29 How To Write Promise Function In Javascript
Known Number of Promises. The ES6 way of doing things async way is .then() and .catch().. According to JavaScript Promise spec, every promise is thenable.. BTW, thenable just means a function which exposes a then method. If you have ever dealt with Promises, you will generally deal with .then and .catch methods.. Now, that the context is set, we can come back to our example from above. Key Takeaways. Promises can handle the asynchronous calls in JavaScript. A promise will be "pending" when executed and will result in "resolved" or "rejected", depending on the response of the asynchronous call. Promises avoid the problem of "callback hell", which happens due to nested callback functions.
 Async Await Vs Promises A Guide And Cheat Sheet By Kait
Async Await Vs Promises A Guide And Cheat Sheet By Kait
Promises are an important concept that is essential for a JavaScript developer to understand. If this concept is clear, the developer can utilize promises in a variety of ways in their day-to-day ...
How to write promise function in javascript. Despite all this mess of error ... hanging around. Promises help you naturally handle errors, and write cleaner code by not having callback parameters, and without modifying the underlying architecture (i.e. you can implement them in pure JavaScript and use them to wrap ... Apr 01, 2019 - JavaScript is a single-threaded programming language, that means only one thing can happen at a time. Before ES6, we used callbacks to handle asynchronous tasks such as network requests. Using… I'm super late to the party here, but I get enough requests for an article about JavaScript Promises that I figured it's probably time I write one. So, what's the fuss about? An introduction to JavaScript Promises A Promise is a JavaScript object (everything is an object in JS) that represents an asynchronous function. // Create a Promise object var sayHello = new Promise(function ...
I have an article here that dives deeper into these concepts: Thrown For a Loop: Understanding Loops and Timeouts in JavaScript. How do we use a promise? Using a promise is also called consuming a promise. In our example above, our function returns a promise object. This allows us to use method chaining with our function. Promises provide a couple of recipes to do that. In this chapter we cover promise chaining. The idea is that the result is passed through the chain of .then handlers. Then the .then handler is called (**). …and so on. As the result is passed along the chain of handlers, we can see a sequence of alert calls: 1 → 2 → 4. "async and await make promises easier to write" async makes a function return a Promise. await makes a function wait for a Promise
Running checkIfItsDone() will specify functions to execute when the isItDoneYet promise resolves (in the then call) or rejects (in the catch call).. Chaining promises. A promise can be returned to another promise, creating a chain of promises. A great example of chaining promises is the Fetch API, which we can use to get a resource and queue a chain of promises to execute when the resource is ... log before use setTimeout function log after use setTimeout function inside timeout Use promises to Wait for a Function to Finish in JavaScript. A promise is an object representing the eventual fulfillment or failure of an asynchronous operation. var promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject){ //do something }); Parameters. Promise constructor takes only one argument,a callback function. Callback function takes two arguments, resolve and reject; Perform operations inside the callback function and if everything went well then call resolve.
Well organized and easy to understand Web building tutorials with lots of examples of how to use HTML, CSS, JavaScript, SQL, Python, PHP, Bootstrap, Java, XML and more. Promises, wrapping the asynchronous operation result, can be returned synchronously from a function, assigned to variables, or used as arguments. That's the idea of promises: encapsulate the asynchronicity and allow function handling asynchronous operations to still look synchronous. 2. What is a promise. A "consuming code" that wants the result of the "producing code" once it's ready. Many functions may need that result. These are the "fans". A promise is a special JavaScript object that links the "producing code" and the "consuming code" together. In terms of our analogy: this is the "subscription list".
The solution is surprisingly simple. Even if you're a little uncomfortable with the idea of promises in JavaScript, you will love how you can solve this issue using them. As pointed out by Erop and Robin in the comments, Nodejs version 8 and above now support turning callback functions into promises using the built-in util module. Jul 01, 2019 - But there is more to promises and I will be showing that to you. JavaScript is a synchronous programming language, but because of callback functions we can make it work like an Asynchronous Programming language. A Promise can be created from scratch using its constructor. This should be needed only to wrap old APIs. In an ideal world, all asynchronous functions would already return promises. Unfortunately, some APIs still expect success and/or failure callbacks to be passed in the old way. The most obvious example is the setTimeout() function:
CodinGame is a challenge-based training platform for programmers where you can play with the hottest programming topics. Solve games, code AI bots, learn from your peers, have fun. The asynchronous functions like a callback, promise are internal to the JavaScript engine which is part of the browser. For example, Chrome uses the Google V8 JavaScript engine. The then () method in JavaScript has been defined in the Promise API and is used to deal with asynchronous tasks such as an API call. Previously, callback functions were used instead of this function which made the code difficult to maintain.
