25 What Is Javascript Promise Object
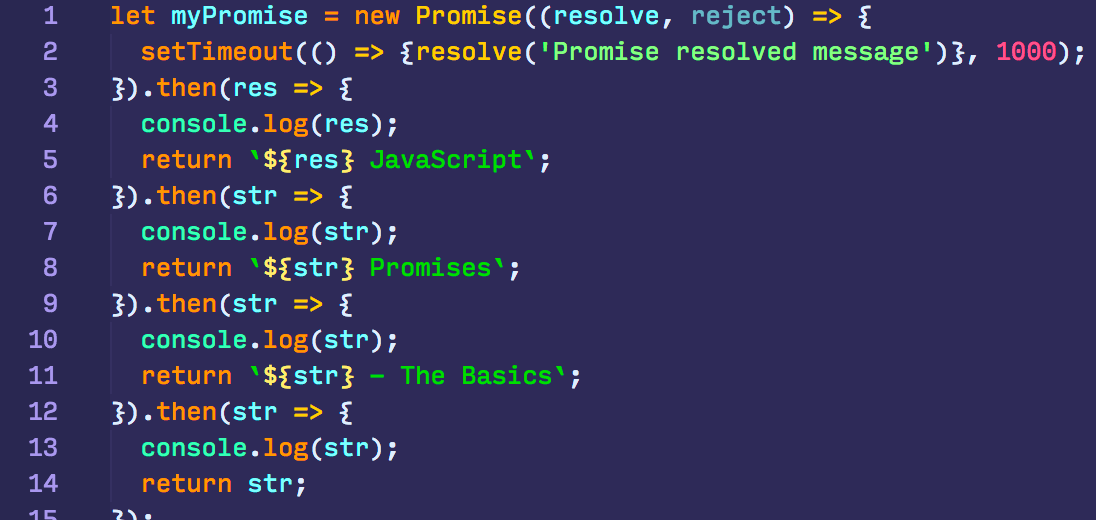
Promise.all takes an array of promises (it technically can be any iterable, but is usually an array) and returns a new promise.. The new promise resolves when all listed promises are resolved, and the array of their results becomes its result. For instance, the Promise.all below settles after 3 seconds, and then its result is an array [1, 2, 3]: The then method returns a Promise which allows for method chaining. If the function passed as handler to then returns a Promise, an equivalent Promise will be exposed to the subsequent then in the method chain. The below snippet simulates asynchronous code with the setTimeout function.
 Javascript How To Access The Return Value Of A Promise
Javascript How To Access The Return Value Of A Promise
Understanding promises Object. As per MDN documentation. The Promise object represents the eventual completion (or failure) of an asynchronous operation, and its resulting value. Promise object has static methods and prototype methodsStatic methods in Promise object can be applied independently, whereas the prototype methods needs to be applied ...
