21 And Or Operator Javascript
Member operators provide access to a property or method of an object (object.property and object["property"]). ... The new operator creates an instance of a constructor. ... In constructors, new.target refers to the constructor that was invoked by new. ... An object exposing context-specific metadata to a JavaScript ... 1 week ago - A comparison operator compares its operands and returns a logical value based on whether the comparison is true. The operands can be numerical, string, logical, or object values. Strings are compared based on standard lexicographical ordering, using Unicode values. In most cases, if the two operands are not of the same type, JavaScript ...
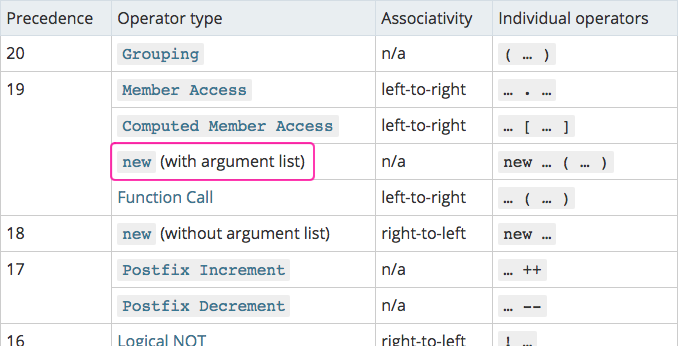 Building A Mental Model For Precedence And The New Operator
Building A Mental Model For Precedence And The New Operator
The And (&&) operator helps us attach two c onditionals to this example, returning a boolean if all variables are true. In the first example, var1 is true, but var2 is false, meaning the example will equal false, as opposed to if both were true as in example two., returning true.
And or operator javascript. To determine whether two boolean values put together are true or false, if you want to check them both (like validation on the web page), you may use the & operator. & is bitwise AND. With the && operator, once it finds the first value is false, it will end evaluation and not to check the second value. JavaScript !! Operator. The other day I was rolling through some JavaScript to figure out how a 3rd party library ticked. As I scanned the lines of code I came across a line like the following: value = !!value; Unless you have been using JavaScript for a while this may look like some advanced VooDoo. Nov 04, 2011 - In JavaScript, logical operators are used for boolean logic where a boolean value may be returned depending on the outcome of an expression. With the || (OR)...
In Javascript, we have couple of options for checking equality: == (Double equals operator): Known as the equality or abstract comparison operator === (Triple equals operator): Known as the identity or strict comparison operator; In this post, we'll explore the similarities and differences between these operators. The application author cannot assume that their JavaScript code will run as intended (or at all) because any secret embedded in the code could be extracted by a determined adversary. Some implications are: Web site authors cannot perfectly conceal how their JavaScript operates because the raw ... Logical Operators. The logical operators used in Javascript are listed below: is true if both a and b are true. is true if either a or b is true. Logical NOT ( ! ) is true if a is not true. The following conditions are true : The following conditions are false :
In classical programming, the logical OR is meant to manipulate boolean values only. If any of its arguments are true, it returns true, otherwise it returns false. In JavaScript, the operator is a little bit trickier and more powerful. But first, let's see what happens with boolean values. Apr 02, 2021 - In classical programming, the logical OR is meant to manipulate boolean values only. If any of its arguments are true, it returns true, otherwise it returns false. In JavaScript, the operator is a little bit trickier and more powerful. But first, let’s see what happens with boolean values. Equal value and equal type operator is an comparison operator which is used to check the whether two operands are having same value and same type. For example, in the Equal operator we can write same value in different types gives the same result, like we declared var a = 5 and we are assigning a == 5 or a == "5" to the opertor gives the same ...
Apr 02, 2018 - JavaScript is a resource for the JavaScript community. You will find resources and examples for JavaScript beginners as well as support for JavaScript experts. Learn JavaScript or free with our easy to use input output machine. = JavaScript operator assigns a value to the left operand depends on the value of operand available on the right side. The first operand should be a variable. The basic assignment operator is =, that assigns the value of one operand to another. That is, a = b assigns the value of b to a. The NOT operator in Javascript is represented in symbolic form with an exclamationmark&&. Syntax. var result = ! y; Like the OR and AND operator, the Boolean or logical ANDoperator is used to evaluate multiple Boolean operands only. It is used to inverse the value of the operand since it returns the opposite value of the operand provided to it.