In this article, we will see how to write a promise function inside a loop. Promises inside a loop - Javascript ES6. If you want to learn more about Javascript. check out this articles. Prototypal Inheritance - Javascript Weekly. Understanding Closures in Javascript - Javascript Weekly. Configuring Babel for Node/Express. Before jumping into ... If you really want a general promiseWhen() function for this and other purposes, then by all means do so, using Bergi's simplifications. However, because of the way promises work, passing callbacks in this way is generally unnecessary and forces you to jump through complex little hoops. Introduction. Javascript Promises can be challenging to understand. Therefore, I would like to write down the way I understand promises. Understanding Promises. A Promise in short: "Imagine you are a kid.Your mom promises you that she'll get you a new phone next week.". You don't know if you will get that phone until next week. Your mom can really buy you a brand new phone, or she ...
Mar 05, 2021 - A promise can be created in our JavaScript code. Or else it can be returned from an external node package · Any promise that performs async operations should call any one of the two methods resolve or reject. The code logic should take care of when and where to call these functions. JavaScript Promises and Async/Await: As Fast As Possible™. Using promises, we can write asynchronous programs in a more manageable way. Using Async/Await syntax, a promise-based asynchronous ... promise.race() This function takes an array of promises and returns the first promise that is settled. Syntax. The syntax for the promise.race() function is mentioned below, where, iterable is an iterable object. E.g. Array. Promise.race(iterable) Example
I'm trying to create a function in Firebase Functions that returns a promise (or returns synchronously, I don't mind), but with no success. Here's the function that I wrote: function doSomethingL... Stack Overflow. ... Javascript: write function that returns a promise. Ask Question Asked 3 years, 8 months ago. Active 3 years, 8 months ago. Jan 18, 2021 - Old APIs will be updated to use promises, if it's possible in a backwards compatible way. XMLHttpRequest is a prime candidate, but in the mean time let's write a simple function to make a GET request: Return Data From Promise using ES6 Async/Await. JavaScript ES6 provides a new feature called async/await which can used as an alternative to Promise.then. Using async/await you can write the above code in synchronous manner without any .then. function getPromise() { return new Promise(function(resolve,reject) { setTimeout(function() { resolve ...
Each item in the array is a promise that needs to be resolved. In the example above, we pass in an array with all three of our invitee functions, each containing a promise. This gives us the array of promises that Promise.all() is looking for. Related Articles: JavaScript - How to use promises in JavaScript Dec 02, 2019 - Old APIs will be updated to use promises, if it's possible in a backwards compatible way. XMLHttpRequest is a prime candidate, but in the mean time let's write a simple function to make a GET request: Apr 18, 2017 - For me, I could use functions that were promised-based and I had heard of promises and could read the MDN documentation, but it was really hard to find a clear tutorial on how to write a Promise. ... If anyone asks you a question about Javascript, ever, your default answer should be 'an ...
Aug 12, 2019 - What is a promise?A JavaScript promise is an object that represents the completion or failure of an asynchronous task and its resulting value.¹ The end. I’m kidding of course. So, what does that definition even mean? First of all, many things in JavaScript are objects. You can create Oct 07, 2018 - JavaScript is a synchronous programming language. But thanks to callback functions we can make it function like Asynchronous programming language. ... Promises in JavaScript are very similar to the promises you make in real life. So first let us look at promises in real life. The methods promise.then(), promise.catch(), and promise.finally() are used to associate further action with a promise that becomes settled.. The .then() method takes up to two arguments; the first argument is a callback function for the resolved case of the promise, and the second argument is a callback function for the rejected case. Each .then() returns a newly generated promise object ...
