32 Access Control Allow Origin Header Javascript Fetch
The headers it will check for on the response depend on the type of request which the browser has made, but the response must at least have the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header set to an allowed value for the web browser to make the response available to the front end JavaScript which requested it. Did you upload a file to S3 to power your web application or visualization, and now it just won't work? Let's figure out what CORS is and how it prevents you...
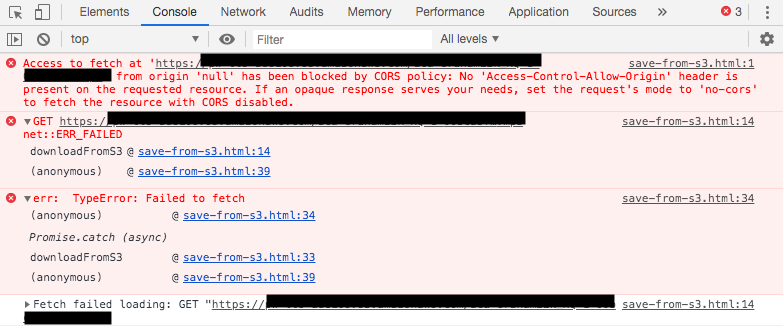
6/5/2017 · No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource. Origin 'null' is therefore not allowed access. If an opaque response serves your needs, set the request's mode to 'no-cors' to fetch the resource with CORS disabled. I set headers for the second fetch:

Access control allow origin header javascript fetch. Access-Control-Allow-Origin can be null, an origin, or * meaning all origins. Notice that you cannot permit a list of origins. Instead, you should check to see if the request's origin is in the list and, if it is, set the value to that origin, otherwise use null. The value of the 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header in the response must not be the wildcard '*' when the request's credentials mode is 'include'. But I already added Access-Control-Allow-Origin, Access-Control-Allow-Credentials and Access-Control-Allow-Headers header to response at server-side (I use sqark java) Please note, if the request body is a string, then Content-Type header is set to text/plain;charset=UTF-8 by default.. But, as we're going to send JSON, we use headers option to send application/json instead, the correct Content-Type for JSON-encoded data.. Sending an image. We can also submit binary data with fetch using Blob or BufferSource objects.. In this example, there's a <canvas ...
Limiting the possible Access-Control-Allow-Origin values to a set of allowed origins requires code on the server side to check the value of the Origin request header, compare that to a list of allowed origins, and then if the Origin value is in the list, to set the Access-Control-Allow-Origin value to the same value as the Origin value. The server must grant access to the requested resource to your remote domain by sending a Access-Control-Allow-Origin response header. These past tips might help too: #280 (comment) This sets a header to allow cross-origin requests for the v2 URI.. Restart the server and go to the web page. If you click on Get v1 you will get blocked by CORS. If you click on Get v2, the request will be allowed.. A response can only have at most one Access-Control-Allow-Origin header. The header can only specify only one domain.
24/7/2021 · Solution 1. try using ”no-cors’ mode. Here is example. fetch ('http://localhost:8080/example', { mode: 'no-cors', method: "post", headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json" }, body: JSON.stringify (ob) }) JavaScript. fetch('http://localhost:8080/example', {. mode: 'no-cors', method: "post", headers: {. 18/6/2020 · The Access-Control-Allow-Origin response header indicates if the response can be shared with requesting code from the given origin or not. Let's explain the process. For example, if Site1 is trying to fetch content from Site2, the Site2 can send an Access-Control-Allow-Origin response header to inform the browser that the page's content is accessible to certain origins. If AllowAnyOrigin is called, the Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *, the wildcard value, is returned. AllowAnyOrigin allows any origin. If the response doesn't include the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header, the cross-origin request fails. Specifically, the browser disallows the request.
