27 How To Use Javascript Promises
Dec 16, 2019 - Before creating this, I didn’t imagine there would be so many different ways to create a Promise. I imagine that it’s likely that I may have also missed a few. There’s a lot of redundancy here, but… Apr 17, 2018 - Many of us have already used promises in the form of libraries such as Q, when.js, RSVP.js, etc. Even jQuery has something called a Deferred object, which is similar to a promise. But now we have native support for promises in JavaScript, which is really exciting.
May 29, 2019 - You can use the materials linked to from this page, but some of the content may be out of date. We're still working on updating written materials, but check out our new codelabs and videos. ... Promises offer a better way to handle asynchronous code in JavaScript.
How to use javascript promises. JavaScript Promises and Async/Await: As Fast As Possible™. Using promises, we can write asynchronous programs in a more manageable way. Using Async/Await syntax, a promise-based asynchronous ... If you want to execute multiple promises in parallel and want to wait for the completion of all the promises before proceeding further, you can use the ".all " function provided by the Promises in JavaScript. In JavaScript, we need to handle asynchronous functions in JavaScript's single-threaded world. Often, developers will use promises to handle asynchronous functions. There are two ways to handle…
What I do next I send the requests to my API creating the promises and using promise.all() What I do when all the data has been loaded Once the data arrives to my app, I can execute the callback of promises.all() and then make visible the table with the users. I hope it helps you to see in which scenario makes sense to use promises.all() In simple words, a promise is a placeholder for a value that's going to be available sometime later. Promises are useful when handling asynchoronous operations. JavaScript provides a helper function Promise.all (promisesArrayOrIterable) to handle multiple promises at once, in parallel, and get the results in a single aggregate array. Mar 11, 2020 - In this tutorial, you will learn how to use JavaScript promises to improve asynchronous programming.
JavaScript - How to Use promises in JavaScript JavaScript is a synchronous language, yet sometimes asynchronous behavior is required. For example, you may need to use an asynchronous function while waiting for data to be fetched from an API, or while waiting for a site's images to load. Aug 05, 2019 - One of the most important questions I faced in interviews was how promises are implemented. Since async/await is becoming more popular, you need to understand promises. What is a Promise?A promise is an object which represents the result of an asynchronous operation which is either resolved ... ES6 came with many new features, but one of the best features was the official introduction of Promises. Promises allow you to write clean non-callback-centr...
Jan 14, 2018 - Browse thousands of programming tutorials written by experts. Learn Web Development, Data Science, DevOps, Security, and get developer career advice. Promise Object Properties. A JavaScript Promise object can be: Pending; Fulfilled; Rejected; The Promise object supports two properties: state and result. While a Promise object is "pending" (working), the result is undefined. When a Promise object is "fulfilled", the result is a value. When a Promise object is "rejected", the result is an ... Once you have a Promise object, configure .then() and .catch() methods to deal with the result of the promise..then() implicitly returns a new Promise. Use Promise.all() when you have a number of long-running actions that depend on each other. Code execution will not continue until all Promises have resolved or one has been rejected.
Promises are used to handle asynchronous operations in JavaScript. They are easy to manage when dealing with multiple asynchronous operations where callbacks can create callback hell leading to unmanageable code. Prior to promises events and callback functions were used but they had limited functionalities and created unmanageable code. How to Create a JavaScript Promise We're going to start by creating a promise which returns a user's name. This function will return a user's name to our program after three seconds. This will help us see how promises are used to write asynchronous code. Unlike old-fashioned passed-in callbacks, a promise comes with some guarantees: Callbacks added with then () will never be invoked before the completion of the current run of the JavaScript event loop. These callbacks will be invoked even if they were added after the success or failure of the asynchronous operation that the promise represents.
JavaScript Promises In JavaScript, a Promise is used for performing asynchronous operations. It represents a result that may be available now, or in the future or never. Promises are easy to manage when dealing with multiple asynchronous operations. Promises provide a couple of recipes to do that. In this chapter we cover promise chaining. The idea is that the result is passed through the chain of .then handlers. Then the .then handler is called (**). …and so on. As the result is passed along the chain of handlers, we can see a sequence of alert calls: 1 → 2 → 4. Promises offer a powerful and legible syntax for writing asynchronous code in JavaScript. This post assumes a basic understanding of Promises and how they work. We'll look at three practical use cases of Promises in JavaScript to get you comfortable with using them.
