24 Extend Object Javascript Es6
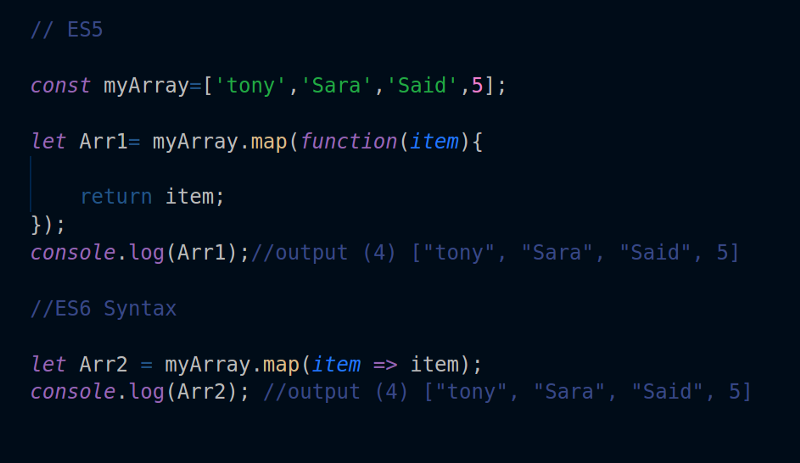
The Object.assign () method only copies enumerable and own properties from a source object to a target object. It uses [ [Get]] on the source and [ [Set]] on the target, so it will invoke getters and setters. Therefore it assigns properties, versus copying or defining new properties. Object literal is one of the widely used patterns to create objects in JavaScript. ES6 makes the object literal more concise and robust by extending the syntax in different ways. Let us see the shorthand for object property initializer. Object Property Initializer. Before ES6, the object literal is a collection of name-value pairs. For example ...
You will be able to do a shallow merge/extend/assign in ES6 by using Object.assign: https://developer.mozilla /en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Object/assign. Syntax: Object.assign(target, sources); where ...sources represents the source object(s). Example:

Extend object javascript es6. Classes are a template for creating objects. They encapsulate data with code to work on that data. Classes in JS are built on prototypes but also have some syntax and semantics that are not shared with ES5 class-like semantics. Jan 22, 2021 - Here’s how we can represent animal object and Animal class graphically: …And we would like to create another class Rabbit. As rabbits are animals, Rabbit class should be based on Animal, have access to animal methods, so that rabbits can do what “generic” animals can do. The syntax to extend ... Classes are a template for creating objects. They encapsulate data with code to work on that data. Classes in JS are built on prototypes but also have some syntax and semantics that are not shared with ES5 class-like semantics.
Jun 02, 2017 - The ES6 spread operator feature in JavaScript allows for merging multiple object properties with a JavaScript library. Mar 31, 2018 · 6 min read. ES6 (ECMAScript2015) is a major upgrade to JavaScript. In this article we will learn the new way of achieving Object Oriented concepts like class, object, static properties, constructor and inheritance with super and extends in JavaScript. act of writing helps us to remember things better. The extends keyword is used in class declarations or class expressions to create a class that is a child of another class.
Jul 17, 2019 - We can extend this feature and also return an object which is super nice. But somehow we need to merge this object into the person object above 🤯 ... Merging objects is possible for a long time already in JavaScript with the Object.assign functionality. 6/12/2019 · [2.2] Extending deeply nested Objects AngularJS 'angular.extend()' and 'angular.merge()': angular.merge() it will be preserving properties in child objects. angular.extend() it will not preserve, it will replace similar properties. It does a deep copy of all properties from source to destination preserving properties in child objects. 5/3/2019 · This p o st will cover the basics of using classes and subclasses to construct objects and how ES6 can be used to extend objects and makes creating new methods for …
Enhancements to object literal notation in ES6 include the addition of computed properties, concise method definitions, and short-hand for properties whose value is initialized to a same-named variable. For more information on object literals, see Creating Objects (JavaScript). Built-in objects have their own static methods, for instance Object.keys, Array.isArray etc. As we already know, native classes extend each other. For instance, Array extends Object. Normally, when one class extends another, both static and non-static methods are inherited. That was thoroughly explained in the article Static properties and methods. Super can also be used in the object initializer / literal notation. In this example, two objects define a method. In the second object, super calls the first object's method. This works with the help of Object.setPrototypeOf() with which we are able to set the prototype of obj2 to obj1, so that super is able to find method1 on obj1.
