28 Javascript Throw Exception In Promise
Quick recap: in Javascript, a Promise is an object used as a proxy for a value not yet known. It's called a Promise because it's saying "I may not know what the value of the return is right now, but I promise to return it at some point, stored inside this thing". Thus, with the help of exception handling, it can be executed and handled. In exception handling: A throw statement is used to raise an exception. It means when an abnormal condition occurs, an exception is thrown using throw. The thrown exception is handled by wrapping the code into the try…catch block.
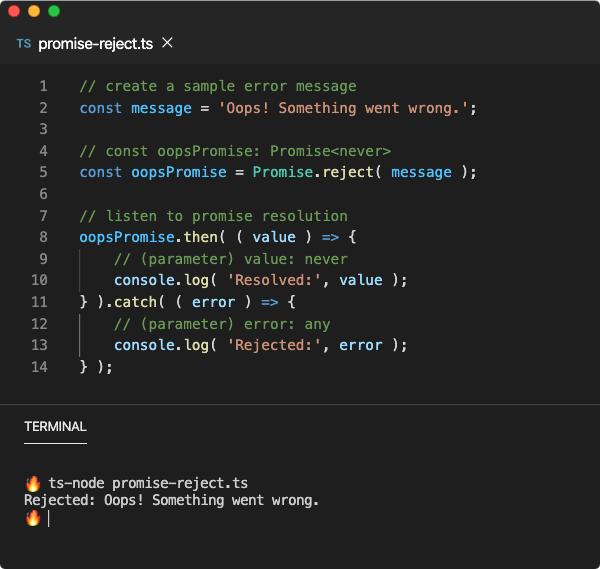 A Quick Introduction To Promises And Async Await With
A Quick Introduction To Promises And Async Await With
Leah J Stevenson. Monday, July 12, 2021 Add Comment Edit Javascript throw exception in promise

Javascript throw exception in promise. The finally() method returns a Promise.When the promise is settled, i.e either fulfilled or rejected, the specified callback function is executed. This provides a way for code to be run whether the promise was fulfilled successfully or rejected once the Promise has been dealt with.. This helps to avoid duplicating code in both the promise's then() and catch() handlers. When an exception is thrown in the try-block, exception_var (i.e., the e in catch (e)) holds the exception value. You can use this identifier to get information about the exception that was thrown. This identifier is only available in the catch-block's scope. If you don't need the exception value, it could be omitted. Async functions and exceptions # Brian Terlson points out that async functions reflect a preference for not mixing exceptions and rejections: Originally, if an async function had a default value that threw an exception then the function would throw an exception. Now, the function rejects the Promise it returns. Further reading #
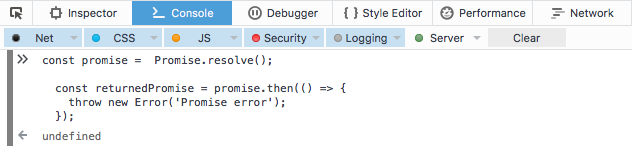
The exception handling in a promise chain only protects us once we have the initial promise object. As such, exceptions raised during the generation of the initial promise will result in an uncaught exception. To see this in action, take a look at the following code: NOTE: In AngularJS, there are actually very few truly "uncaught" exceptions ... 16/8/2019 · However, because our catch doesn't re-throw or explicitly reject, it returns a resolved promise and so the next then (sendWelcomeEmail) will run, and because there is no user, it will throw, and we'll create a queued email for a non-existing user. The casual promise API makes unintentionally recovering from an exception easy/sleek/elegant. A Promise in JavaScript can be created like so. let promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) { // do something }); Copy. As you can see, the Promise object here accepts a callback. The callback function then takes two arguments: resolve and reject. The arguments resolve and reject are callbacks provided by JavaScript itself.