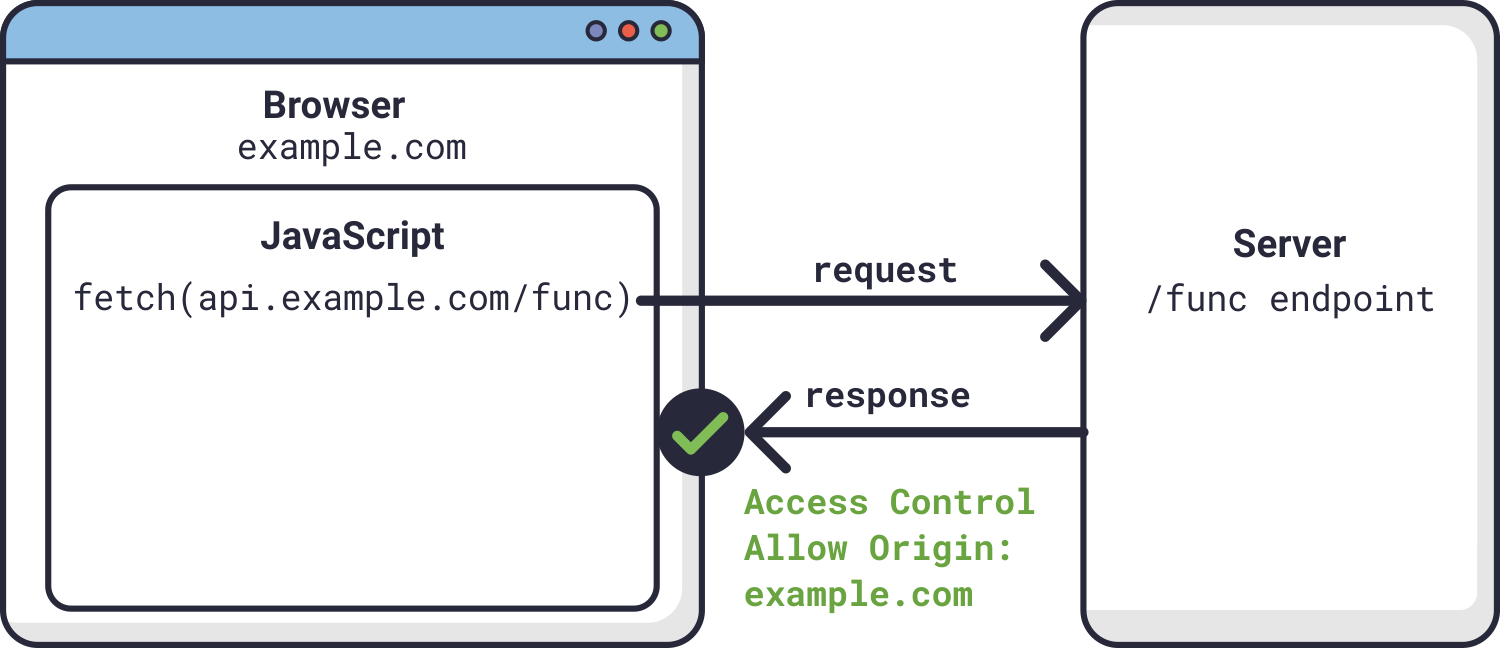
Adds the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header to the response. Passes that response, with that added header, back to the requesting frontend code. The browser then allows the frontend code to access the response, because that response with the Access-Control-Allow-Origin response header is what the browser sees. No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present with JavaScript fetch request. Ask Question Asked 1 month ago. Active 1 month ago. Viewed 150 times ... No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource. If an opaque response serves your needs, set the request's mode to 'no-cors' to fetch the resource with CORS ... i'm using javascript fetch(url, { method : 'GET' , mode : 'cors' , cache : 'no-cache' , credentials : 'same-origin' , headers : myHeaders , referrer : 'no-referrer' , } ... No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource. If an opaque response serves your needs, set the request's mode to 'no-cors' to fetch the ...
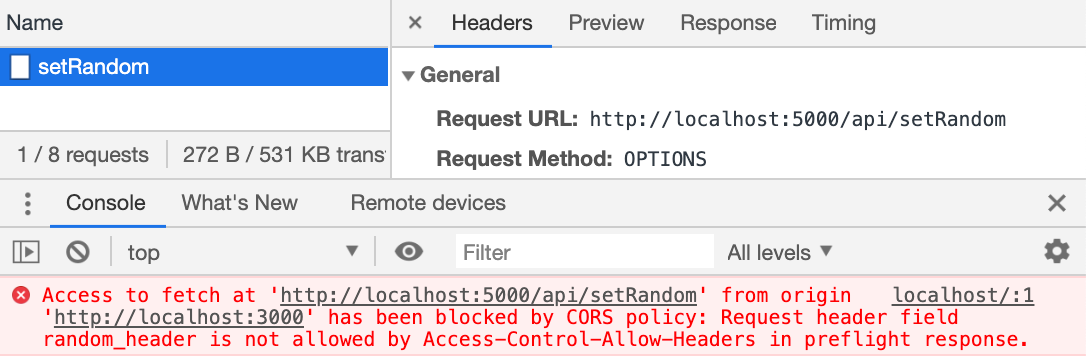
If Access-Control-Allow-Originnot available in response header, browser disallow to use response in your JavaScript code and throw exception at network level. You need to configure corsat your server side. You can fetch request using mode: 'cors'. Access-Control-Request-Method header has the requested method. Access-Control-Request-Headers header provides a comma-separated list of non-simple HTTP-headers. If the server agrees to serve the requests, then it should respond with status 200, without body. The response header Access-Control-Allow-Methods must have the allowed method. The Access-Control-Allow-Headers response header is used in response to a preflight request which includes the Access-Control-Request-Headers to indicate which HTTP headers can be used during the actual request. This header is required if the request has an Access-Control-Request-Headers header.