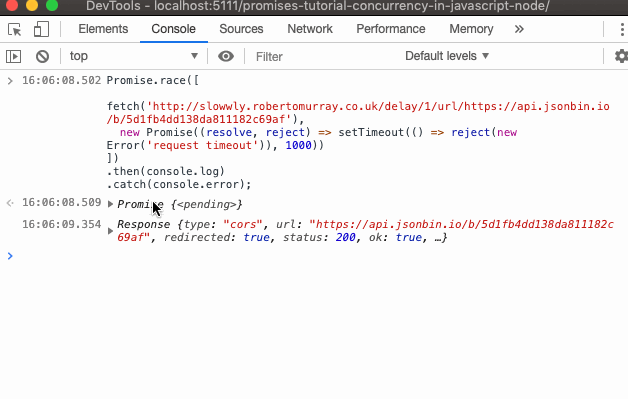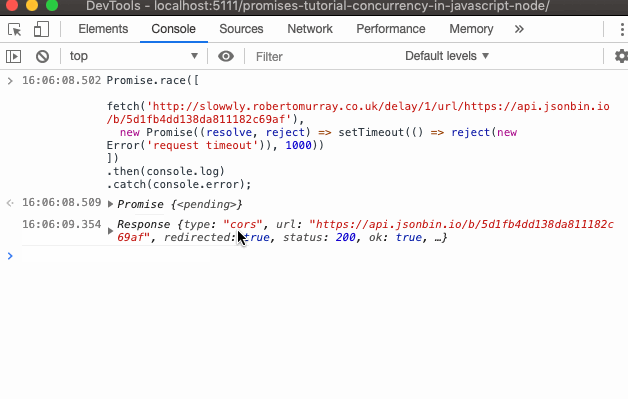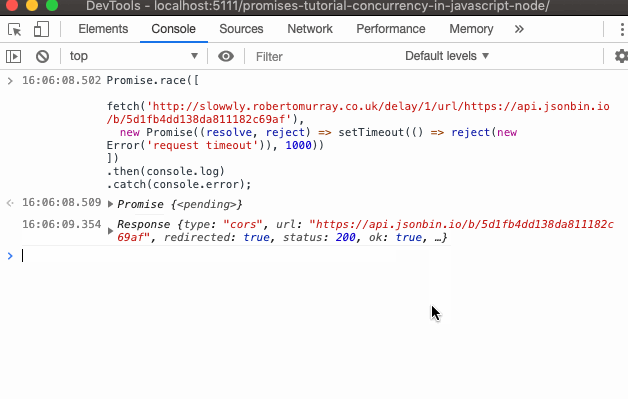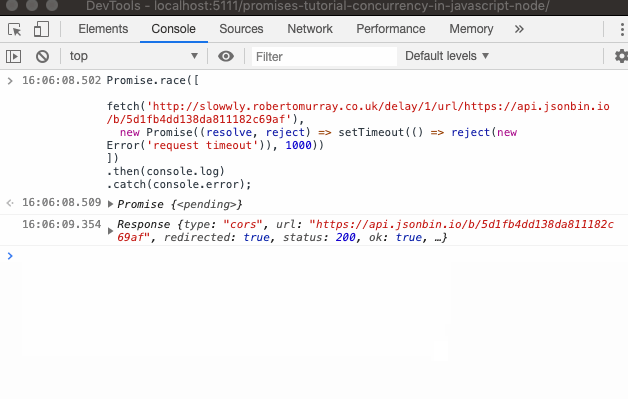
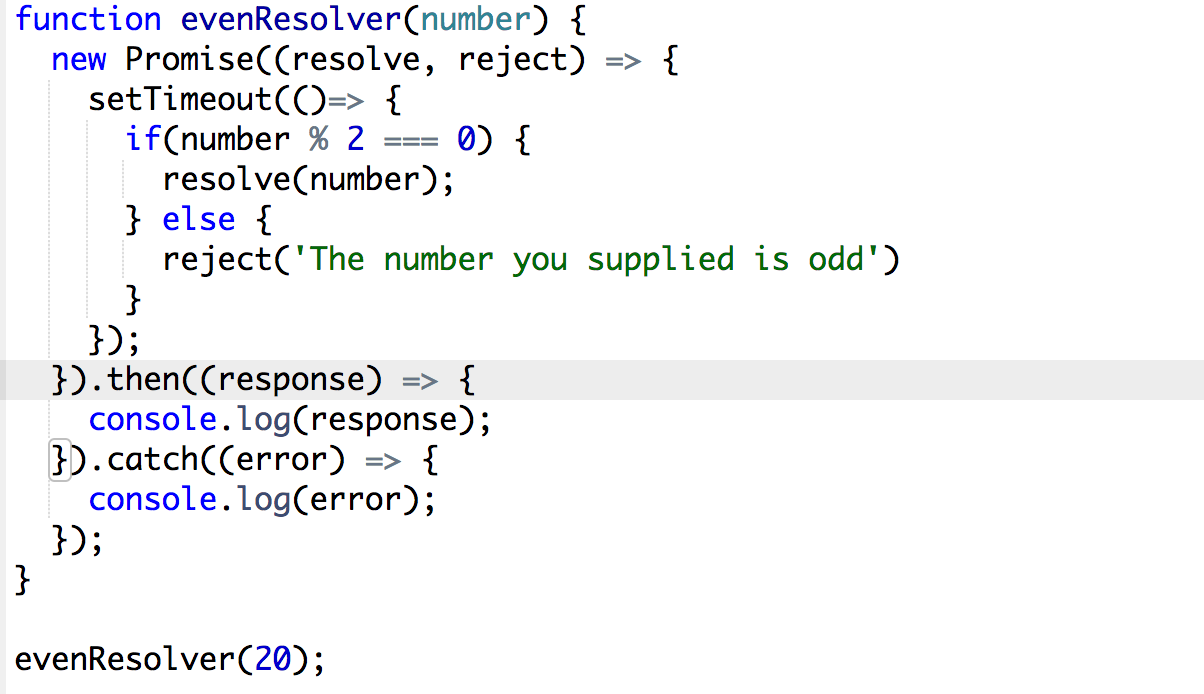
What is javascript promise object. How to Define a Promise Object. The following example demonstrates an Auth module within an API login that returns a Promise that will either be resolved/fulfilled or rejected. The returned object ... A promise is an object which can be returned synchronously from an asynchronous function. It will be in one of 3 possible states: Fulfilled: onFulfilled () will be called (e.g., resolve () was ... The methods promise.then(), promise.catch(), and promise.finally() are used to associate further action with a promise that becomes settled.. The .then() method takes up to two arguments; the first argument is a callback function for the resolved case of the promise, and the second argument is a callback function for the rejected case. Each .then() returns a newly generated promise object ...