ES6 allows to extend special objects. So it's possible to inherit from the function. Such object can be called as a function, but how can I implement the logic for such call? class Smth extends Function { constructor (x) { // What should be done here super (); } } (new Smth (256)) () // to get 256 at this call? Prior to ES6, it was common to use similar `.extend()` methods from Lodash, Underscore, or jQuery. ... powerful, and flexible JavaScript's object system can be. ... Feb 06, 2019 - However, JavaScript was not so simple before ES6 came in, especially for classes. So how did people code without using class syntax, super and extends keywords? Or they never used such concepts before and suddenly decided to add them? Let’s find out! ... Truth is, object-oriented JavaScript ...
Using Object.defineProperty() to Extend Native JavaScript Objects. An ideal approach would be to use Object.defineProperty() (which is available since ES5). It provides us with finer control over the property we wish to add to an existing object, by allowing us to add descriptors. For example, we can decide whether we want to allow the property ... Apr 16, 2018 - Now with ES6 classes, objects are allocated before invoking the superclass constructor, and the superclass makes that object available to the subclass constructor. This lets Array allocate an exotic object even when we invoke new on our subclass. // ES6 class D extends Array {} let d = new ... The JavaScript for/of statement loops through the values of an iterable objects. for/of lets you loop over data structures that are iterable such as Arrays, Strings, Maps, NodeLists, and more. The for/of loop has the following syntax: for ( variable of iterable) {. // code block to be executed.
Nov 23, 2018 - They are not true classes in a way that would be familiar to users of most other object-oriented languages. Which keywords can be used to implement inheritance in ES6? One can implement inheritance in JavaScript ES6 through the "class" and "extends" keywords. May 28, 2021 - ES6 allows the child class and parent class to have methods with the same name. In this case, when you call the method of an object of the child class, the method in the child class will shadow the method in the parent class. The following Dog class extends the Animal class and redefines the ... JavaScript supports extending data types. JavaScript objects are a great way to define custom data types. An object is an instance which contains a set of key value pairs. Unlike primitive data types, objects can represent multiple or complex values and can change over their life time.
JavaScript ES6: Classes. Objects in programming languages provide us with an easy way to model data. Let's say we have an object called user. The user object has properties: values that contain ... May 28, 2021 - The object literal is one of the most popular patterns for creating objects in JavaScript because of its simplicity. ES6 makes the object literal more succinct and powerful by extending the syntax in some ways. All JavaScript objects created by assigning an identifier the value of object literals share the same prototype object. This means that their private prototype property points to the same object in the prototype chain and hence, inherits its properties. This object can be referred to in JavaScript code as Object.prototype.
The object literal is one of the most popular patterns for creating objects in JavaScript because of its simplicity. ES6 makes the object literal more succinct and powerful by extending the syntax in some ways. Object property initializer shorthand. Prior to ES6, an object literal is a collection of name-value pairs. For example: 6/1/2019 · ES6 Shortcuts. ES6 introduces a few shortcuts for working with objects: let name = "John" let person = { name } console.log(person) //logs {name: 'John'} Conclusion. Objects allow you to build and extend custom data types. Objects make it easy to create and dynamically change properties and are fundamental to JavaScript programming. 14/7/2019 · Whenever you try to access a property that doesn’t exist on an object, you don’t really get an error, JavaScript is permissive like that. All you get is undefined returned instead of its value. What if, instead of getting that behavior, we wanted to customize the returned value, or even throw an exception since the developer is trying to access a non-existing property.