The protocol that is used. Usually it is the HTTP protocol or its secured version, HTTPS. <hostname>. The domain name of the server (for virtual hosting) or the IP. <port> Optional. TCP port number on which the server is listening. If no port is given, the default port for the service requested (e.g., "80" for an HTTP URL) is implied. Access-Control-Allow-Origin is a CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) header. When Site A tries to fetch content from Site B, Site B can send an Access-Control-Allow-Originresponse header to tell the browser that the content of this page is accessible to certain origins. (An origin is a domain, plus a scheme and port number.) 2/1/2021 · Access-Control-Allow-Origin must be either * or the requesting origin, such as https://javascript.info, to allow it. Access-Control-Allow-Methods must have the allowed method. Access-Control-Allow-Headers must have a list of allowed headers. Additionally, the header Access-Control-Max-Age may specify a number of seconds to cache the permissions.
The Fetch API provides a JavaScript interface for accessing and manipulating parts of the HTTP pipeline, such as requests and responses. It also provides a global fetch () method that provides an easy, logical way to fetch resources asynchronously across the network. This kind of functionality was previously achieved using XMLHttpRequest. Access-Control-Allow-Origin: <origin> | * Access-Control-Allow-Origin specifies either a single origin, which tells browsers to allow that origin to access the resource; or else — for requests without credentials — the " * " wildcard, to tell browsers to allow any origin to access the resource. As you see Access-Control-Allow-Origin "*" allows you to access all resources and webfonts from all domains. We got excellent question from Andreas on adding Access-Control-Allow-Origin on Subdomains. Just add below lines to .htaccess file and we should be good.
What is the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header? Access-Control-Allow-Origin is a CORS header. CORS, or Cross Origin Resource Sharing, is a mechanism for browsers to let a site running at origin A to request resources from origin B. Cross-Origin Resource Sharing ( CORS (en-US)) is a mechanism that uses additional HTTP (en-US) headers to tell a browser to let a web application running at one origin (domain) have permission to access selected resources