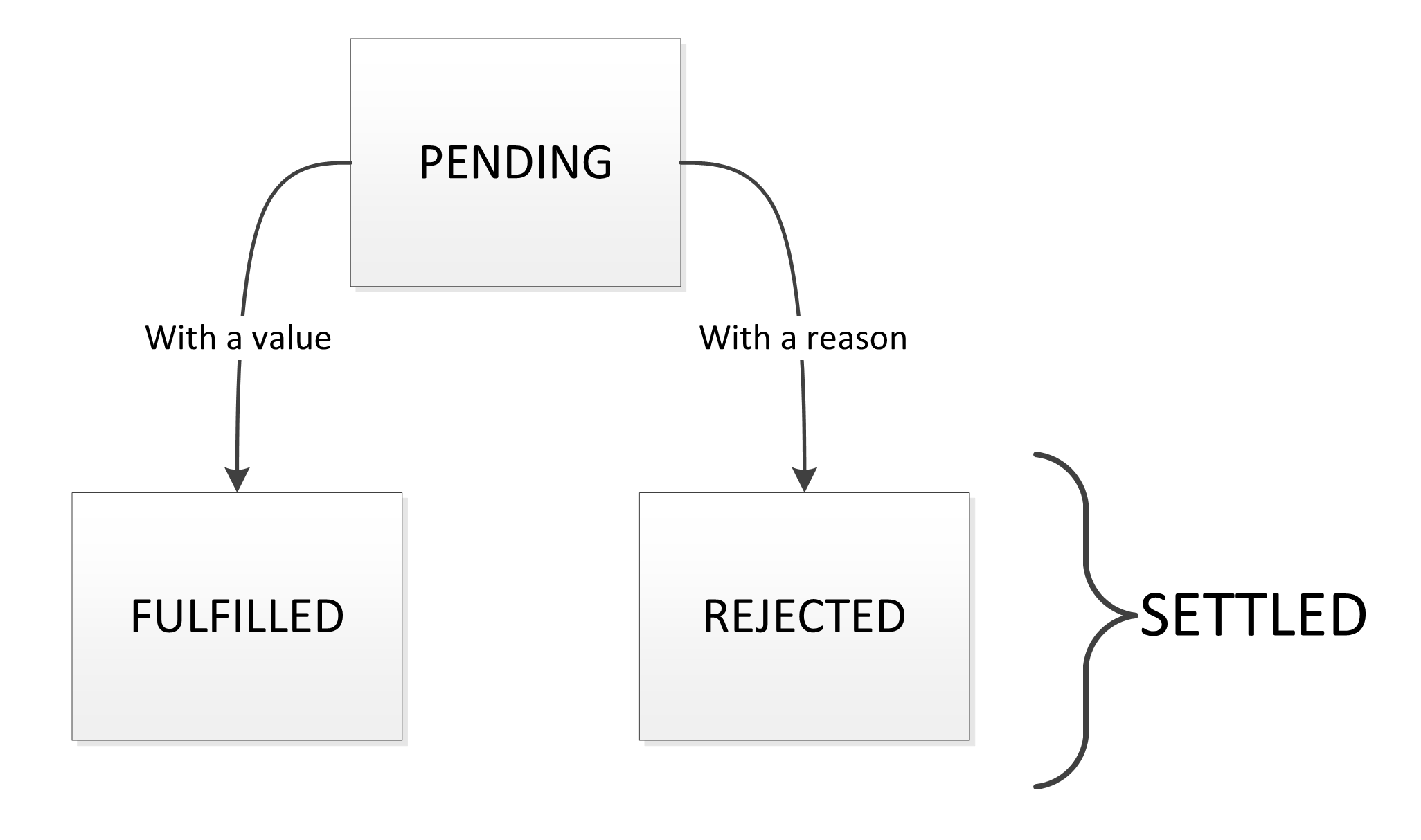
This function will return a user's name to our program after three seconds. This will help us see how promises are used to write asynchronous code. To create a promise, we need to create a Promise object: new Promise ( (resolve, reject) => { // Your code here }); Promises accept two arguments: a function that handles the success of the ... Sep 21, 2020 - Javascript Promises are not difficult. However, lots of people find it a little bit hard to understand at the beginning. Therefore, I would like to write down the way I understand promises, in a dummy way. Promise Object Properties. A JavaScript Promise object can be: Pending; Fulfilled; Rejected; The Promise object supports two properties: state and result. While a Promise object is "pending" (working), the result is undefined. When a Promise object is "fulfilled", the result is a value. When a Promise object is "rejected", the result is an ...
Jun 20, 2019 - Use this JavaScript runtime environment to run JavaScript code outside the browser. Mar 11, 2020 - In this tutorial, you will learn how to use JavaScript promises to improve asynchronous programming. Promises in javascript are very similar to promises made in real life. Definition of promise -Google After a promise is made, we get an assurance about ' something ' and we can plan accordingly.