**Before ES6, developers often used similar `.extend()` methods from Lodash, Underscore, or jQuery. Eric Schwartz Full stack web developer with experience in JavaScript, React/Redux, and Ruby on ... Apr 27, 2017 - I'm sure this question has been asked before but I can't quite find the answer I'm looking for, so here goes: I have two objects, as follows: const response = { lat: -51.3303, lng: 0.39440 } ... 16/7/2019 · This is a super slick example on how to extend objects conditionally in JavaScript and really shows that when using modern language we can use a more crisp syntax to express ourself. These functions become especially important when you create the same type of object, sometimes with some properties and sometimes not.
Extending Base class to make a sub Class in ES2015Article and code samples from this tutorial * Please be my patreons on patreaon* https://www.patreon /te... For the built-in class as a parent, ES6 extends (green) is doing 6.12 ops/sec while ES5 Object.create (red) is doing 151 ops/sec. So, the performance difference is quite huge when built-in class functionality is extending. I will definitely add more cases here. Nearly all objects in JavaScript are instances of Object which sits on the top of a prototype chain. While this confusion is often considered to be one of JavaScript's weaknesses, the prototypal inheritance model itself is, in fact, more powerful than the classic model. It is, for example, fairly trivial to build a classic model on top of a ...
ES6 Classes formalize the common JavaScript pattern of simulating class-like inheritance hierarchies using functions and prototypes. They are effectively simple sugaring over prototype-based OO, offering a convenient declarative form for class patterns which encourage interoperability. The extends keyword can be used to subclass custom classes as well as built-in objects. The.prototype of the extension must be an Object or null. Aug 12, 2019 - An alternative approach is to use the object spread syntax recently added to the JavaScript specification. It lets you use the spread (...) operator to copy enumerable properties from one object to another in a more succinct way. The object spread operator is conceptually similar to the ES6 array ...
Like traditional class systems (C++ or Java, for example), ES6 allows for inheritance, where one class uses another as a base, and then extends it by adding more features of its own. Let's take a closer look at the possibilities of this new feature. Feb 01, 2018 - A description of the new spread operator introduced in ES6. My problem is that the line ClassName.constructor.call(object); does not work as intended, i.e. The passed object does not get the instance properties of the class. I have tried s few ways to rewrite this (even some unorthodox ones) to no avail. How do I extend an object with a class' instance properties, using ES6? DISCLAIMER:
Learning OOP JavaScript-ES6 will significantly help you become a better developer. Concepts such as the class declaration, constructors, getter and setter, methods, static properties, static method, and inheritance can definitely help you leverage those concepts when working with other JavaScript frameworks or libraries. Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to implement JavaScript inheritance by using extends and super in ES6. Implementing JavaScript inheritance using extends and super. Prior to ES6, implementing a proper inheritance required multiple steps. One of the most commonly used strategies is the prototypal inheritance. 10/5/2021 · Due to this simplicity of operation and widely used, many javascript frameworks have built-in utility functions named extend() to perform similar copying operations. Similarly, in Javascript ES6, they have created an Object.assign() function that will perform the copying operation. This Object.assign() method expects two or more objects as an arguments. So, the first argument is the target object which will be modified by the assign method while the rest arguments objects …
Here, class Rabbit extends Animal and overrides name field with its own value.. There's no own constructor in Rabbit, so Animal constructor is called.. What's interesting is that in both cases: new Animal() and new Rabbit(), the alert in the line (*) shows animal. In other words, parent constructor always uses its own field value, not the overridden one.