JavaScript includes operators same as other languages. An operator performs some operation on single or multiple operands (data value) and produces a result. For example, in 1 + 2, the + sign is an operator and 1 is left side operand and 2 is right side operand. The + operator performs the addition of two numeric values and returns a result. Bit operators work on 32 bits numbers. Any numeric operand in the operation is converted into a 32 bit number. The result is converted back to a JavaScript number. The examples above uses 4 bits unsigned examples. But JavaScript uses 32-bit signed numbers. Because of this, in JavaScript, ~ 5 will not return 10. It will return -6. When comparing a string with a number, JavaScript will convert the string to a number when doing the comparison. An empty string converts to 0. A non-numeric string converts to NaN which is always false. When comparing two strings, "2" will be greater than "12", because (alphabetically) 1 is less than 2.
What is equal to (===) Operator in JavaScript? Triple equals(===) is a strict equality comparison operator in JavaScript, that returns false for the values which are not of a similar type. It performs type casting for equality. Uses of equal to (=) Operator in JavaScript. These are the following important uses of = in JavaScript: Inversely, for the && operator, if the test is true, the && expression results in the value of the second operand (b). If the test is false, the && expression results in the value of the first operand (a or c) So what exactly is happening when you use the && and || operators with chaining values like: 3 weeks ago - In this tutorial, you will learn how to use JavaScript logical operators including logical NOT (!) AND (&&), and OR (|) operators.
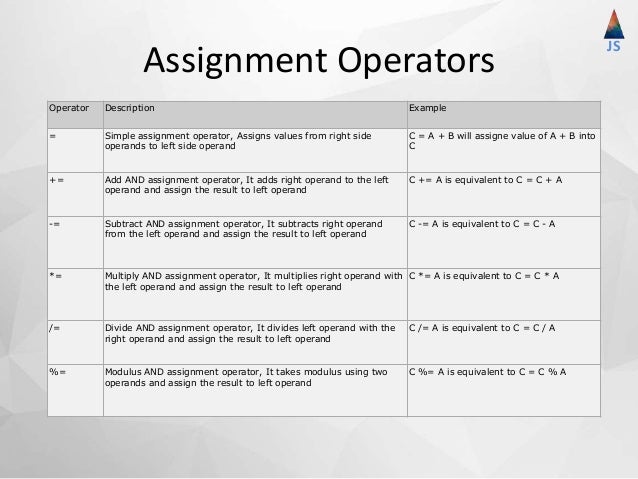
Today I am comparing equality (==) and identity operator (===) in javascript. Both of these operators work pretty similarly with value checks. But, there is a fundamental concept that makes these two operators very much different. Equality Operator (==) Before any comparison, the equality operator checks for type conversion between two values. In addition to the standard assignment operator, JavaScript has compound assignment operators, which combine an arithmetic operator with =. For example, the addition operator will start with the original value, and add a new value. 5 days ago - An operator is capable of manipulating a certain value or operand. Operators are used to perform specific mathematical and logical computations on operands. In other words, we can say that an operator operates the operands. In JavaScript operators are used for compare values, perform arithmetic ...
JavaScript operators are symbols that are used to perform operations on operands. Operator Works in JavaScript. The conditional or question mark operator, represented by a ?, is one of the most powerful features in JavaScript. The ? operator is used in conditional statements, and when paired with a :, can function as a compact alternative to if...else statements. But there is more to it than meets the eye. Dec 13, 2018 - !(Not), $$ (AND), || (OR). Tagged with javascript, webdev, coding, beginners.
When you use the mixed logical operators in an expression, the JavaScript engine evaluates the operators based on a specified order, and this order is called the operator precedence. In other words, the operator precedence is the order that an operator is executed. Before jumping into how the operators work, let's start with the basic concepts of truthy and falsy. 1. Falsy value. Because JavaScript is a loosely typed language, logical operations can be performed on any type. The expressions like 1 && 2, null || undefined, 'hello' && true are weird, but still valid in JavaScript. Expressions and operators. This chapter describes JavaScript's expressions and operators, including assignment, comparison, arithmetic, bitwise, logical, string, ternary and more. A complete and detailed list of operators and expressions is also available in the reference.
We will discuss two operators here that are quite useful in JavaScript: the conditional operator (? :) and the typeof operator. ... The conditional operator first evaluates an expression for a true or false value and then executes one of the two given statements depending upon the result of ... The logical AND (&&) operator (logical conjunction) for a set of operands is true if and only if all of its operands are true. It is typically used with Boolean (logical) values. When it is, it returns a Boolean value. Here 4 and 5 are called operands and '+' is called the operator. JavaScript supports the following types of operators. Arithmetic Operators. Comparison Operators. Logical (or Relational) Operators. Assignment Operators. Conditional (or ternary) Operators. Lets have a look on all operators one by one.