from a server at a different origin. A web application makes a cross-origin HTTP request when it requests a resource that ... To allow any site to make CORS requests without using the * wildcard (for example, to enable credentials), your server must read the value of the request's Origin header and use that value to set Access-Control-Allow-Origin, and must also set a Vary: Origin header to indicate that some headers are being set dynamically depending on the origin.
"include" - always send, requires Access-Control-Allow-Credentials from cross-origin server in order for JavaScript to access the response, that was covered in the chapter Fetch: Cross-Origin Requests, "omit" - never send, even for same-origin requests. Cross-Origin Resource Sharing. CORS is a mechanism that defines a procedure in which the browser and the web server interact to determine whether to allow a web page to access a resource from different origin. Figure 2. Cross domain ajax request. When you do a cross-origin request, the browser sends Origin header with the current domain value. using fetch in react no-cors'. javascript get fetch req example. cors fetch js. access-control-allow-origin fetch api. No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource. If an opaque response serves your needs, set the request's mode to 'no-cors' to fetch the resource with CORS disabled.
In web apps, browsers work with a SameSite policy that prevents a cross-domain XMLHttpRequest or Fetch request from being made. ... you will learn about cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) and the role of the "Allow Access Control Origin" header. With the knowledge gained in this guide, you will find it easy to resolve issues relating to CORS.
 Cors Access Control Allow Origin Solved
Cors Access Control Allow Origin Solved
 Http Headers Access Control Allow Credentials Geeksforgeeks
Http Headers Access Control Allow Credentials Geeksforgeeks
 Cors Cross Origin Resource Sharing
Cors Cross Origin Resource Sharing
 Enabling Cors In Haproxy Haproxy Technologies
Enabling Cors In Haproxy Haproxy Technologies
 Understanding Cross Origin Resource Sharing Cors Dev
Understanding Cross Origin Resource Sharing Cors Dev
 Cross Origin Resource Sharing Access Control Allow Origin
Cross Origin Resource Sharing Access Control Allow Origin
 10 Resolve Cors Issue In Angular Mean Stack Codez Up
10 Resolve Cors Issue In Angular Mean Stack Codez Up