 Static Methods Are Inherited When Using Es6 Extends Syntax In
Static Methods Are Inherited When Using Es6 Extends Syntax In
 2 Classes Object Oriented Programming In Javascript Es6
2 Classes Object Oriented Programming In Javascript Es6
 Javascript Object Function Bernadette Codes
Javascript Object Function Bernadette Codes
Top 10 Es6 Features Every Busy Javascript Developer Must Know
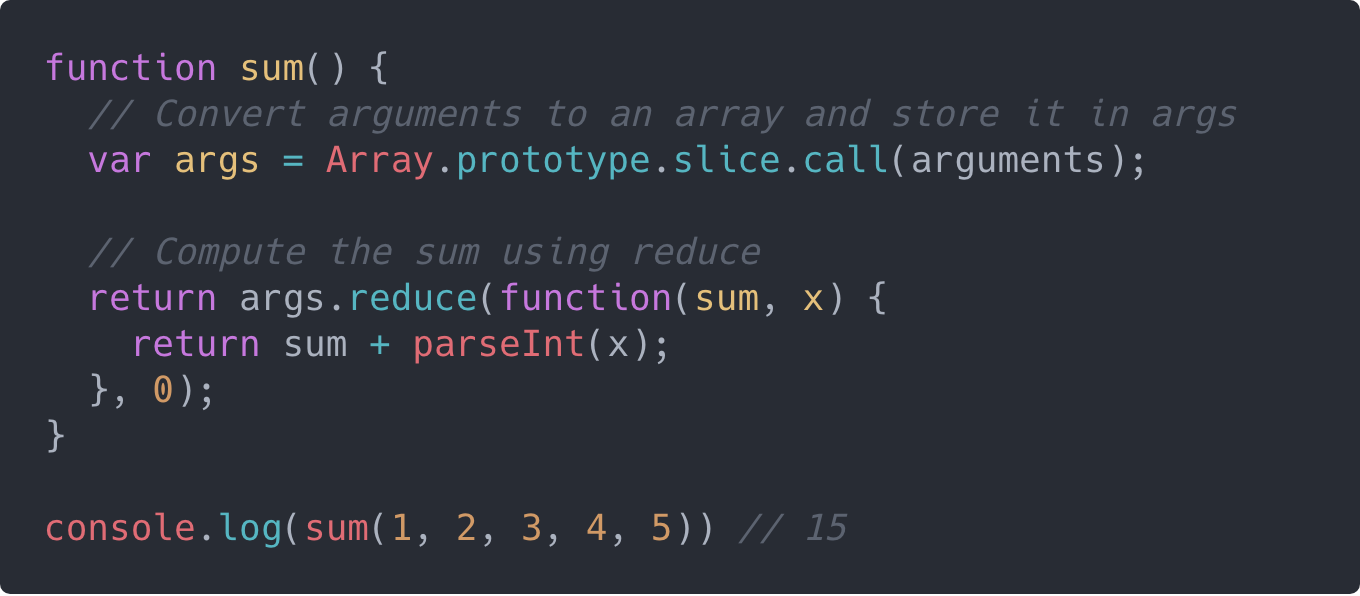 Es6 Amp Es7 Tips And Tricks Hacks In Javascript Tkssharma
Es6 Amp Es7 Tips And Tricks Hacks In Javascript Tkssharma