 How To Rewrite A Callback Function In Promise Form And Async
How To Rewrite A Callback Function In Promise Form And Async
Javascript Promises Tutorial How To Use Them Ictshore Com
 Understanding Javascript Promises Digitalocean
Understanding Javascript Promises Digitalocean
 Javascript Async Await Serial Parallel And Complex Flow
Javascript Async Await Serial Parallel And Complex Flow
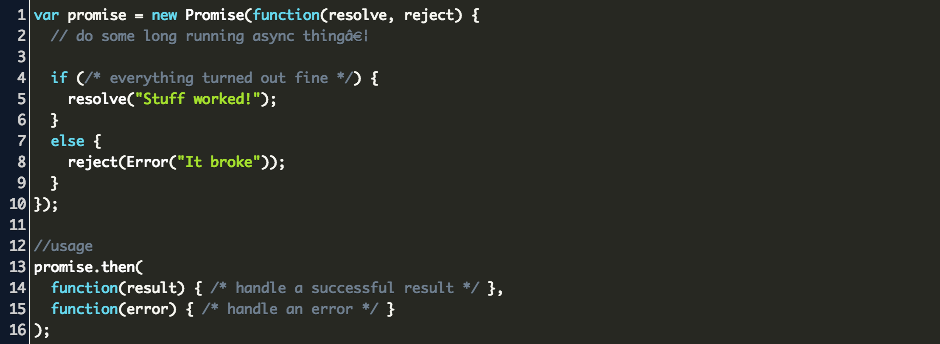 Javascript Promise Code Example
Javascript Promise Code Example
 Async Programming With Javascript Callbacks Promises And
Async Programming With Javascript Callbacks Promises And
 Tools Qa What Are Promises In Javascript And How To Use
Tools Qa What Are Promises In Javascript And How To Use
 Javascript Promise And Promise Chaining
Javascript Promise And Promise Chaining
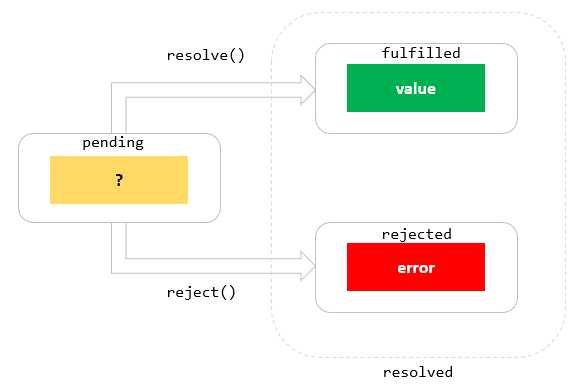 The Definitive Guide To The Javascript Promises
The Definitive Guide To The Javascript Promises
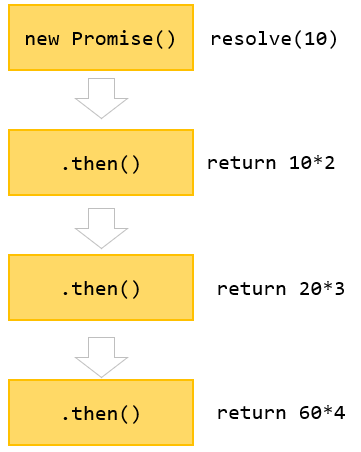 Promise Chaining In Javascript
Promise Chaining In Javascript
 Write Asynchronous Javascript Unit Salesforce Trailhead
Write Asynchronous Javascript Unit Salesforce Trailhead