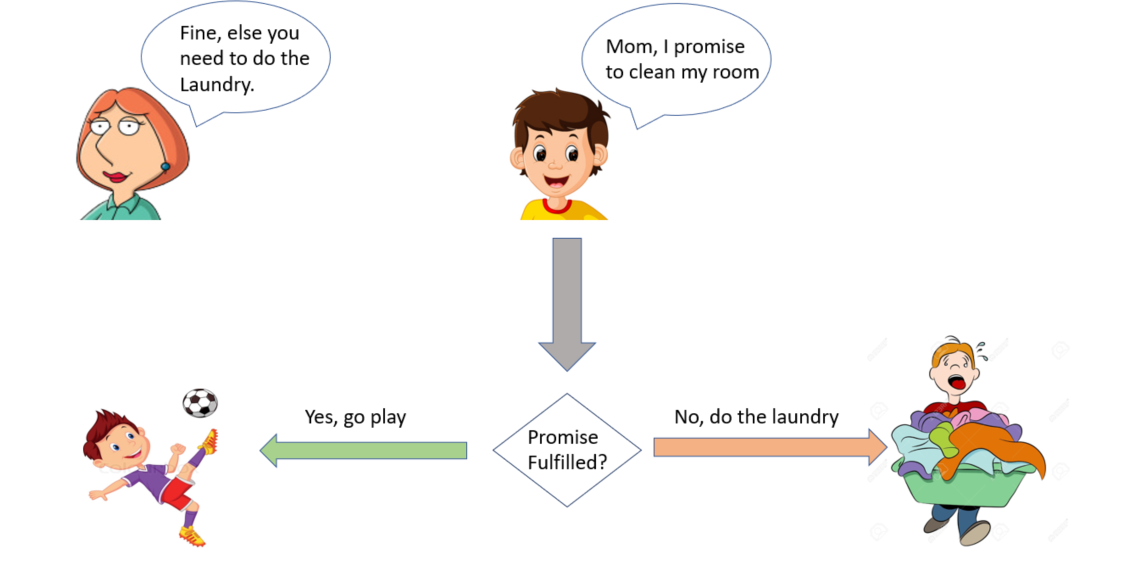
What is a promise in JavaScript?JavaScript is single threaded, meaning that two bits of script cannot run at the same time; they have to run one after another. A Promise is an object that represents the eventual completion (or failure) of an asynchronous operation, and its resulting value. var A JavaScript promise is an object that represents the completion or failure of an asynchronous task and its resulting value.¹ The end. I'm kidding of course. In JavaScript, a promise is just like a promise that you make in real life to show that you are committed to doing something. For example, I promise to get good marks in mathematics, and then this Promise has two outcomes, either it will be fulfilled (or resolved) or not fulfilled (or be rejected).
The Promise.resolve() method returns a Promise object that is resolved with a given value. If the value is a promise, that promise is returned; if the value is a thenable (i.e. has a "then" method), the returned promise will "follow" that thenable, adopting its eventual state; otherwise the returned promise will be fulfilled with the value.. This function flattens nested layers of promise-like ... Promises are important building blocks for asynchronous operations in JavaScript. You may think that promises are not so easy to understand, learn, and work with. And trust me, you are not alone! Promises are challenging for many web developers, even after spending years working with them. In this article, I 30/7/2021 · Promise Object: What is a Promise object in JavaScript? A promise object is an object that represents the eventual result of an asynchronous operation. If it succeeds, then we call its resolve function with any arguments given to the constructor as parameters (usually these are just success data).