But if any of the promises above rejects (a network problem or invalid json or whatever), then it would catch it. Implicit try…catch. The code of a promise executor and promise handlers has an "invisible try..catch" around it. If an exception happens, it gets caught and treated as a rejection. For instance, this code: Yes, but if the throw happens in a Promise it must have been awaited with the await syntax, and resolve must not have been called before the throw. Will not catch errors thrown in another call stack via a setTimeout() or setInterval() callback. It works just like with try/catch: when you re-throw an exception from the catch block, you will have to catch that again somewhere else, or your program crashes. - Bergi Jan 24 at 14:09. ... JavaScript Promises - reject vs. throw. 3. Unhandled promise rejection in Node.js. 0. i keep getting unhandled promise rejection. 0.
Throwing errors in JavaScript. ... Another great feature of .NET is that throwing an exception on the server in a web service automatically can automatically throw that exception in a client using the service — whether the client is C#, Java, PHP or JavaScript. ... It's best to avoid throwing errors from inside a Promise, ... Throw an error inside the Promises Inside the promise, the catch () method will catch the error caused by the throw statement and reject (). We have modified the existing function so as to throw an error inside the promises and then consume the promise. The technical term for this is: throw an exception. The exception can be a JavaScript String, a Number, a Boolean or an Object: throw "Too big"; // throw a text
Error handling in async/await causes a lot of confusion. There are numerous patterns for handling errors in async functions, and even experienced developers sometimes ... The try and catch statements handle exceptions in a standard way which is provided by JavaScript. However, you can use the throw statement to pass user-defined exceptions. In JavaScript, the throw statement handles user-defined exceptions. For example, if a certain number is divided by 0, and if you need to consider Infinity as an exception ... Syntax: Throwing a generic exception throw new Error([message]) OR throw([message]) Syntax: Throwing a specific exception throw new Error_name([message]) Exception Handling. Exception handling is accomplished with a try...catch statement. When the program encounters an exception, the program will terminate in an unfriendly fashion.
throw. The throw statement throws a user-defined exception. Execution of the current function will stop (the statements after throw won't be executed), and control will be passed to the first catch block in the call stack. If no catch block exists among caller functions, the program will terminate. The throw keyword is used to throw an exception from within a method, whenever a throw statement gets encountered, gets executed. The execution of the current method is stopped and returned to the caller. 24/12/2017 · Answers: If you are using native Promise, it’s pretty simple. You only need to .catch this reject some where. ajax (request).catch (function (rejected) { console.log (rejected); }); If I don’t catch it somewhere, the uncaught in promise will keep showing. But If I catch it somewhere…. Tags: exception.
}); // Errors thrown inside asynchronous functions will act like uncaught errors var p2 = new Promise (function (resolve, reject) {setTimeout (function {throw new Error ('Uncaught Exception!');}, 1000);}); p2. catch (function (e) {console. error (e); // This is never called}); // Errors thrown after resolve is called will be silenced var p3 = new Promise (function (resolve, reject) {resolve (); throw new Error ('Silenced … a basic understanding of JavaScript and ES6; a working installation of Node.Js, and Jest; How to Throw Errors From Regular Functions in JavaScript "Use exceptions rather than return codes" (Clean code). Throwing errors is a best practice for dealing with unknowns. The same rule applies for every modern language: Java, JavaScript, Python, Ruby. This is because "exceptions thrown in then callbacks are consumed and transformed into rejections, [so] exceptions at the end of the chain are easy to accidentally, silently ignore" where as with done "the resulting rejection reason is thrown as an exception in a future turn of the event loop" (Q API).
Code language: JavaScript (javascript) In this example, instead of throwing an error inside the promise, we called the reject() explicitly. The catch() method also handles the error in this case. … Expecting Async Functions to Throw Exceptions . Writing a unit test to expect an async function to throw an exception can be done as follows. First we define the async function in a module, then in the test code we use the rejects property to test for any thrown errors. Essentially, we are asserting that our function causes a promise rejection. And this is the key characteristic which distinguishes throw from return: after a function throws an exception, the runtime system will try to find a way to handle the exception. In other words ...