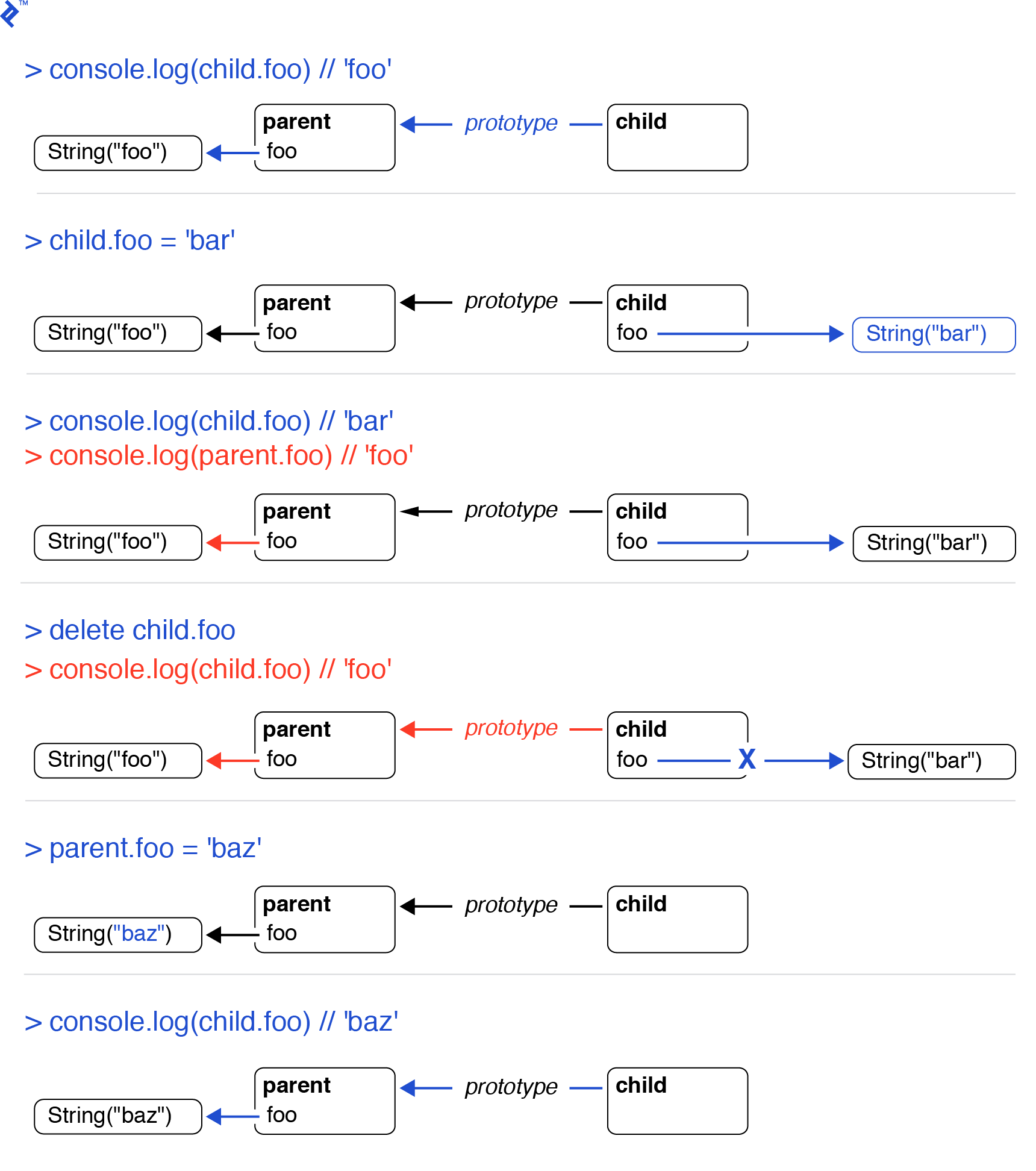 Making Sense Of Es6 Class Confusion Toptal
Making Sense Of Es6 Class Confusion Toptal
 Making Sense Of Es6 Class Confusion Toptal
Making Sense Of Es6 Class Confusion Toptal
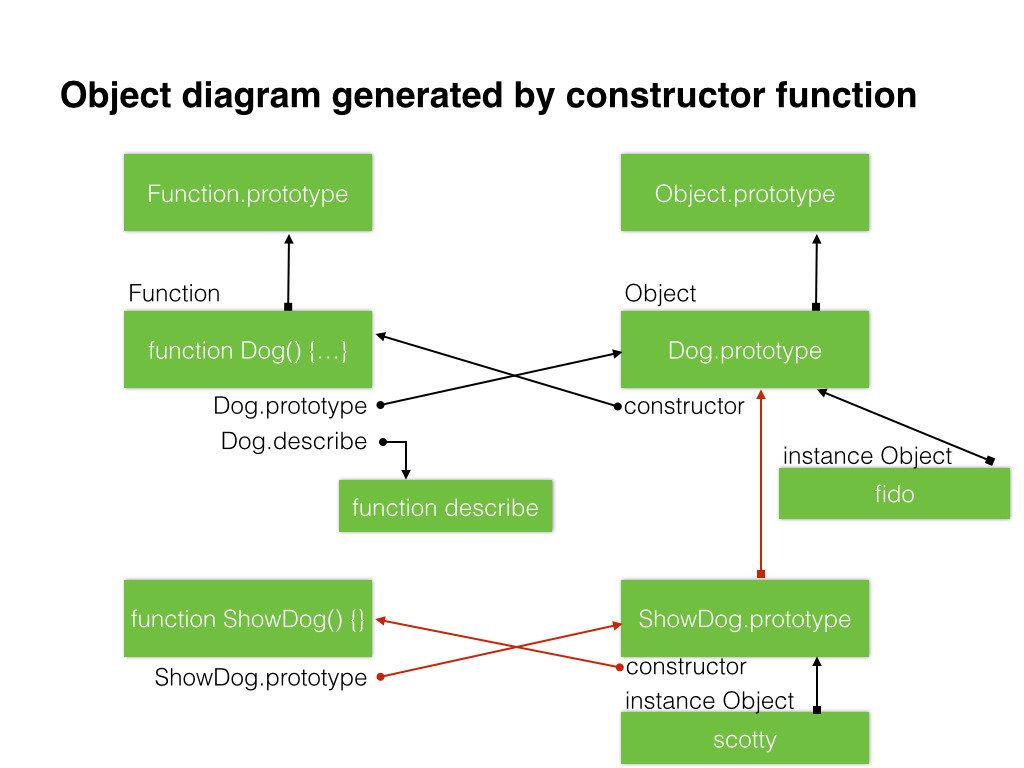 Javascript S New Way To Make Objects Wickedlysmart Com
Javascript S New Way To Make Objects Wickedlysmart Com
 The Hidden Truths In Es6 Classes Dzone Web Dev
The Hidden Truths In Es6 Classes Dzone Web Dev
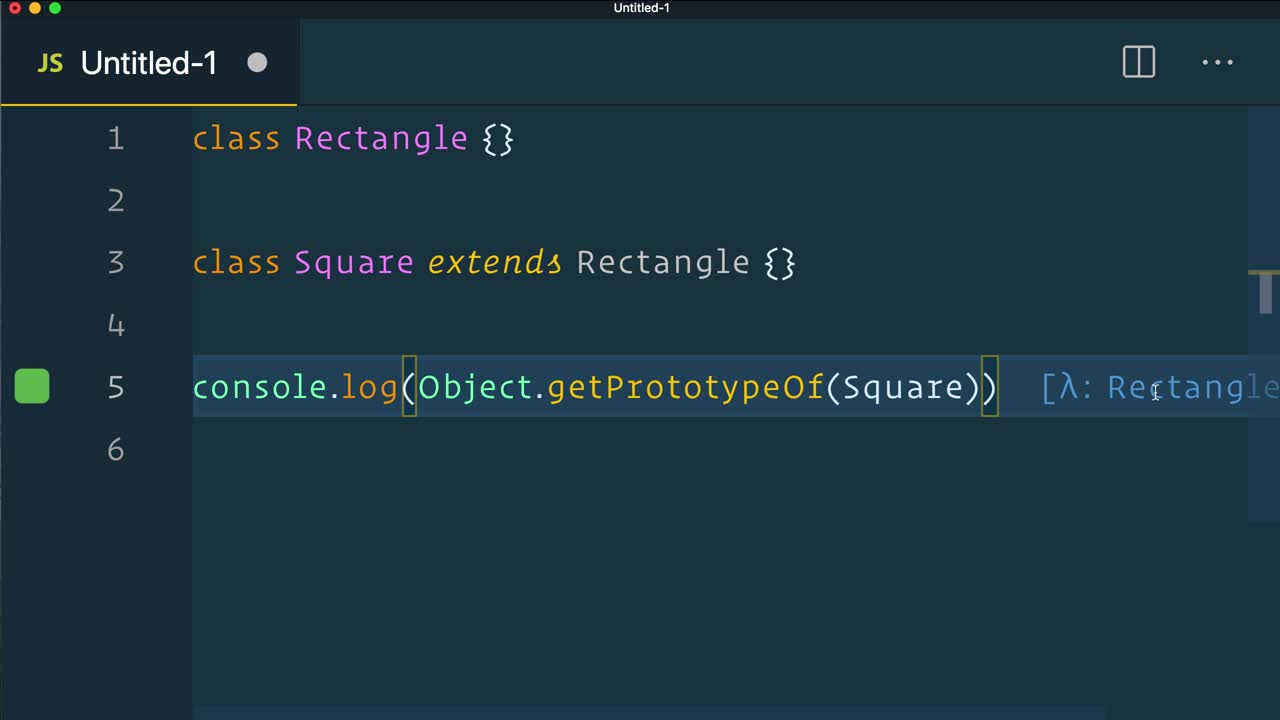 De Sugar An Es6 Class And The Extends Keyword