A promise is a new Object type of EcmaScript 6 (ES6), for which there are numerous polyfills and libaries (i.e. implementations for ES5 JavaScript engines), and allows (among other benefits) to get out of the infamous callback hell, and to write and read asynchronous code easily. If the promise is rejected or fulfilled, it also has a settled ... A Promise object is widely used in Javascript async programming. And it's sometimes confusing for developers how to use it properly. In this blog post, I've attempted to describe a use case when a developer needs to use a returned value from a Promise object somewhere later in code. A promise is an object that will produce a value in the future. On Career Karma, learn how to use JavaScript promises.
A Promise is an object that represents an asynchronous operation that will eventually produce a value. Use the then() method to hook up a callback that will be called when the result of the asynchronous operation is ready. ECMAScript 2017 introduced async function()s which return Promises and the await keyword which can simplify Promise based code. let promise1 = new Promise ( (resolve, reject) => { ... } ); The Promise () object is a built-in object in JavaScript ES6. When this object is instantiated using the new keyword, it takes a ... RRP $11.95. Get the book free! This tutorial covers the basics of JavaScript promises, showing how you can leverage them in your JavaScript development. The concept of promises is not new to web ...
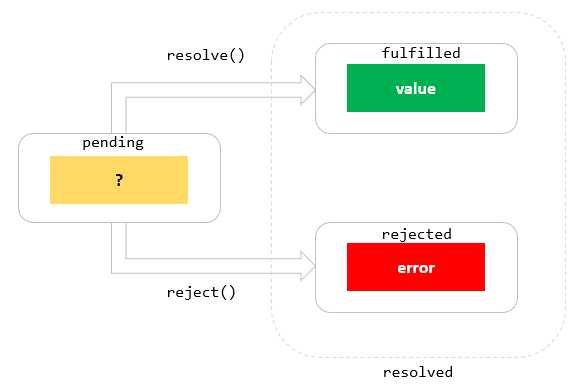
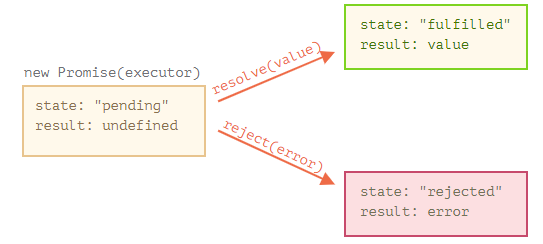
A Promise has four states: fulfilled: Action related to the promise succeeded. rejected: Action related to the promise failed. pending: Promise is still pending i.e not fulfilled or rejected yet. settled: Promise has fulfilled or rejected. A promise can be created using Promise constructor. Syntax. var promise = new Promise (function (resolve ... Promise Object Properties. A JavaScript Promise object can be: Pending; Fulfilled; Rejected; The Promise object supports two properties: state and result. While a Promise object is "pending" (working), the result is undefined. When a Promise object is "fulfilled", the result is a value. When a Promise object is "rejected", the result is an ... In JavaScript, a promise is an object that represents an asynchronous operation. Promises have several methods that let you register a callback that the JavaScript runtime will call when the operation succeeds or fails. In the below example, the Axios HTTP library returns a promise.
Promise should not be rejected. A Promise is an object representing the eventual completion or failure of an asynchronous operation. This is what MDN define Promise for JS. A Promise is an object representing the eventual completion or failure of an asynchronous operation. Since most people are consumers of already-created promises, this guide will explain consumption of returned promises before explaining how to create them. 26/6/2021 · 1. A Promise in JavaScript What is a promise? A promise is the JavaScript object that represents the completion or failure of an asynchronous operation and its resulting value. How does it work? The idea of a promise is the object which can be in a certain state. The initial state is ‘pending’ where the promise is waiting for the asynchronous operation to finish.
JavaScript's way of expressing a Promise to clean the room. In JavaScript, a Promise takes in two callbacks: resolve and reject. Reading through the above code, it is evident that our small child fulfilled his promise to clean his room. Therefore, our Promise object here— once called upon— will resolve to return 'Clean' as its response. The Promise.reject() method returns a Promise object that is rejected with a given reason. A promise is a special JavaScript object that links the "producing code" and the "consuming code" together. In terms of our analogy: this is the "subscription list". The "producing code" takes whatever time it needs to produce the promised result, and the "promise" makes that result available to all of the subscribed code ...