JS Callbacks JS Asynchronous JS Promises JS Async/Await JS HTML DOM ... Technically you can throw an exception (throw an error). The exception can be a JavaScript String, a Number, a Boolean or an Object: throw "Too big"; // throw a text throw 500; // throw a number. Stack trace conveys some portion of the data whenever an exception is thrown. The stack trace is a collection of all the methods used in the program. It starts with the method that throws an exception and ends with the method that catches the exception. In case if an exception is re-thrown, the stack trace is restarted at the current method. Like promise.then, await allows us to use thenable objects (those with a callable then method). The idea is that a third-party object may not be a promise, but promise-compatible: if it supports .then, that's enough to use it with await. Here's a demo Thenable class; the await below accepts its instances:
Output: Here the catch block is able to recognise reject() and print the corresponding message. promise failed! 2. This is a very basic difference. If throw is encountered anywhere inside a function the exception is thrown immidiately and the control flow is terminated.In other words after throwing the exception control comes out of the function inside which the exception was thrown.
 Handling Error Http Responses In Javascript Fetch
Handling Error Http Responses In Javascript Fetch
 Javascript Promises The Definitive Guide Nearform
Javascript Promises The Definitive Guide Nearform
 How To Rewrite A Callback Function In Promise Form And Async
How To Rewrite A Callback Function In Promise Form And Async
 Throw An Exception In Promise Catch Block Stack Overflow
Throw An Exception In Promise Catch Block Stack Overflow
 Co Exception Causes Node Promise Reject To Throw In
Co Exception Causes Node Promise Reject To Throw In
 Advanced Javascript Node Js Promises Chaining Collections
Advanced Javascript Node Js Promises Chaining Collections
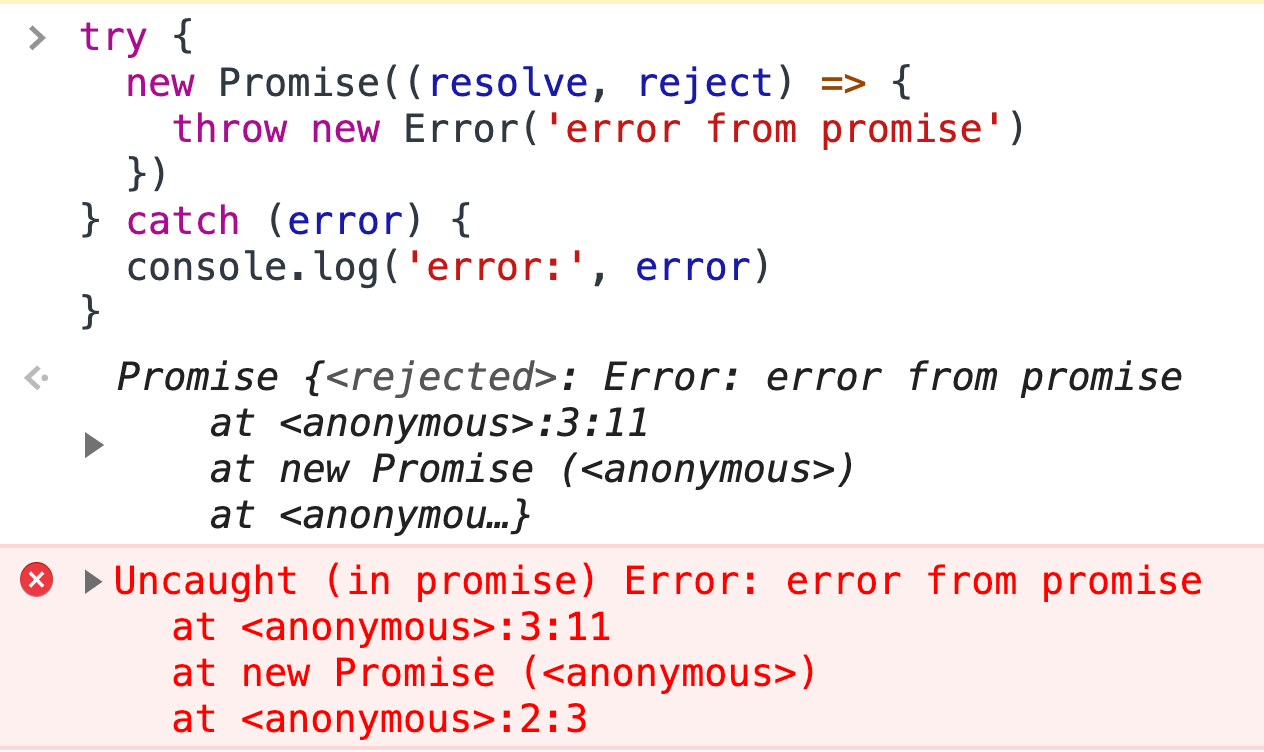 What Exceptions Cannot Be Caught By Try Catch By Bytefish
What Exceptions Cannot Be Caught By Try Catch By Bytefish
 Unhandledrejection Non Error Promise Rejection Captured
Unhandledrejection Non Error Promise Rejection Captured
Promises Chaining Semantic Portal Learn Smart
 Javascript Throw Exception Examples Of Javascript Throw
Javascript Throw Exception Examples Of Javascript Throw
 Angular 2 Webworkers Http Uncaught In Promise Not
Angular 2 Webworkers Http Uncaught In Promise Not
 Async Await In Node Js How To Master It Risingstack
Async Await In Node Js How To Master It Risingstack
 Node Js Error Handling Best Practices Hands On Experience
Node Js Error Handling Best Practices Hands On Experience
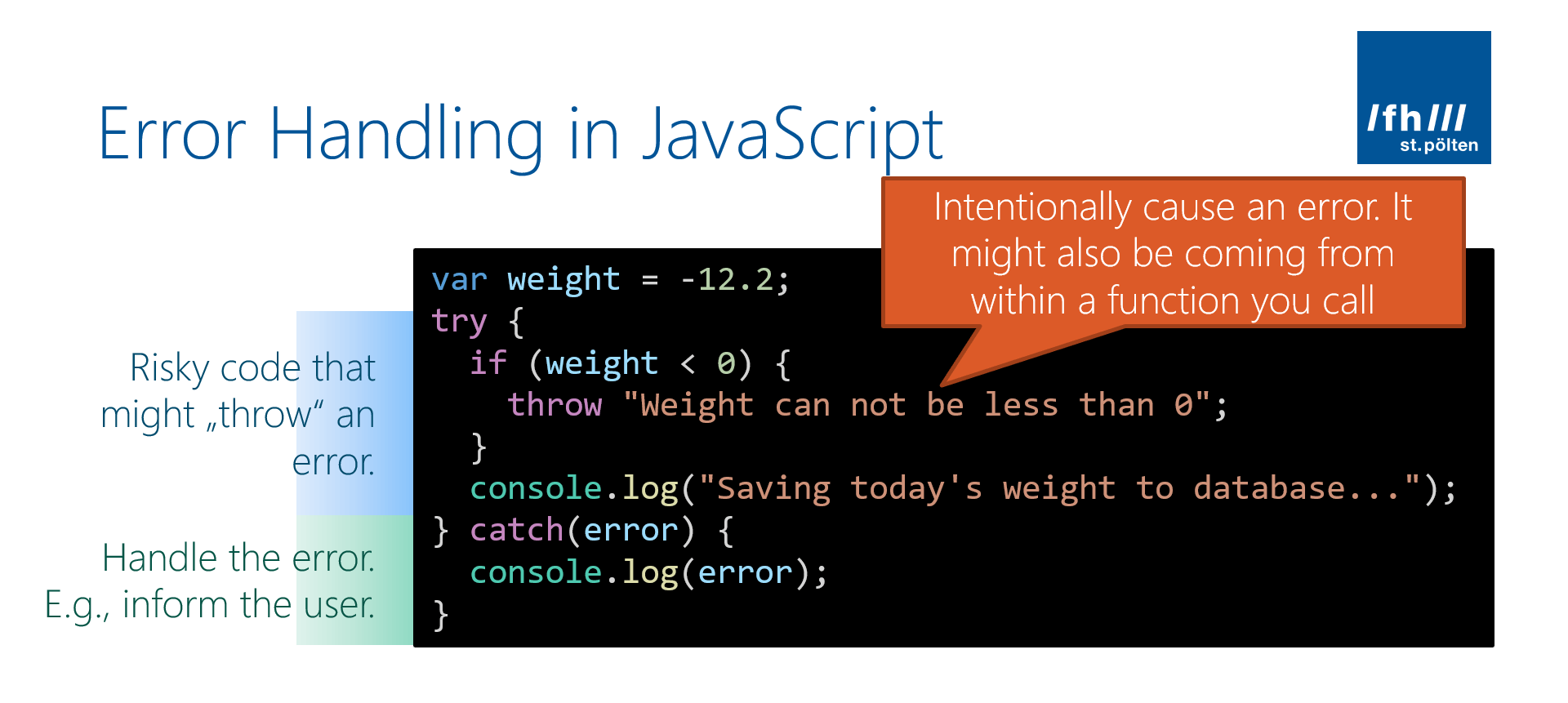 Asynchronous Javascript With Promises Amp Async Await In
