21 Javascript History Back Url
Go to your profile, put history.back() in the console, and when arriving this page again, try document.referrer, it doesn't return the URL of your profile. – Alejandro Veltri May 26 '15 at 18:20 That's right, the idea of history.back() is to work just like the Back button. The JavaScript browser history API lets you go to a new URL. You can use the following methods to navigate to a new URL: Assigning a new value to window.location. Using the window.assign () method.
 Javascript History Back Method Stack Overflow
Javascript History Back Method Stack Overflow
Note: Calling history.pushState() or history.replaceState() won't trigger a popstate event. The popstate event is only triggered by performing a browser action, such as clicking on the back button (or calling history.back() in JavaScript), when navigating between two history entries for the same document.

Javascript history back url. This method can be used with '-1' as the delta value to go back one page in history. The onclick event can be specified with the method to go back one page in history. Syntax: history.ho(number\URL) Example 2: This example uses window.history.go() method to redirect the browser into previous page. The History.replaceState () method modifies the current history entry, replacing it with the stateObj, title, and URL passed in the method parameters. This method is particularly useful when you want to update the state object or URL of the current history entry in response to some user action. The benefit of using the window.location.replace function is that the current URL isn't added to the visitor's navigation history, whereas the popular JavaScript redirect window.location.href would. That could cause a visitor to get stuck in back-button loops. Therefore, don't use it when redirecting visitors immediately to another URL.
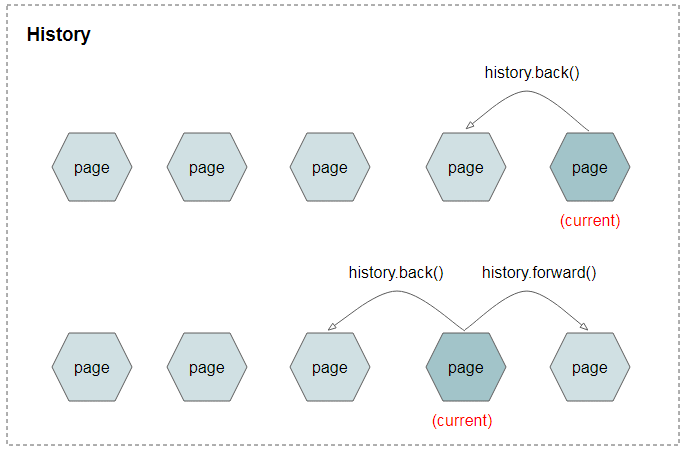
var element = document.getElementById('back-link'); // Provide a standard href to facilitate standard browser features such as // - Hover to see link // - Right click and copy link // - Right click and open in new tab element.setAttribute('href', document.referrer); // We can't let the browser use the above href for navigation. The back() method loads the previous URL in the history list. This is the same as clicking the "Back button" in your browser. Note: This method will not work if the previous page does not exist in the history list. Tip: To load the next URL in the history list, use the history.forward() method. Call history.back () and then window.close (). If the browser is able to go back in history it won't be able to get to the next statement. If it's not able to go back, it'll close the window. However, please note that if the page has been reached by typing a url, then firefox wont allow the script to close the window.
The URL location can be determined with document.location (document.location.search and document.location.hash return the parameters and hash name respectively). The historic state object set by... The HTML5 History API gives developers the ability to modify a website's URL without a full page refresh. This is particularly useful for loading portions of a page with JavaScript, such that the content is significantly different and warrants a new URL. Here's an example. Let's say a person navigates from the homepage of a site to the ... The new history entry's URL is given by this parameter. Note that the browser won't attempt to load this URL after a call to pushState (), but it might attempt to load the URL later, for instance after the user restarts the browser. The new URL does not need to be absolute; if it's relative, it's resolved relative to the current URL.
The assign method loads the resource at the new URL and preserves the previous entry in the browser's navigation history. This means the user can hit the back button and go to the original page. The replace method does the same thing, except the original or 'current' resource is not retained in the browser's history. If the user copies or bookmarks a stateful URL and visits it later, your back-end can be configured to interpret such a URL and jump the user right to the correct page and/or state. In this article, I'll cover the client-side use of the History API, so make sure you set up your server to work with the new URLs. The history is a JavaScript object available in window object, which contains details about the browser session history of the tab. The list of URL's you have visited will be stored, top on each…
Redirect (Go) back to Previous Page without Refresh using JavaScript. The HTML Anchor Link in Page 2 is assigned an OnClick event handler and when clicked, it is redirected to the Previous Page using history.back function in JavaScript. The history.back is an in-built JavaScript function which belongs to the JavaScript window object. T he History API is one of those JavaScript techniques that every web developer needs to know cold. Without it, a single click of the Back button will jump straight out of your application. You ... Fortunately for us, the functionality behind the back and forward buttons is provided to us by the browser's history object. To go back to the previous page, we can simple call history.back() in our Javascript code and the browser will go "one element back" in our history. This way, the previous element will now be marked as the ...
26/2/2018 · To load the next URL in the history list, use the history.back() method in JavaScript.ExampleYou can try to run the following code to load next URL − Live De ... The JavaScript history back method finds the URL of the previous page and loads it. Basically, JavaScript back method does the exact same function as pressing the browsers BACK button. Let's see an example on how to use history.back () correctly: If you want to go to the previous page without knowing the url, you could use the new History api. history.back (); //Go to the previous page history.forward (); //Go to the next page in the stack history.go (index); //Where index could be 1, -1, 56, etc. But you can't manipulate the content of the history stack on browser that doesn't support ...