Running checkIfItsDone() will specify functions to execute when the isItDoneYet promise resolves (in the then call) or rejects (in the catch call).. Chaining promises. A promise can be returned to another promise, creating a chain of promises. A great example of chaining promises is the Fetch API, which we can use to get a resource and queue a chain of promises to execute when the resource is ... A Javascript Promise. A Promise is a built-in javascript object that, when created, gets passed a callback function, which returns a resolve() or reject() function. There are two main properties of the Promise object, state and value. The default 'state' is 'pending', the default 'value' is 'undefined'. JavaScript Promises work in the same way, and we'll cover this shortly. Promise States. A Promise in JavaScript is an object consisting of three different states: Pending: The initial state of the Promise. This is the first state of the Promise after it has been initiated. Resolved: The Promise has completed successfully. Rejected: The Promise ...
 Javascript Async Consuming Promises
Javascript Async Consuming Promises
 Javascript Promise And Promise Chaining
Javascript Promise And Promise Chaining
 The Definitive Guide To The Javascript Promises
The Definitive Guide To The Javascript Promises
 Javascript Promises Theoretically Js Promises Are No By
Javascript Promises Theoretically Js Promises Are No By
 The Basics Of Javascript Promises By Adam Hollister Medium
The Basics Of Javascript Promises By Adam Hollister Medium
 Exploring Javascript Promises In Depth Javascript In Plain
Exploring Javascript Promises In Depth Javascript In Plain
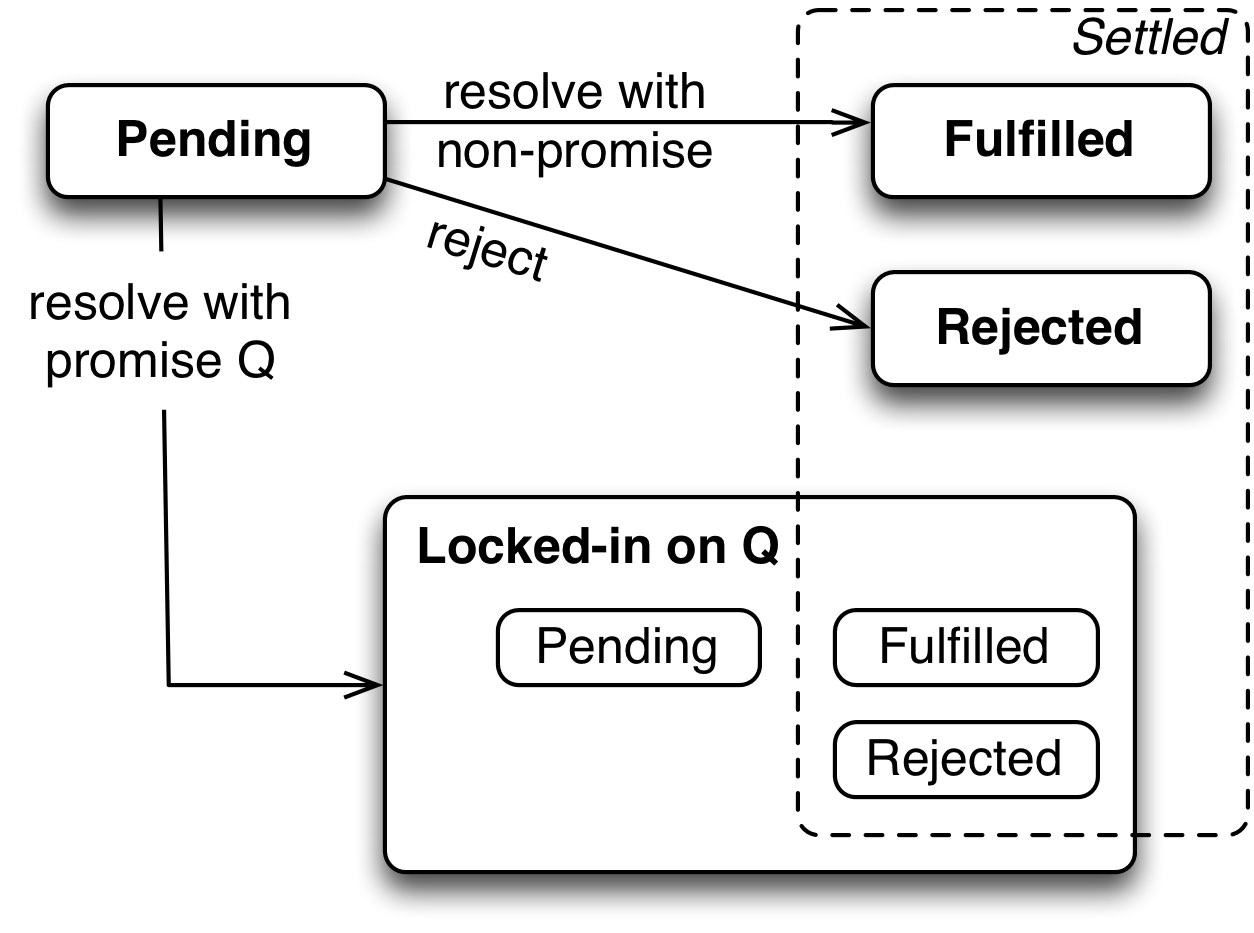 25 Promises For Asynchronous Programming