The Promise.all() returns a promise that resolves to an array of values from the input promises while the Promise.race() returns a promise that resolves to the value from the first settled promise. JavaScript Promise.race() examples. Let's take some examples of using the Promise.race() static method. 1) Simple JavaScript Promise.race() examples With a JavaScript Promise, that is also called the return value. If the message is a "success", we will proceed to sign the candidate in and grant him the position. If it fails, we proceed to reject his application. With JavaScript promises, we do this by using a callback function (promise handlers). Mar 01, 2020 - Promises in JavaScript are very similar to the promises you make in real life. As promises in real life are either kept or broken, JavaScript Promises get either resolved or rejected. However…
Dec 02, 2019 - JavaScript promises started out in the DOM as "Futures", renamed to "Promises", and finally moved into JavaScript. Having them in JavaScript rather than the DOM is great because they'll be available in non-browser JS contexts such as Node.js (whether they make use of them in their core APIs ... The JavaScript promises API will treat anything with a then () method as promise-like (or thenable in promise-speak sigh), so if you use a library that returns a Q promise, that's fine, it'll play nice with the new JavaScript promises. Although, as I mentioned, jQuery's Deferreds are a bit … unhelpful. ECMAScript 2015, also known as ES6, introduced the JavaScript Promise object. The following table defines the first browser version with full support for Promise objects: ... Get certified by completing a course today!
2 weeks ago - The main difference between Callback ... callback to a Promise rather than passing it. So we still use callback functions with Promises, but in a different way (chaining). This is one of the greatest advantages of using Promises, but why? ... Callback functions have been used alone for asynchronous operations in JavaScript for many ... 1 week ago - Async functions are stage 3 at the time of this writing, but I predict that they will soon become a very popular, very commonly used solution for asynchronous programming in JavaScript — which means that learning to appreciate promises is going to be even more important to JavaScript developers ... You can create a promise using the promise constructor like this: let promise = new Promise (function (resolve, reject) { // Make an asynchronous call and either resolve or reject }); In most cases, a promise may be used for an asynchronous operation. However, technically, you can resolve/reject on both synchronous and asynchronous operations.
The keyword await before a function makes the function wait for a promise: let value = await promise; The await keyword can only be used inside an async function. A promise can be returned to another promise, creating a chain of promises. A great example of chaining promises is the Fetch API, which we can use to get a resource and queue a chain of promises to execute when the resource is fetched. 3 days ago - Promises are a comparatively new feature of the JavaScript language that allow you to defer further actions until after a previous action has completed, or respond to its failure. This is useful for setting up a sequence of async operations to work correctly.
Mar 31, 2021 - For instance, this might happen when we start to do a job but then see that everything has already been completed and cached. That’s fine. We immediately have a resolved promise. ... The properties state and result of the Promise object are internal. We can’t directly access them. We can use ... Promises in JavaScript represent processes that are already happening, which can be chained with callback functions. If you are looking to lazily evaluate an expression, consider the arrow function with no arguments: f = () => expression to create the lazily-evaluated expression, and f () to evaluate. Sep 21, 2020 - Get yourself familiar with callbacks and promises. Understand them and use them. Don’t worry about Observables, just yet. All three can factor into your development depending on the situation. That’s it. Hopefully this article smoothen your path to tame the JavaScript promises. Happy coding!
This screencast explains the Javascript Promise pattern at a very high level. Promises are a fundamental tool for modern Javascript development, but it's eas... pixelbits answer is correct and you should always use .then() to access the value of a promise in production code. However, there is a way to access the promise's value directly after it has been resolved by using the following unsupported internal node.js binding: process.binding('util').getPromiseDetails(myPromise)[1] Promise is an important building block for the asynchronous concept in JavaScript. You can create a promise using the constructor function. The constructor accepts an executor function as an argument and returns a promise object. A promise object has two internal properties, state and result. These properties are not code-accessible.