 Handling Cors Cross Origin Resource Sharing In Web Apps
Handling Cors Cross Origin Resource Sharing In Web Apps
 No Access Control Allow Origin Header Is Present On The
No Access Control Allow Origin Header Is Present On The
 The Access Control Allow Origin Header Has A Value Issue
The Access Control Allow Origin Header Has A Value Issue
 Cross Origin Resource Sharing Access Control Allow Origin
Cross Origin Resource Sharing Access Control Allow Origin
 Handle Amazon S3 Download No Access Control Allow Origin
Handle Amazon S3 Download No Access Control Allow Origin
![]() Solution Access To Fetch Has Been Blocked By Cors Policy
Solution Access To Fetch Has Been Blocked By Cors Policy
 Understanding Cross Origin Resource Sharing Cors Miguel
Understanding Cross Origin Resource Sharing Cors Miguel
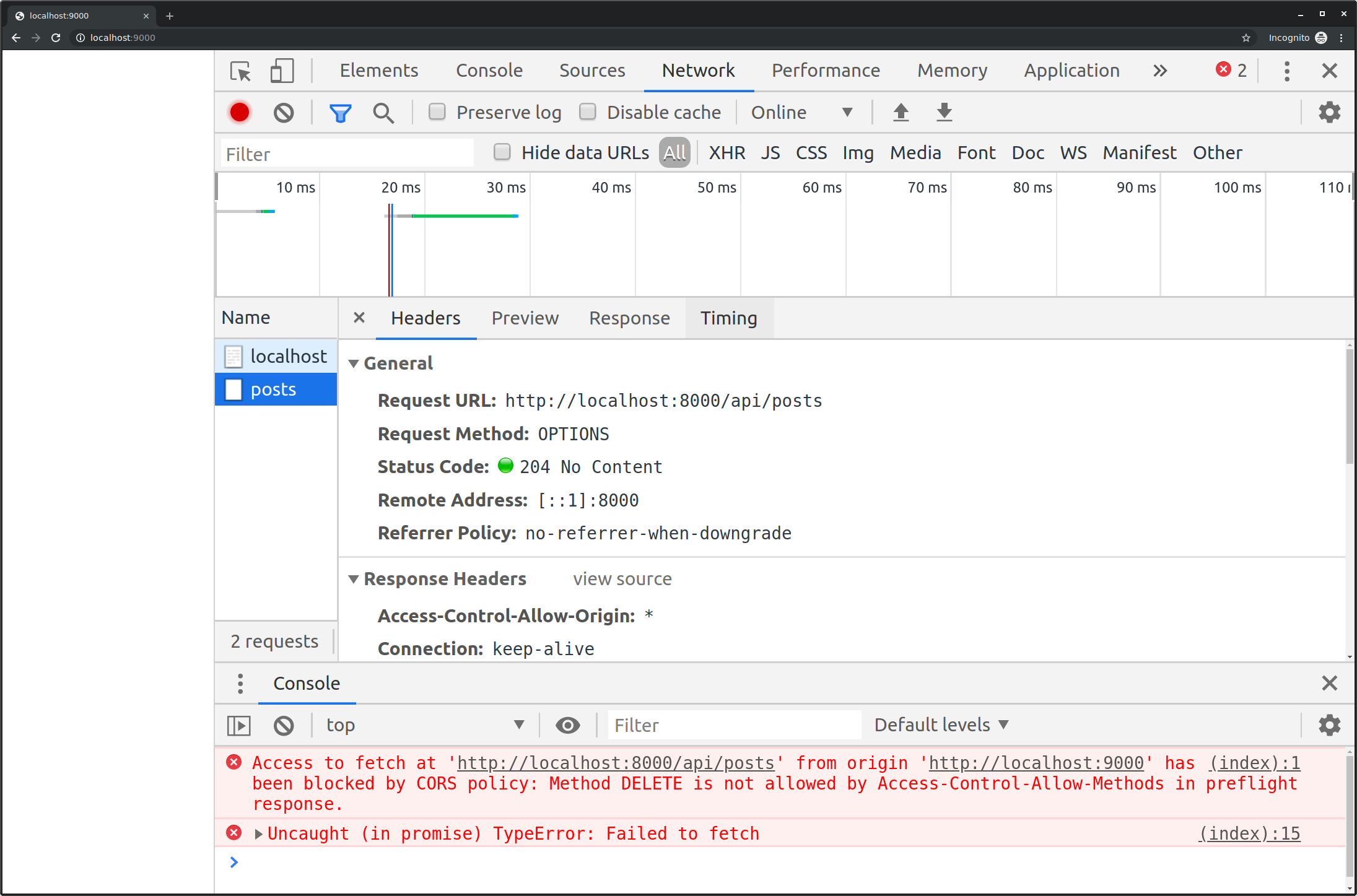
 Why Does My Javascript Code Receive A No 39 Access Control
Why Does My Javascript Code Receive A No 39 Access Control
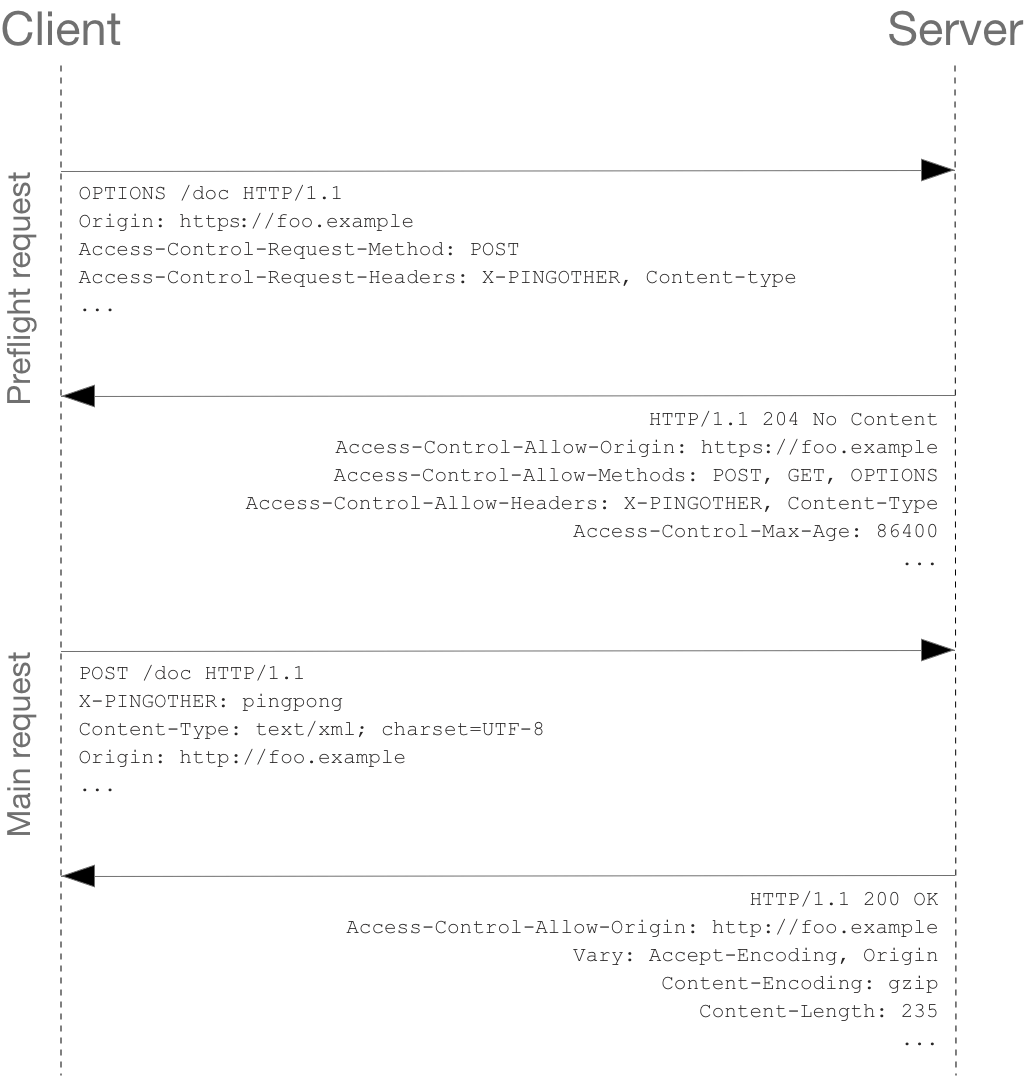 Cross Origin Resource Sharing Cors Http Mdn
Cross Origin Resource Sharing Cors Http Mdn

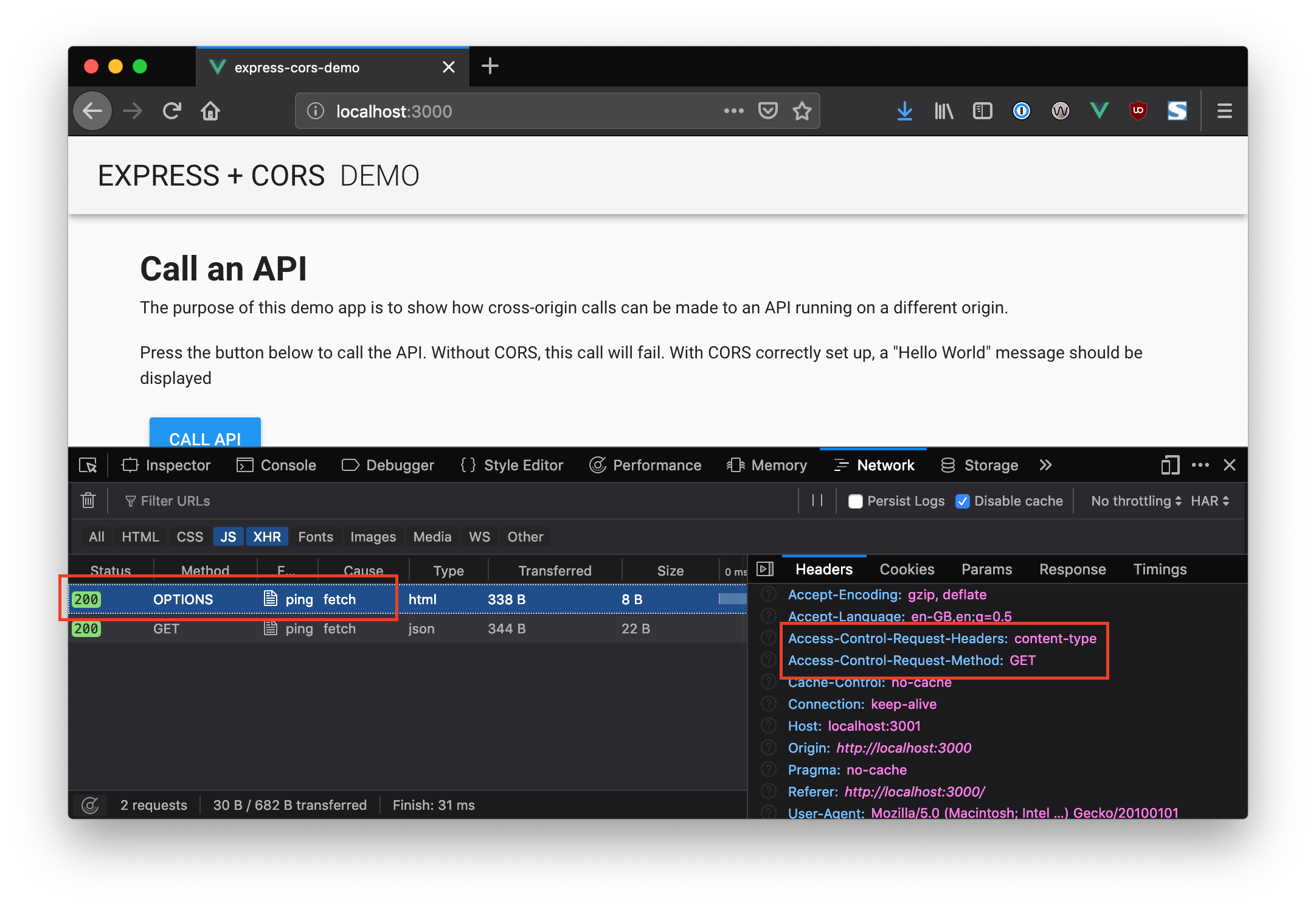
 Fetch Api Cors Request Throws Error No Access Control Allow