25 Promises For Asynchronous Programming
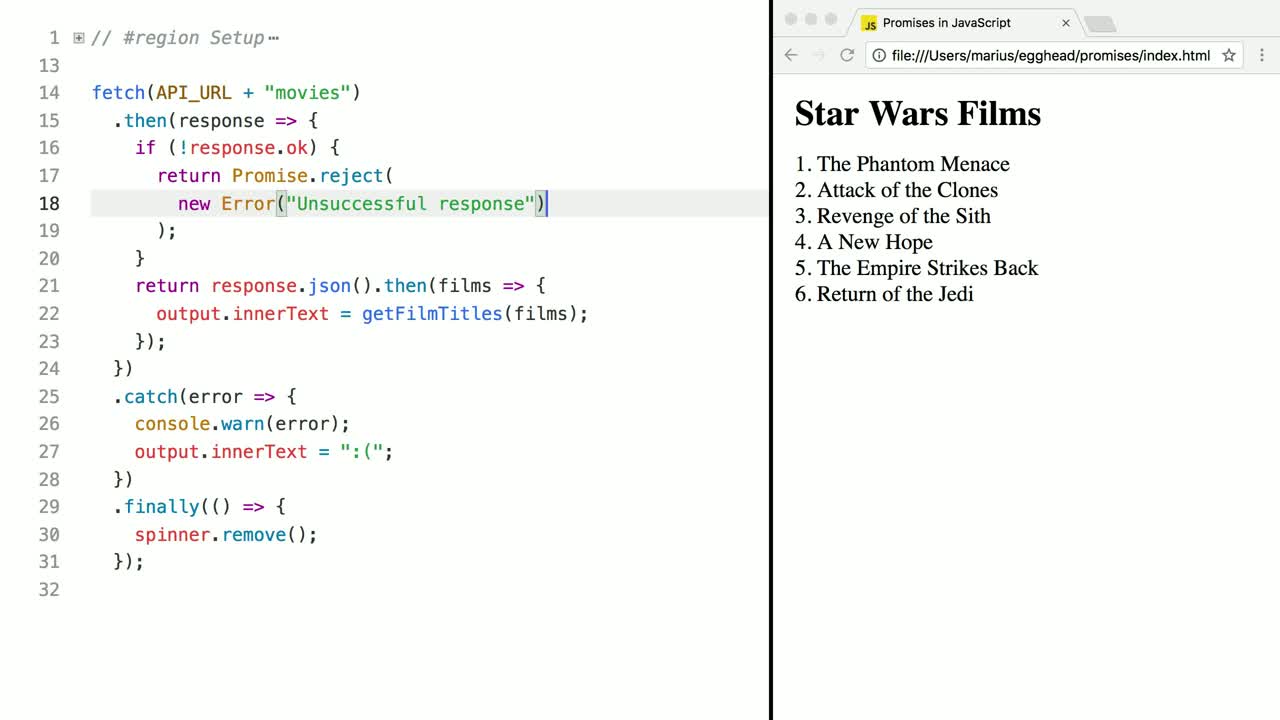 Javascript Promises In Depth Egghead Io
Javascript Promises In Depth Egghead Io
 Asynchronous Javascript Part 2 Promises
Asynchronous Javascript Part 2 Promises
 The Javascript Promise Tutorial Adrian Mejia Blog
The Javascript Promise Tutorial Adrian Mejia Blog
 Callback Vs Promises Vs Async Await Loginradius Engineering
Callback Vs Promises Vs Async Await Loginradius Engineering
 The Javascript Promise Tutorial Adrian Mejia Blog
The Javascript Promise Tutorial Adrian Mejia Blog
 How To Resolve Javascript Promises Sequentially One By One
How To Resolve Javascript Promises Sequentially One By One
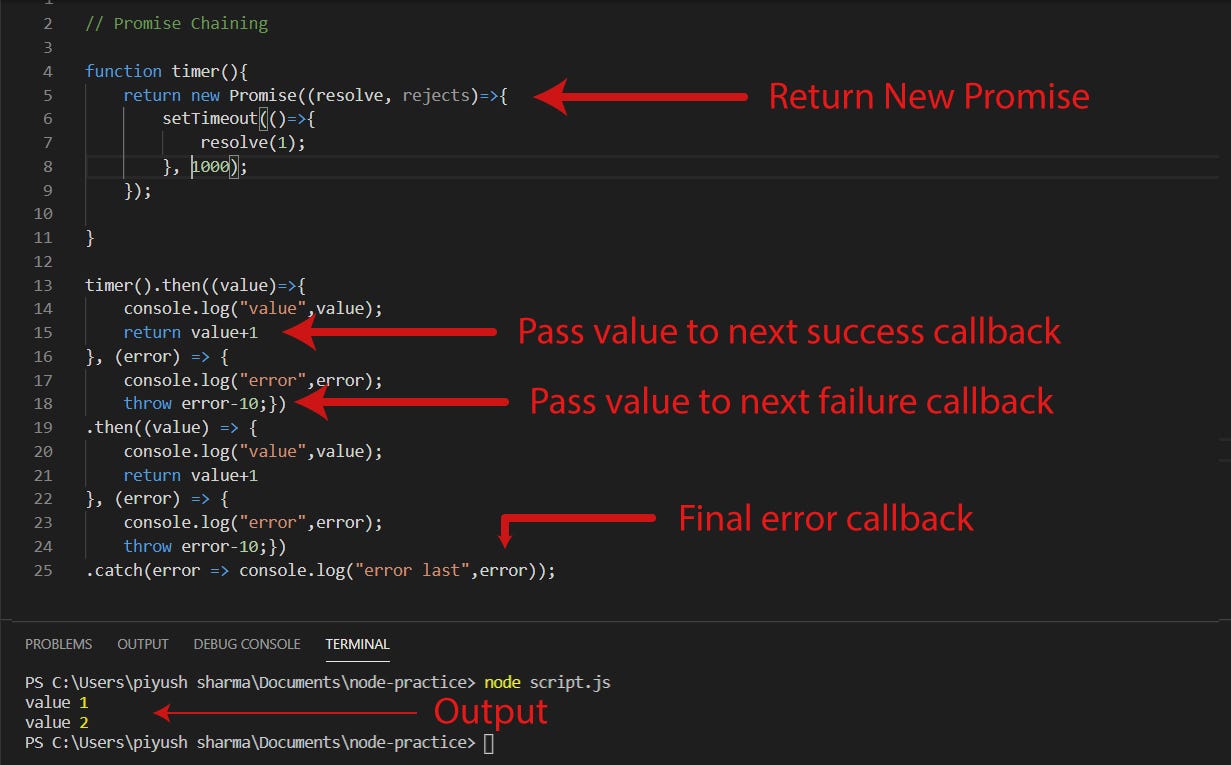 Javascript Promises In 5 Concepts By Piyush Sharma Codeburst
Javascript Promises In 5 Concepts By Piyush Sharma Codeburst