In JavaScript, a common way to coerce any value into a boolean is to apply the logical NOT operator ! twice: function isAdministrator (user) {return!! (user && user. isAdmin);} The ! operator, produces the value false if its single operand can be coerced into true; otherwise, it returns true. The result is always a proper boolean, but the ... The operator is also called "ternary", because it has three operands. It is actually the only JavaScript operator which has that many. Conditional (ternary) statements are an integral part of all programming languages, which used to perform different actions based on different conditions. Whenever a wrong data type is used for an operator, JavaScript silently converts that value into an appropriate type using a set of rules that often aren't what you want or expect. This is called type coercion.
Difference between == and === operator in JavaScript. The '==' operator tests for abstract equality i.e. it does the necessary type conversions before doing the equality comparison. But the '===' operator tests for strict equality i.e it will not do the type conversion hence if the two values are not of the same type, when compared, it ... The strict inequality operator (!==) is the logical opposite of the strict equality operator. It means "Strictly Not Equal" and returns true where strict equality would return false and vice versa. Strict inequality will not convert data types. For example 1 !== '1' will return true since 1 is an integer and '1' is a character and ...
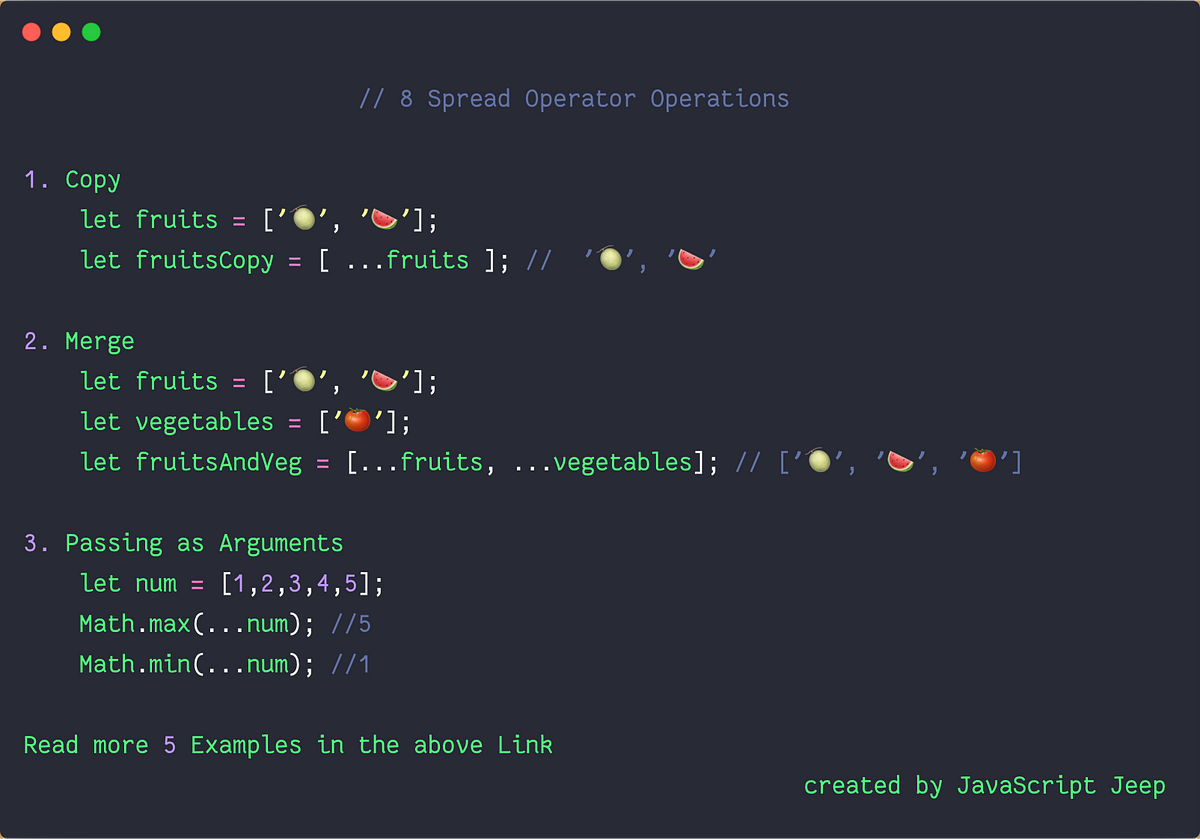 8 Ways To Use The Spread Operator In Javascript By
8 Ways To Use The Spread Operator In Javascript By
 Javascript Lesson 10 Logical Operators In Javascript Geeksread