Introduction. Javascript Promises can be challenging to understand. Therefore, I would like to write down the way I understand promises. Understanding Promises. A Promise in short: "Imagine you are a kid.Your mom promises you that she'll get you a new phone next week.". You don't know if you will get that phone until next week. Your mom can really buy you a brand new phone, or she ... Oct 07, 2018 - While that might have been a pleasant ... more to Promises and here is what I have been able to figure out till now. This is going to be a long article, if you would like highlight some parts you can use our extension http://bit.ly/highlights-extension ... When you start working on JavaScript for the first ... We can use fetch in JavaScript to retrieve the data from a certain API endpoint. The fetch in JavaScript is a promise that returns the data if the request is successfully processed. Let's take an example. We have 1st person that's giving the promise and 2nd person that's waiting for the promise to fulfill.
 The Ultimate Guide To Javascript Promises By
The Ultimate Guide To Javascript Promises By
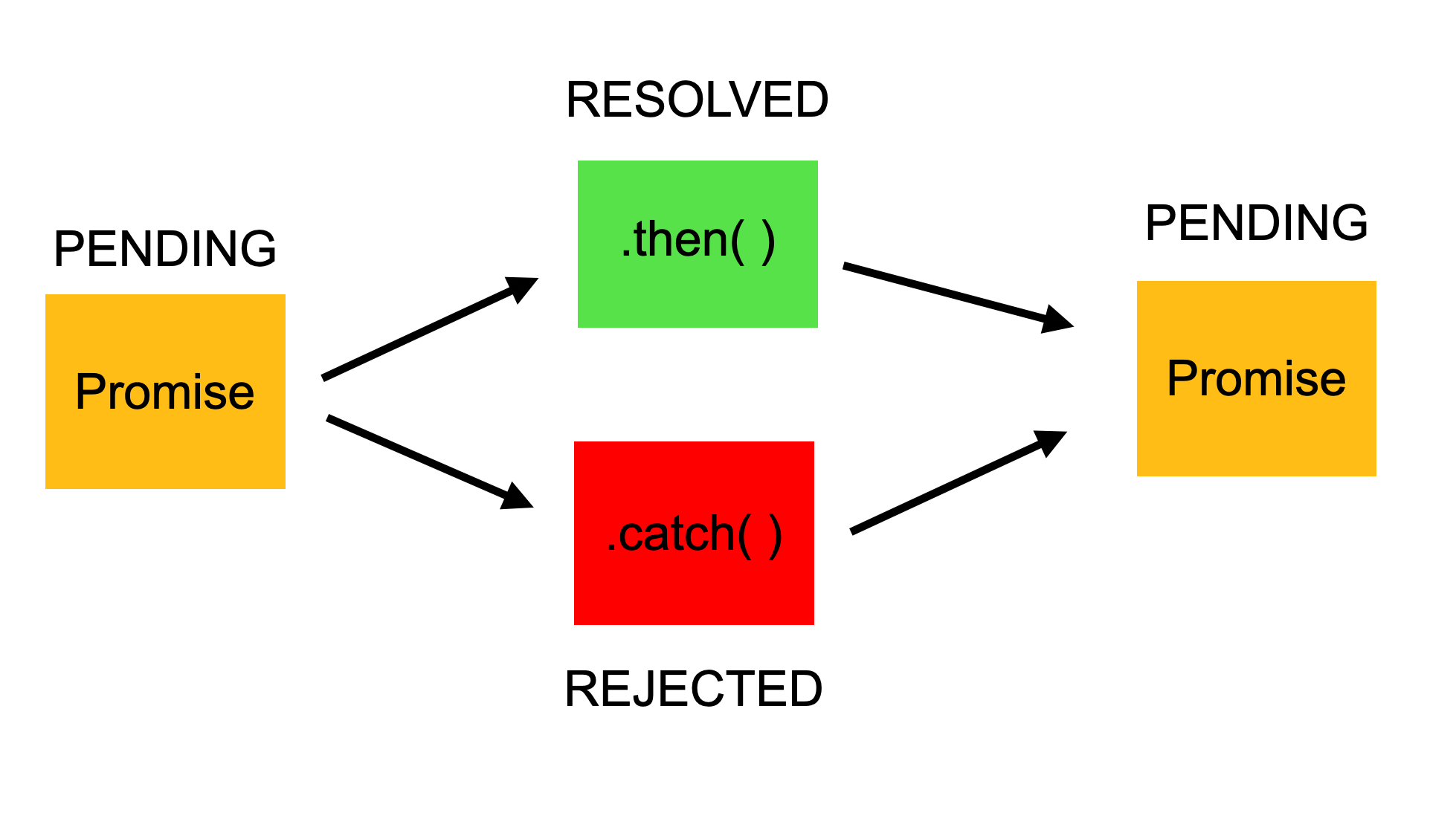 Javascript Promise Tutorial Resolve Reject And Chaining In
Javascript Promise Tutorial Resolve Reject And Chaining In
How To Run Async Javascript Functions In Sequence Or Parallel
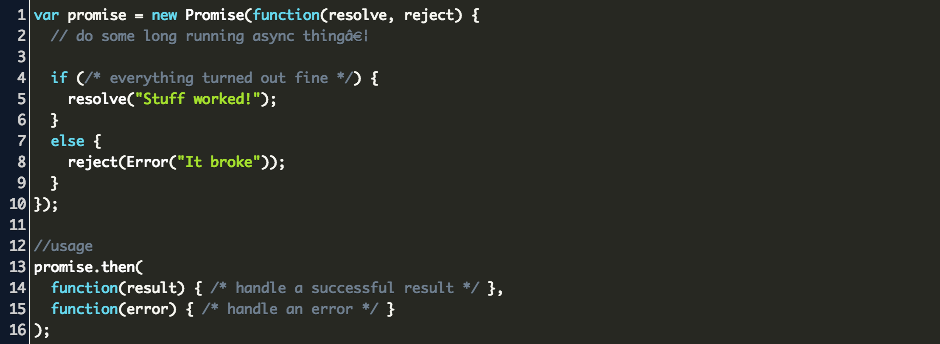 Javascript Promise Code Example
Javascript Promise Code Example
 Asynchronous Javascript Refactoring Callbacks To Promises
Asynchronous Javascript Refactoring Callbacks To Promises
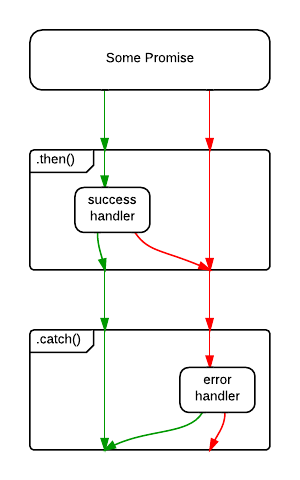 Master The Javascript Interview What Is A Promise By Eric
Master The Javascript Interview What Is A Promise By Eric
 Javascript Promises A Practical Guide Digital Product
Javascript Promises A Practical Guide Digital Product