De Sugar An Es6 Class And The Extends Keyword
 Inheritance In Javascript Es6 Class Inheritance
Inheritance In Javascript Es6 Class Inheritance
 Javascript Object Prototypes Es6 By Ankit Kamboj Medium
Javascript Object Prototypes Es6 By Ankit Kamboj Medium
 Writing Reusable Components In Es6 Smashing Magazine
Writing Reusable Components In Es6 Smashing Magazine
 Object Oriented Programming In Es2015 Es6 Jstobigdata
Object Oriented Programming In Es2015 Es6 Jstobigdata
 Differences In Defining Es6 Class Methods Cmichel
Differences In Defining Es6 Class Methods Cmichel
 Inheritance And The Prototype Chain In Es6 Classes Stack
Inheritance And The Prototype Chain In Es6 Classes Stack
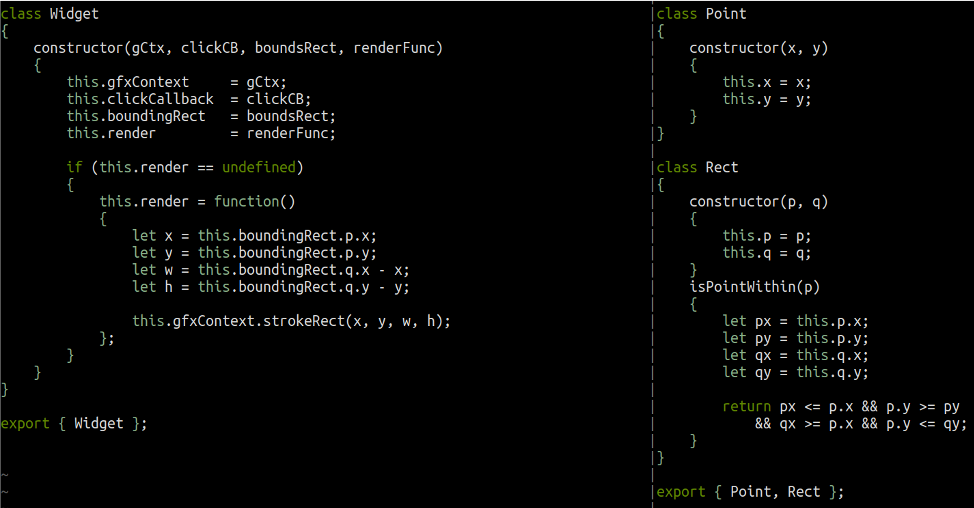 Modern Object Oriented Javascript With Es6 Capgemini Schweiz
Modern Object Oriented Javascript With Es6 Capgemini Schweiz
 Update Object With Another Object Javascript With Es6 Code
Update Object With Another Object Javascript With Es6 Code



0 Response to "24 Extend Object Javascript Es6"
Post a Comment