 How To Check If A Javascript Promise Has Been Fulfilled
How To Check If A Javascript Promise Has Been Fulfilled
 How To Check If A Javascript Promise Has Been Fulfilled
How To Check If A Javascript Promise Has Been Fulfilled
 Understanding Promises In Javascript Modev
Understanding Promises In Javascript Modev
 Deeply Understanding Javascript Async And Await With Examples
Deeply Understanding Javascript Async And Await With Examples
 Understanding Promises In Javascript By Sukhjinder Arora
Understanding Promises In Javascript By Sukhjinder Arora

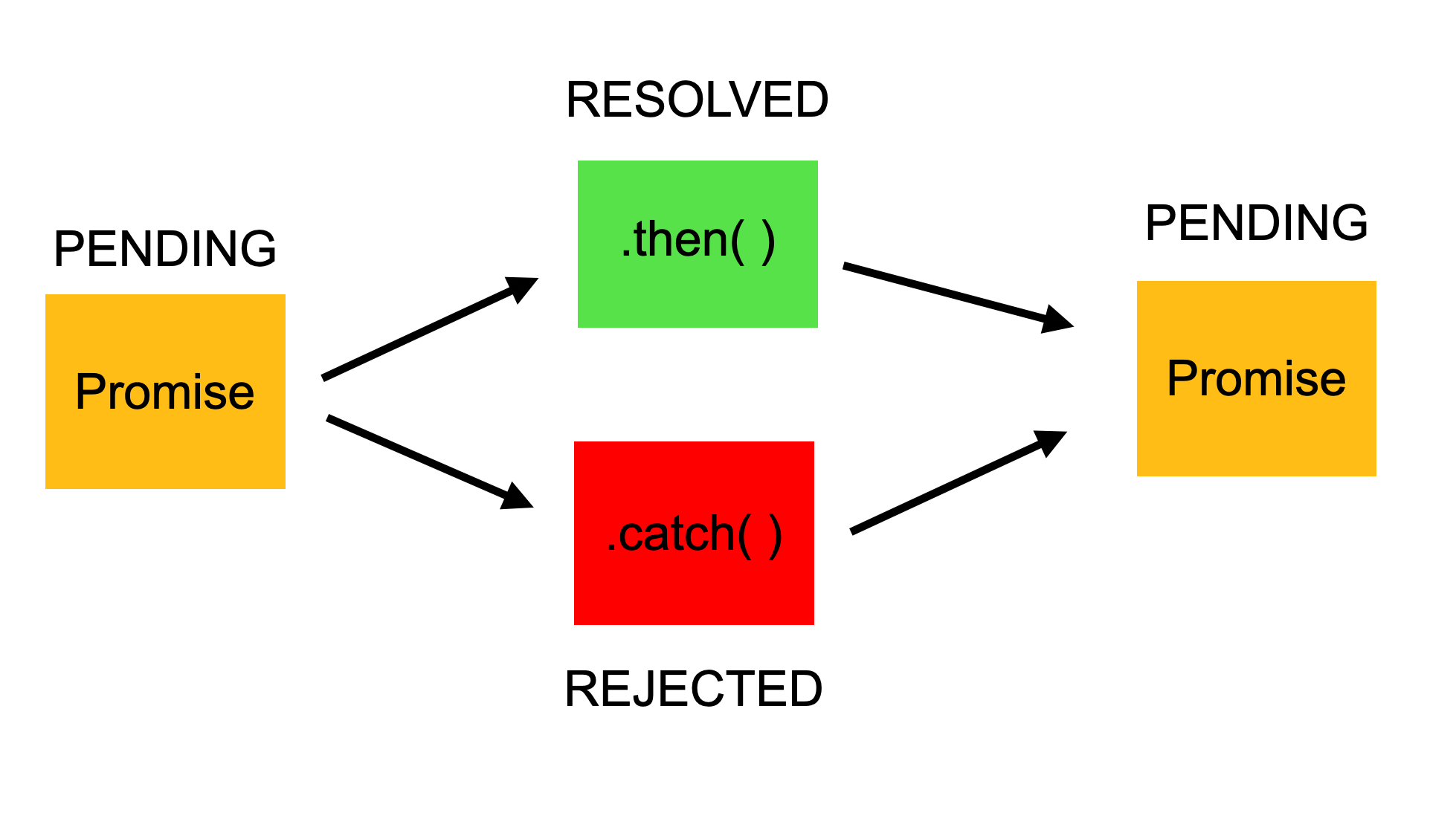 Javascript Promise Tutorial Resolve Reject And Chaining In
Javascript Promise Tutorial Resolve Reject And Chaining In
 Simple Explanation Of Javascript Promises Steemit
Simple Explanation Of Javascript Promises Steemit


0 Response to "25 What Is Javascript Promise Object"
Post a Comment