 Advanced Javascript Node Js Promises Chaining Collections
Advanced Javascript Node Js Promises Chaining Collections
 Async Await In Node Js How To Master It Risingstack
Async Await In Node Js How To Master It Risingstack
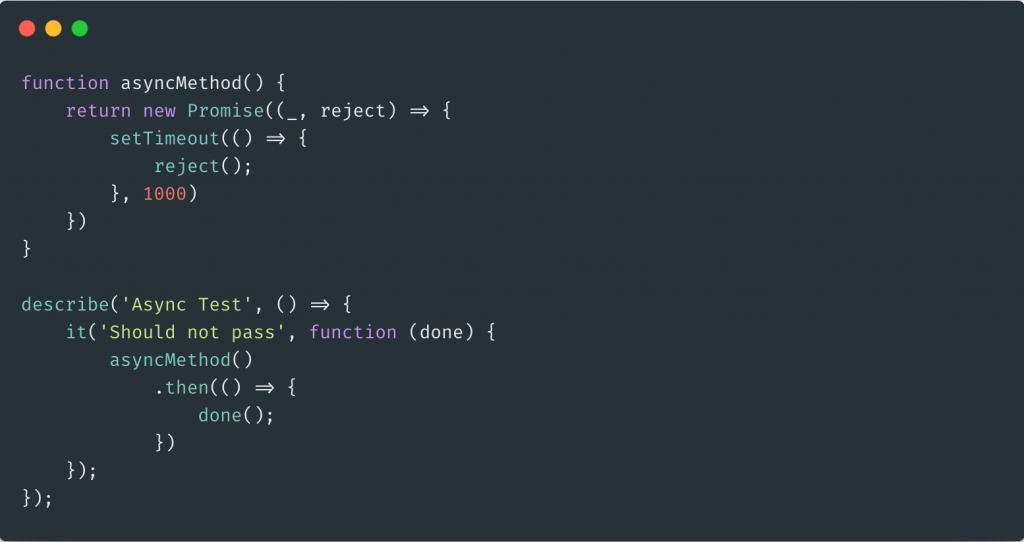 A Helpful Guide To Testing Promises Using Mocha Testim Blog
A Helpful Guide To Testing Promises Using Mocha Testim Blog
 Javascript Promise Resolve Method Geeksforgeeks
Javascript Promise Resolve Method Geeksforgeeks
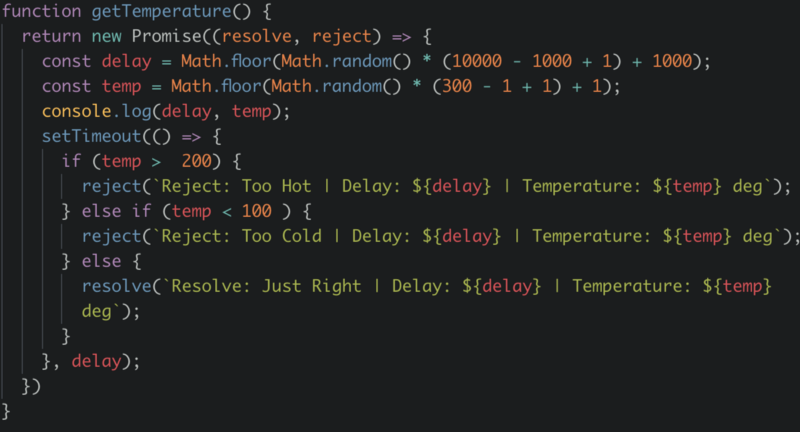 How To Write A Javascript Promise
How To Write A Javascript Promise
 How To Check If A Javascript Promise Has Been Fulfilled
How To Check If A Javascript Promise Has Been Fulfilled
 Introduction To The Javascript Promises Our Code World
Introduction To The Javascript Promises Our Code World
 How To Use Javascript Promises
How To Use Javascript Promises
Faster Async Functions And Promises V8