30/9/2019 · Method 2: Using the history.back() method: The back() method of the window.history object is used to go back to the previous page in the current session history. In case there is no previous page, this method call does nothing. The onclick event can be specified with this method to go back one page in history. Syntax: window.history.back() Example: Name History.back( ): return to the previous URL — JavaScript 1.0 Synopsis history.back( ) Description back( ) causes the window or frame to which the History object belongs to revisit … - Selection from JavaScript: The Definitive Guide, 5th Edition [Book] To manipulate the history stack, you use the history object which is a property of the window object: window .history. Code language: JavaScript (javascript) For the security reason, it's not possible to query the pages that a user have visited. However, you can use the history object to navigate back and forth without knowing the exact URL.
Call history.back () and then window.close (). If the browser is able to go back in history it won't be able to get to the next statement. If it's not able to go back, it'll close the window. However, please note that if the page has been reached by typing a url, then firefox wont allow the script to close the window. The popstate event will be triggered by doing a browser action such as a click on the back or forward button (or calling history.back () or history.forward () in JavaScript). Browsers tend to handle the popstate event differently on page load. Chrome (prior to v34) and Safari always emit a popstate event on page load, but Firefox doesn't. In one page list of records display.When I click on edit button of that record it redirect to new page and again when I click on back button it will redirect to my first page.Now when I am redirecting to first page I want previous page URL i.e second page URL using javascript... i.e I want previous page URL using javascript
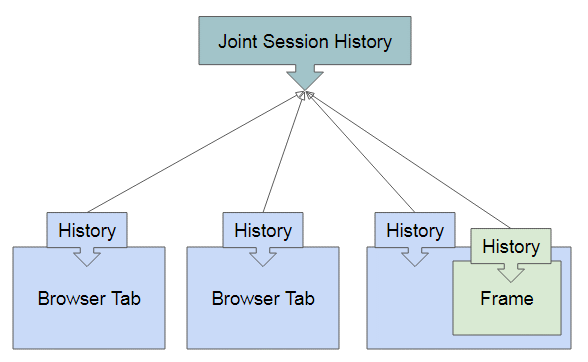
The DOM Window object provides access to the browser's session history (not to be confused for WebExtensions history) through the history object. It exposes useful methods and properties that let you navigate back and forth through the user's history, and manipulate the contents of the history stack. For example, if you call history.go (-3) it will take the user back three pages. Similarly, calling history.go (3) will take the user three pages forward. Calling history.go (-1) and history.go (1)... The "Go Back" button below moves one step back to the browsing history and the "Go Forward" button moves one step forward to the browsing history. A third method, go (), takes an integer argument and can skip any number of pages forward or backward in the history list. history.go (-2) //go back 2, like clicking the back button twice.
Window History Back. The history.back() method loads the previous URL in the history list. This is the same as clicking the Back button in the browser.
 A Simple Introduction To The History Api In Javascript By
A Simple Introduction To The History Api In Javascript By
 History Api Javascript Api For
History Api Javascript Api For
 Using History Js With Ajax Carlo Fontanos
Using History Js With Ajax Carlo Fontanos
 Javascript History Back Code Example
Javascript History Back Code Example
 Javascript 1 Javascript 1 Introduction And Dom Dr Kevin
Javascript 1 Javascript 1 Introduction And Dom Dr Kevin
 Vanilla Javascript History Api
Vanilla Javascript History Api
Navigate To A Url Without Adding An Entry In The History
 Reflected Xss In A Javascript Url With Some Characters Blocked Video Solution Audio
Reflected Xss In A Javascript Url With Some Characters Blocked Video Solution Audio
 Blog Post How To Modify Current Url Without Reloading Or
Blog Post How To Modify Current Url Without Reloading Or
 View And Delete Browsing History In Chrome Firefox And Vivaldi
View And Delete Browsing History In Chrome Firefox And Vivaldi
 Rejection Issue Querying Nih Via Api Stack Overflow
Rejection Issue Querying Nih Via Api Stack Overflow
 Latest Code Programming Help Redirect Url Using Javascript
Latest Code Programming Help Redirect Url Using Javascript
 A Simple Introduction To The History Api In Javascript By
A Simple Introduction To The History Api In Javascript By
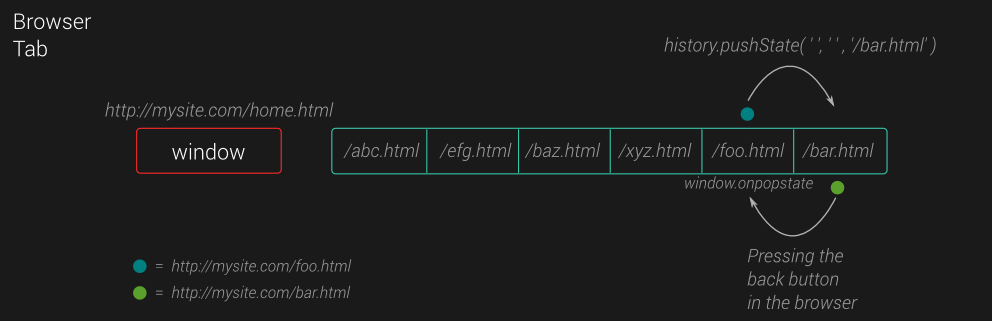 Dynamically Change Url Using Push And Pop State By Sean
Dynamically Change Url Using Push And Pop State By Sean
 A Simple Introduction To The History Api In Javascript By
A Simple Introduction To The History Api In Javascript By



0 Response to "21 Javascript History Back Url"
Post a Comment