 Angular 12 Promises Example Handle Http Requests Positronx Io
Angular 12 Promises Example Handle Http Requests Positronx Io
 Understanding And Effectively Using Asynchronous Javascript
Understanding And Effectively Using Asynchronous Javascript
How To Run Async Javascript Functions In Sequence Or Parallel
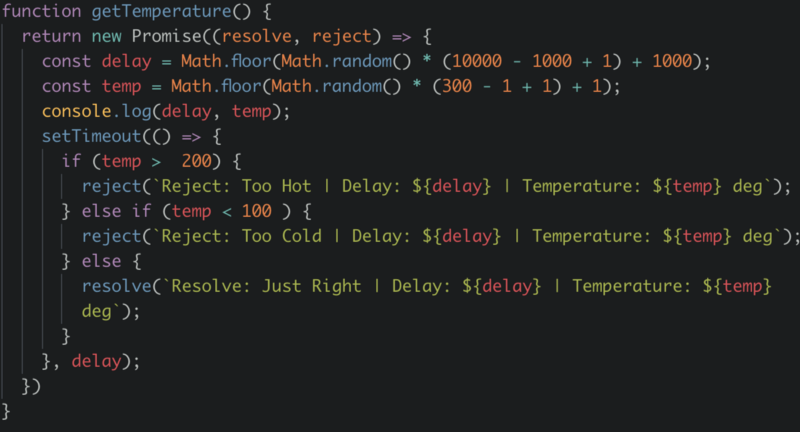 How To Write A Javascript Promise
How To Write A Javascript Promise
 Understanding Javascript Promises
Understanding Javascript Promises
 Tools Qa What Are Promises In Javascript And How To Use
Tools Qa What Are Promises In Javascript And How To Use
 Javascript Callbacks Promises And Async Functions Part 2
Javascript Callbacks Promises And Async Functions Part 2
 Javascript Promise With Examples Dot Net Tutorials
Javascript Promise With Examples Dot Net Tutorials
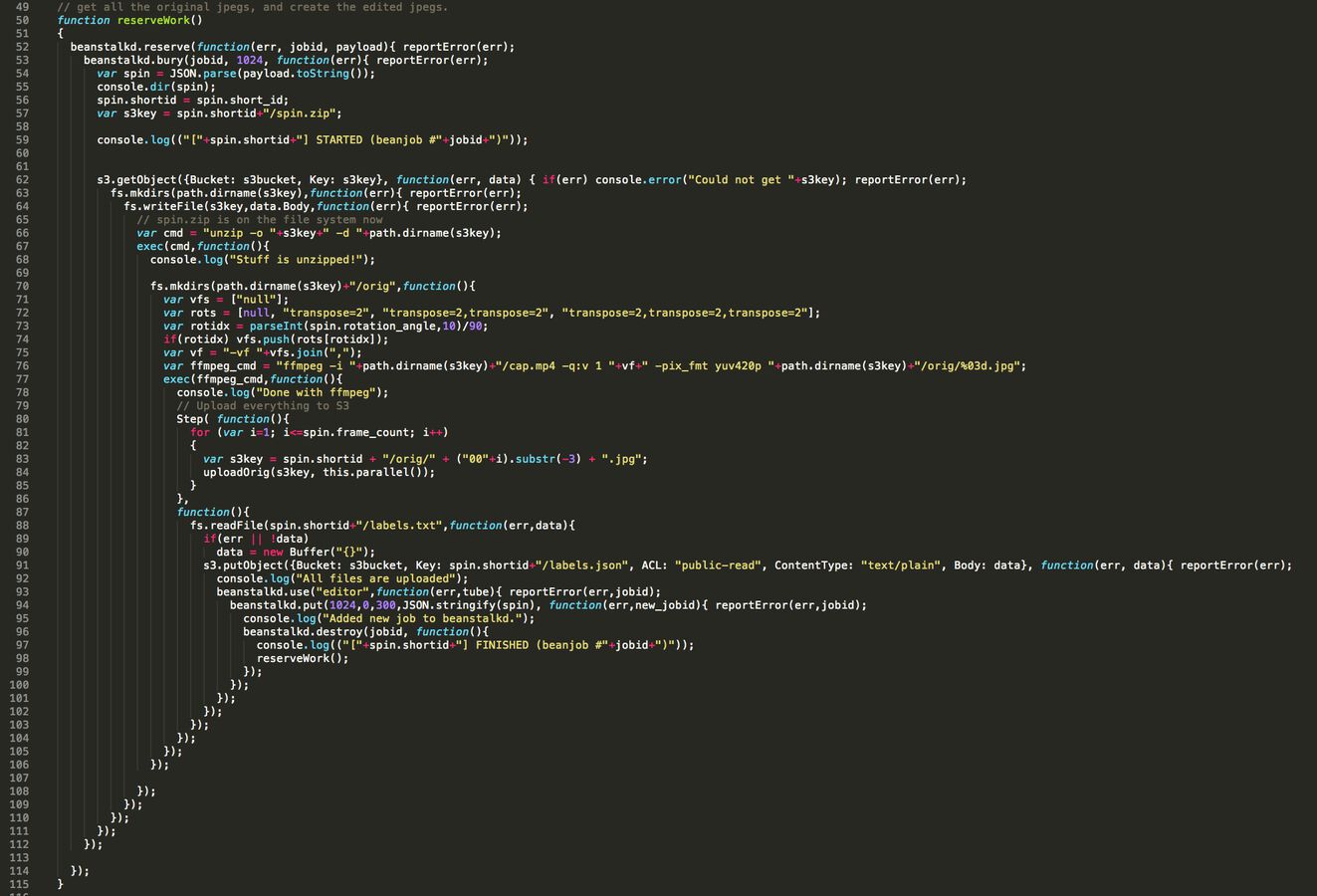 How To Avoid Infinite Nesting Callbacks
How To Avoid Infinite Nesting Callbacks
 Understanding Promises In Javascript By Sukhjinder Arora
Understanding Promises In Javascript By Sukhjinder Arora




0 Response to "29 How To Write Promise Function In Javascript"
Post a Comment