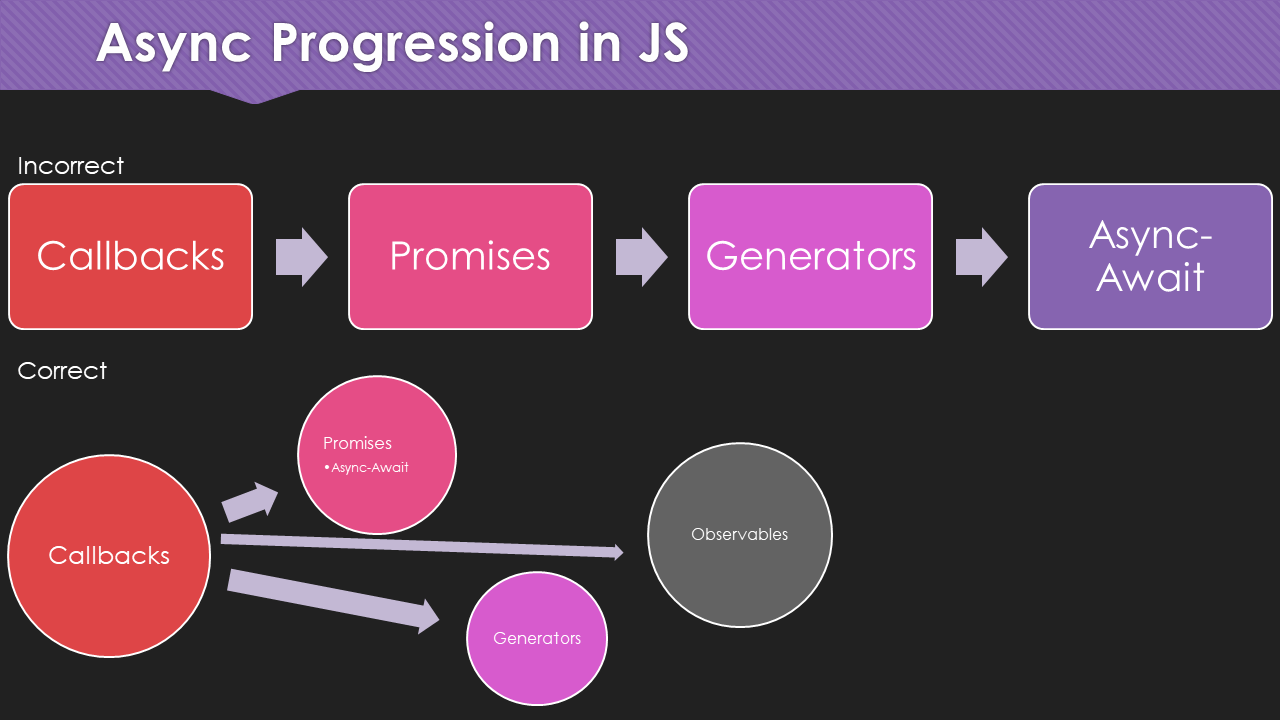 Promises The Definitive Guide Not As Powerful As You Think
Promises The Definitive Guide Not As Powerful As You Think
Javascript Promises Tutorial How To Use Them Ictshore Com
 Javascript Promises While Simultaneous Code Is Simpler To
Javascript Promises While Simultaneous Code Is Simpler To
 Async Await Vs Promises A Guide And Cheat Sheet By Kait
Async Await Vs Promises A Guide And Cheat Sheet By Kait
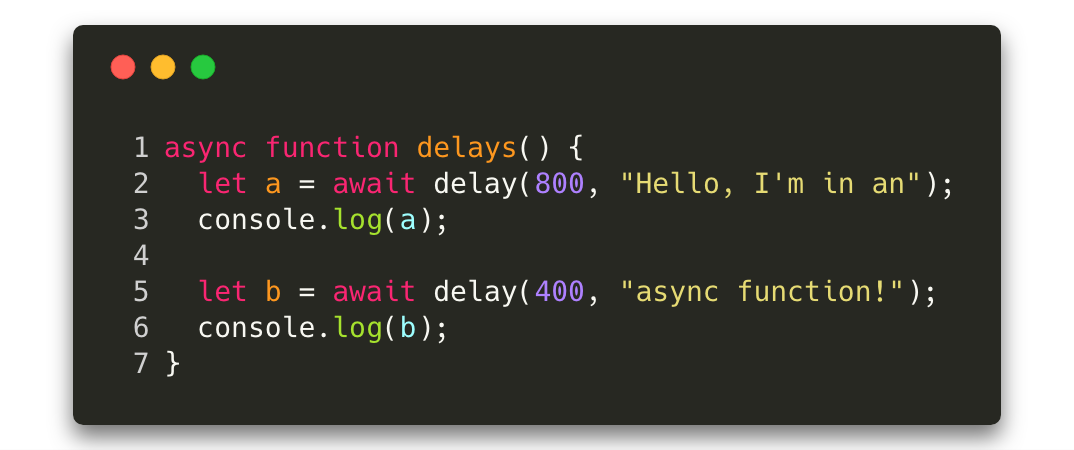 Async Await Vs Coroutines Vs Promises Vs Callbacks By Adam
Async Await Vs Coroutines Vs Promises Vs Callbacks By Adam
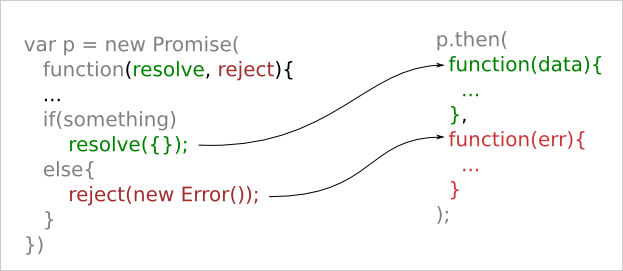 Asynchronous Adventures In Javascript Promises By Benjamin
Asynchronous Adventures In Javascript Promises By Benjamin
 Javascript Asynchronous Method Comparison Callbacks
Javascript Asynchronous Method Comparison Callbacks

0 Response to "27 How To Use Javascript Promises"
Post a Comment