sharing Cors Http Mdn
Cross Origin Resource Sharing Cors Http Mdn
 Cors Cross Origin Request Sharing In Mule
Cors Cross Origin Request Sharing In Mule
 How Does Access Control Allow Origin Header Work Stack
How Does Access Control Allow Origin Header Work Stack
 A New Default Referrer Policy For Chrome Strict Origin When
A New Default Referrer Policy For Chrome Strict Origin When
 Solution For Cross Domain Request To Consume Api In Sap Cloud
Solution For Cross Domain Request To Consume Api In Sap Cloud
Sending Cross Domain Requests Exchanging Data Ajax Iphone
 Jsonp And Httpclient Cross Domain Request Programmer Sought
Jsonp And Httpclient Cross Domain Request Programmer Sought
 Cross Domain Request In Abap And Java With Two Workaround
Cross Domain Request In Abap And Java With Two Workaround
 Express Cross Domain Request Chrome Can T Display Set Cookie
Express Cross Domain Request Chrome Can T Display Set Cookie
 Chrome Could Access Cross Domain Api Although There Is An
Chrome Could Access Cross Domain Api Although There Is An
 Authoritative Guide To Cors Cross Origin Resource Sharing
Authoritative Guide To Cors Cross Origin Resource Sharing
 How Does Access Control Allow Origin Header Work Stack
How Does Access Control Allow Origin Header Work Stack
 How To Make Cross Domain Request With Ajax And Jquery And
How To Make Cross Domain Request With Ajax And Jquery And
 How To Make A Cross Origin Ajax Request Webucator
How To Make A Cross Origin Ajax Request Webucator
 Enabling Cross Origin Requests In Asp Net Web Api 2
Enabling Cross Origin Requests In Asp Net Web Api 2
 Chapter 3 Handling Cors Requests Cors In Action Creating
Chapter 3 Handling Cors Requests Cors In Action Creating
 How To Understand Sop Same Origin Policy Whitepaper Netsparker
How To Understand Sop Same Origin Policy Whitepaper Netsparker
 Detailed Explanation Of The Internal Mechanism Of Cors Cross
Detailed Explanation Of The Internal Mechanism Of Cors Cross
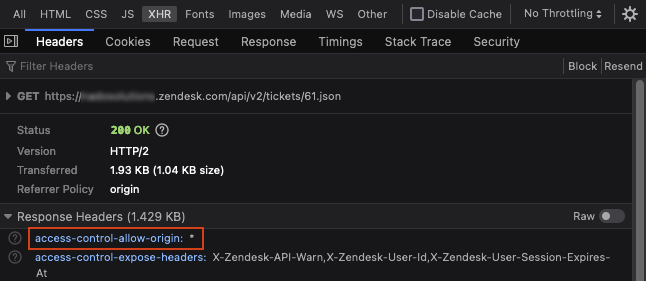 Making Cross Origin Browser Side Api Requests Zendesk
Making Cross Origin Browser Side Api Requests Zendesk
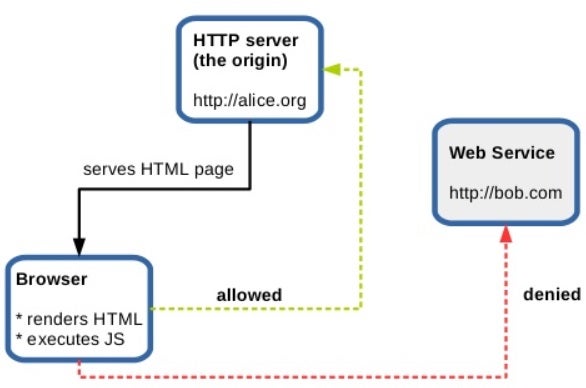 Display Cross Domain Data Using Postmessage Html Goodies
Display Cross Domain Data Using Postmessage Html Goodies


0 Response to "35 Javascript Cross Domain Request"
Post a Comment