Javascript Lesson 10 Logical Operators In Javascript Geeksread
 Know Existing Operator In Javascript Programming
Know Existing Operator In Javascript Programming
 Logical Operators In Javascript Logic Web Development
Logical Operators In Javascript Logic Web Development
 Difference Between And Operator In Javascript
Difference Between And Operator In Javascript
 List Of All Binary Operators In Javascript Newbedev
List Of All Binary Operators In Javascript Newbedev
 Javascript Comparison And Logical Operators
Javascript Comparison And Logical Operators
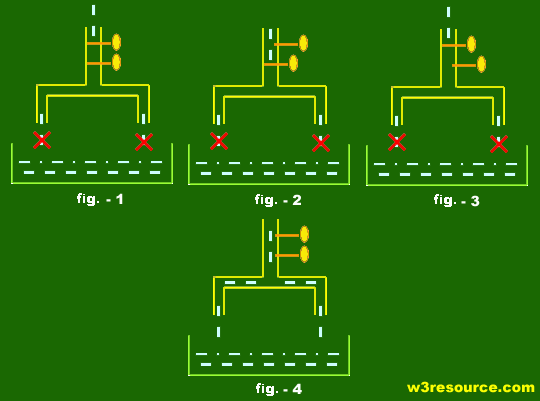 Javascript Logical Operators And Or Not W3resource
Javascript Logical Operators And Or Not W3resource

 Bitwise Javascript Operators According To Wikipedia Bitwise
Bitwise Javascript Operators According To Wikipedia Bitwise
 Understanding Javascript Operators With Types And Examples
Understanding Javascript Operators With Types And Examples
 Comparison Or Relational Operators In Javascript
Comparison Or Relational Operators In Javascript
 Logical Operators In Javascript Devopsschool Com
Logical Operators In Javascript Devopsschool Com
 Javascript Operators With Examples Dot Net Tutorials
Javascript Operators With Examples Dot Net Tutorials
 5 Simple Applications Of Javascript Bitwise Operators Dev
5 Simple Applications Of Javascript Bitwise Operators Dev
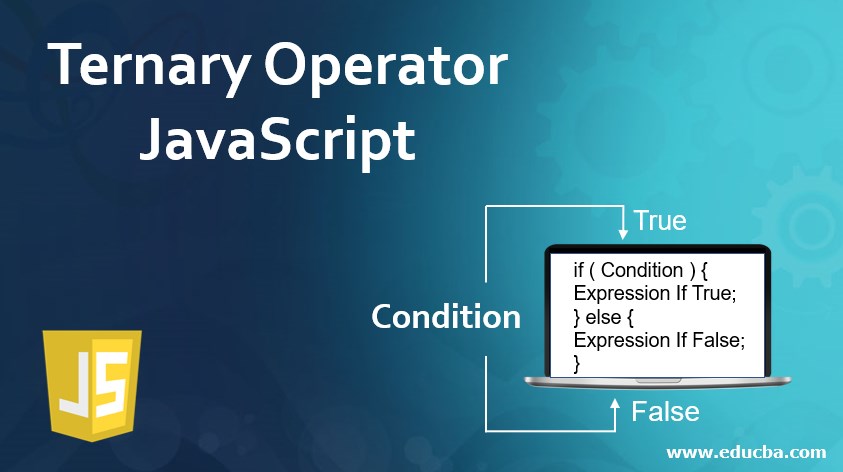 Ternary Operator Javascript Examples To Implement Ternary
Ternary Operator Javascript Examples To Implement Ternary
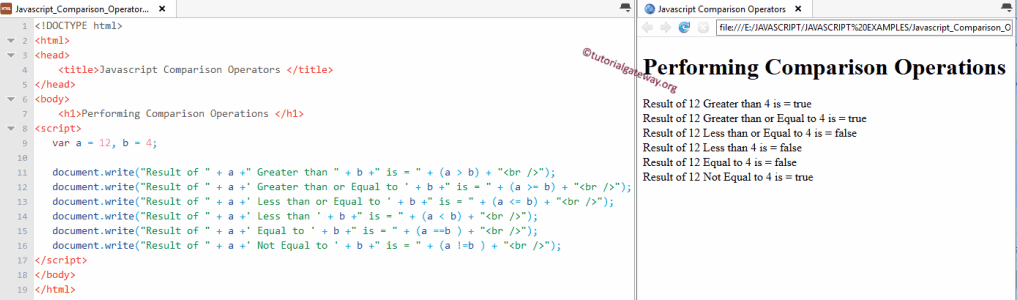
 Javascript Comparison Operators
Javascript Comparison Operators
0 Response to "21 And Or Operator Javascript"
Post a Comment