Fetch Api Cors Request Throws Error No Access Control Allow
 Get Request Error Might Be Related To Cross Origin Resource
Get Request Error Might Be Related To Cross Origin Resource
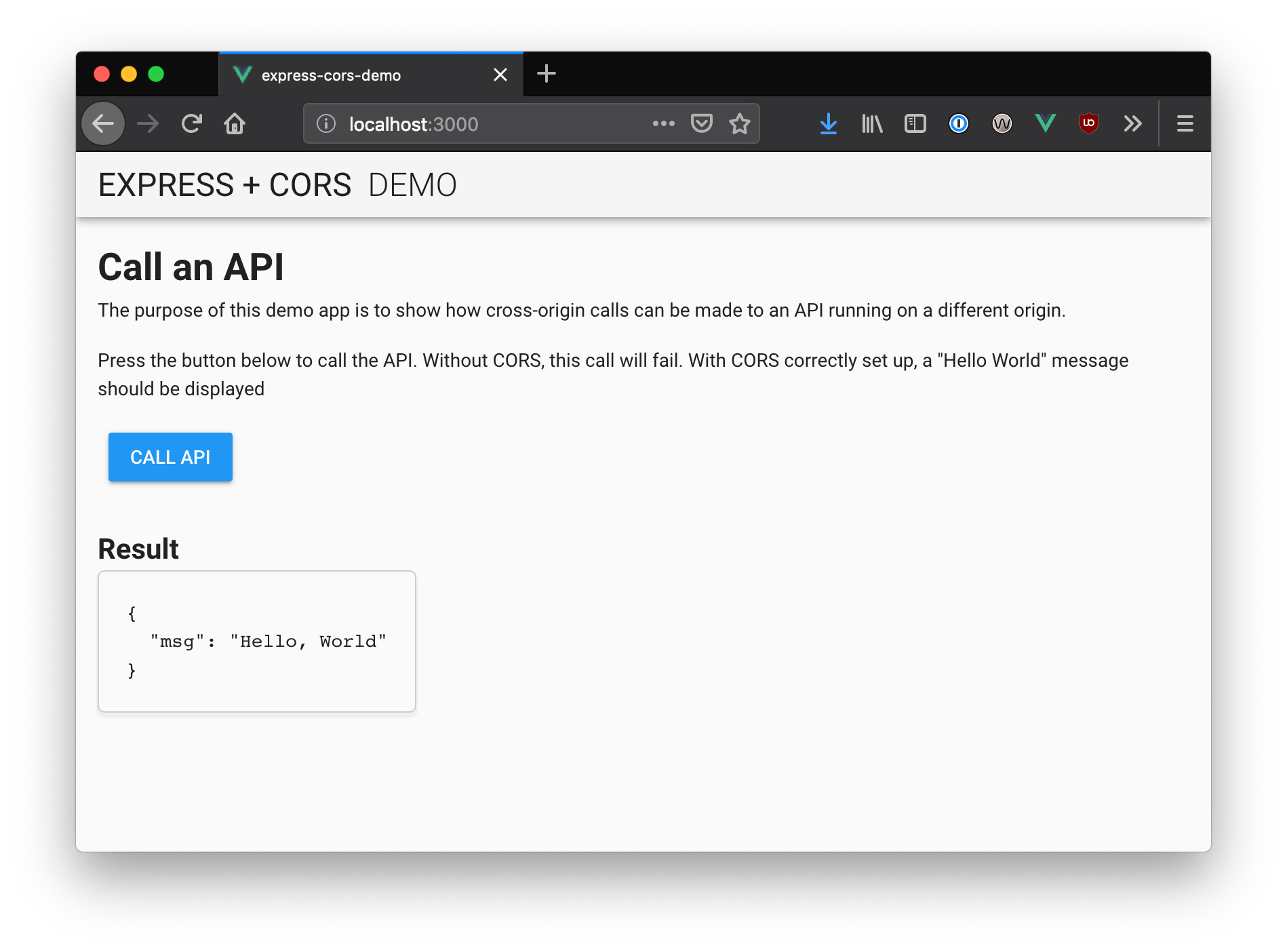
 Cors Cloudflare For Teams Documentation
Cors Cloudflare For Teams Documentation
 Get Request Error Might Be Related To Cross Origin Resource
Get Request Error Might Be Related To Cross Origin Resource
 Cross Origin Resource Sharing Cors Http Mdn
Cross Origin Resource Sharing Cors Http Mdn
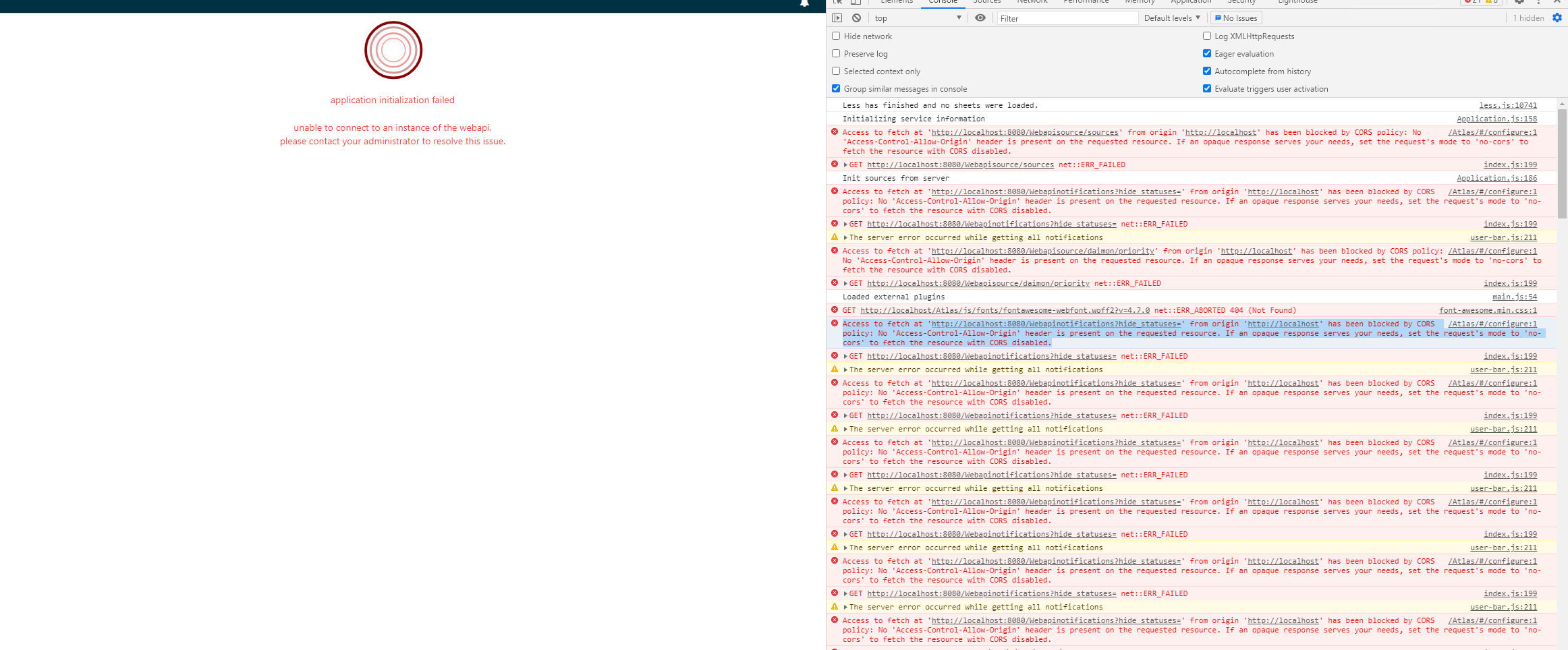 Cors Error Atlas Implementers Ohdsi Forums
Cors Error Atlas Implementers Ohdsi Forums
 Cors And Fiori Ui5 Everything You Need To Know Sap Blogs
Cors And Fiori Ui5 Everything You Need To Know Sap Blogs
 Trying To Fetch Response From Goodreads Api The
Trying To Fetch Response From Goodreads Api The
 Get Call Failing Access Control Allow Origin Issue 652
Get Call Failing Access Control Allow Origin Issue 652
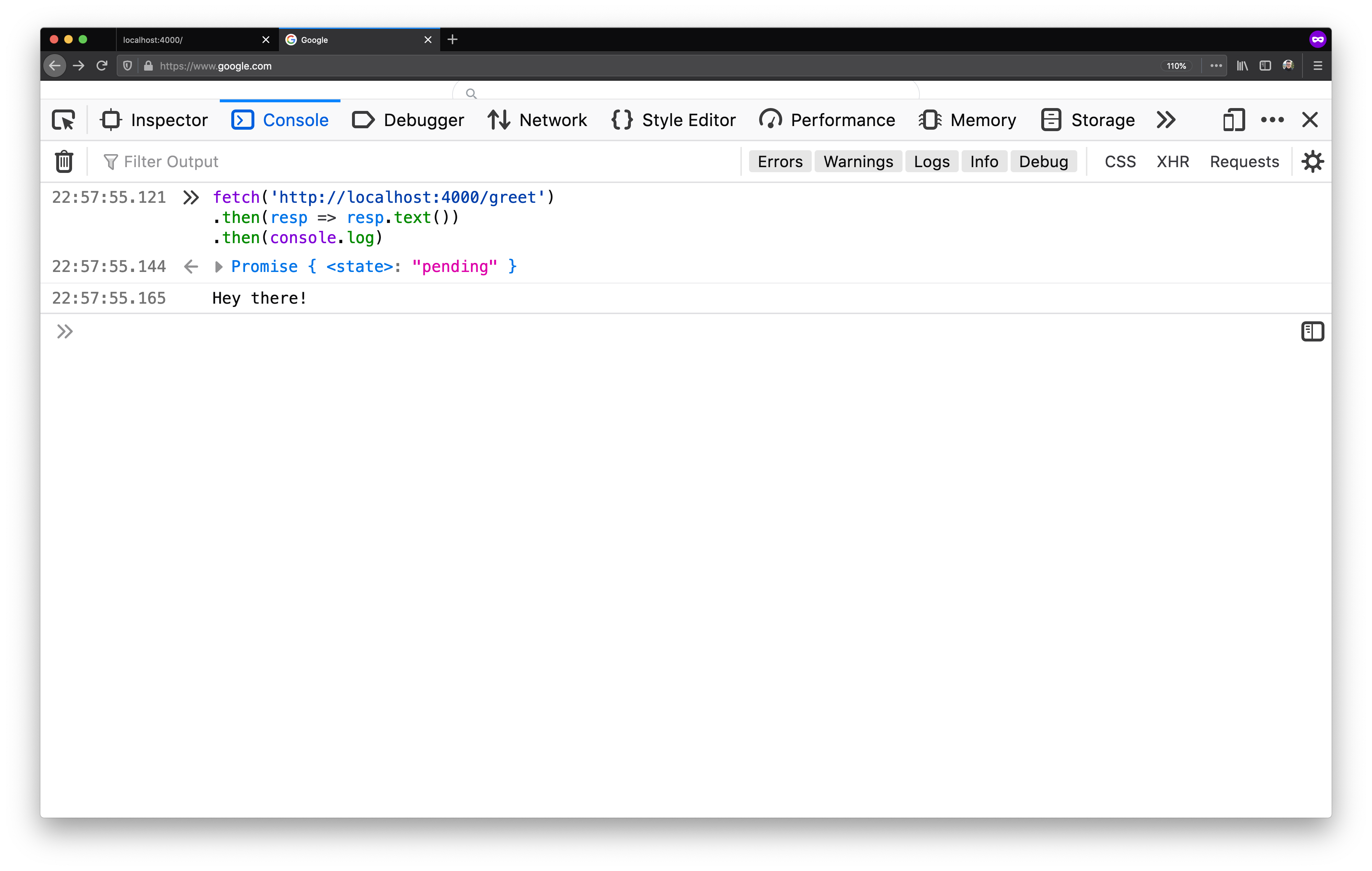 Deep Dive In Cors History How It Works And Best Practices
Deep Dive In Cors History How It Works And Best Practices


0 Response to "32 Access Control Allow Origin Header Javascript Fetch"
Post a Comment