Asynchronous Javascript With Promises Amp Async Await In
 Javascript Promise Reject How To Reject Promise In Javascript
Javascript Promise Reject How To Reject Promise In Javascript
 Exception Handling In Javascript Logrocket Blog
Exception Handling In Javascript Logrocket Blog
 In Angular A Promise With A Finally Block Does Not Reject
In Angular A Promise With A Finally Block Does Not Reject
 Asynchronous Javascript Using Promises With Rest Apis In Node Js
Asynchronous Javascript Using Promises With Rest Apis In Node Js
 Javascript Promises 9 Questions Dan Levy S Programming Blog
Javascript Promises 9 Questions Dan Levy S Programming Blog
 Finally In Promises Amp Try Catch Dev Community
Finally In Promises Amp Try Catch Dev Community
 Javascript Promises And Async Await Cheatsheet Beginner To
Javascript Promises And Async Await Cheatsheet Beginner To
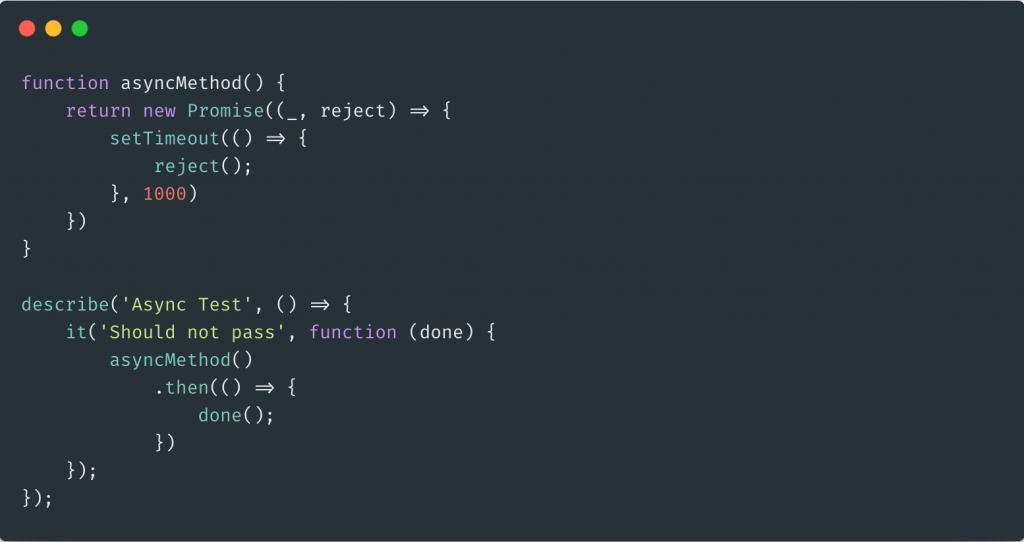 A Helpful Guide To Testing Promises Using Mocha Testim Blog
A Helpful Guide To Testing Promises Using Mocha Testim Blog
 Javascript Promises The Definitive Guide Nearform
Javascript Promises The Definitive Guide Nearform
 Lucy Js Promises A Jquery Deferreds And Errors
Lucy Js Promises A Jquery Deferreds And Errors
 Promises And Async Await Cheatsheet
Promises And Async Await Cheatsheet

0 Response to "28 Javascript Throw Exception In Promise"
Post a Comment