33 Javascript Promise Catch Error
In order to handle errors, we can add catch at last after all then callback or we can add catch after then callback. Above example of chaining promises and handling errors with a single catch at last. The reject can only be used with a Javascript promise but throw unlike reject can be used to create and throw user-defined exceptions in any try-catch block and not only the ones with promises. If you use Promise.reject () in a try-catch block which is not associated with a promise, UnhandledPromiseRejectionWarning error will pop up. Program 1:
 Asynchronous Javascript With Promises Amp Async Await In
Asynchronous Javascript With Promises Amp Async Await In
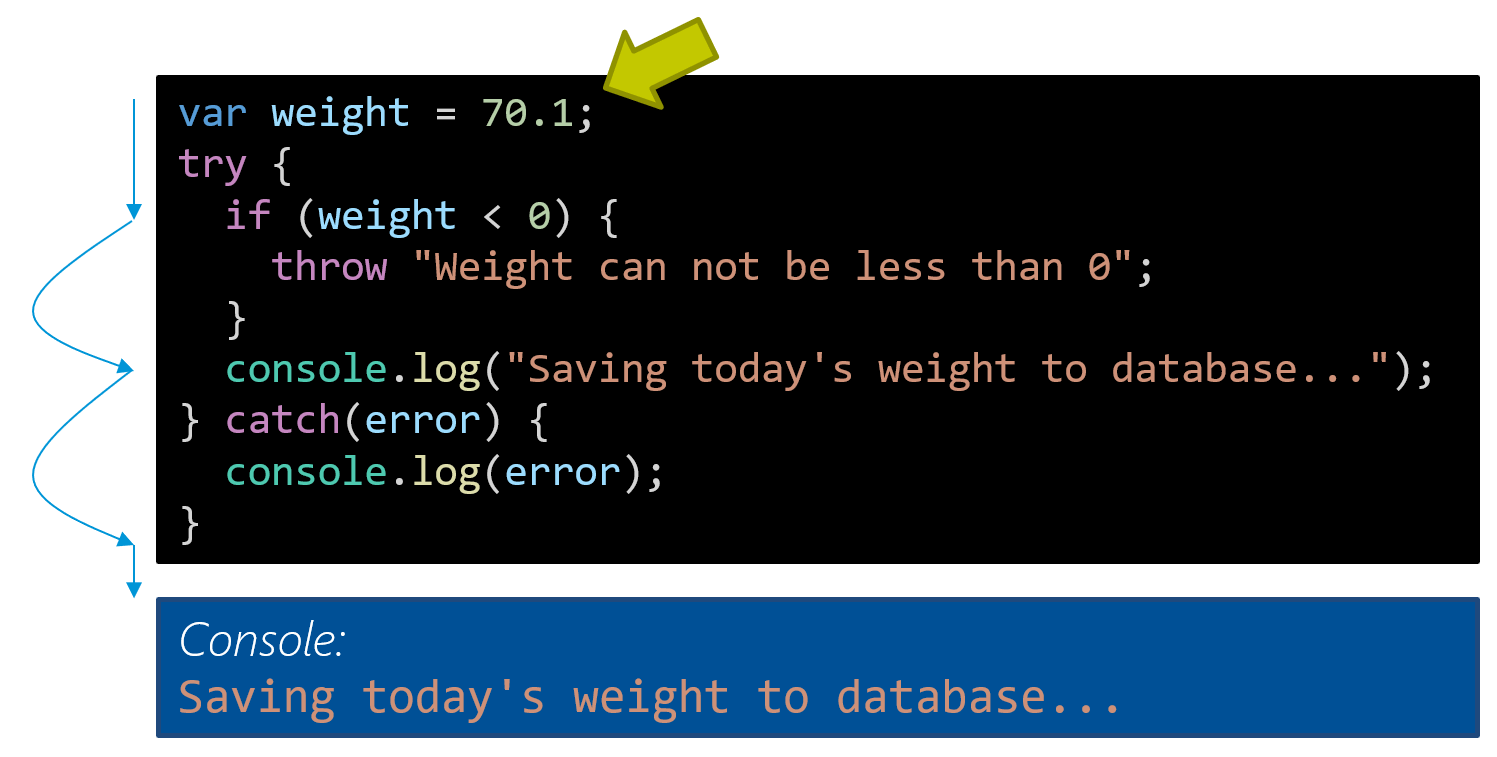
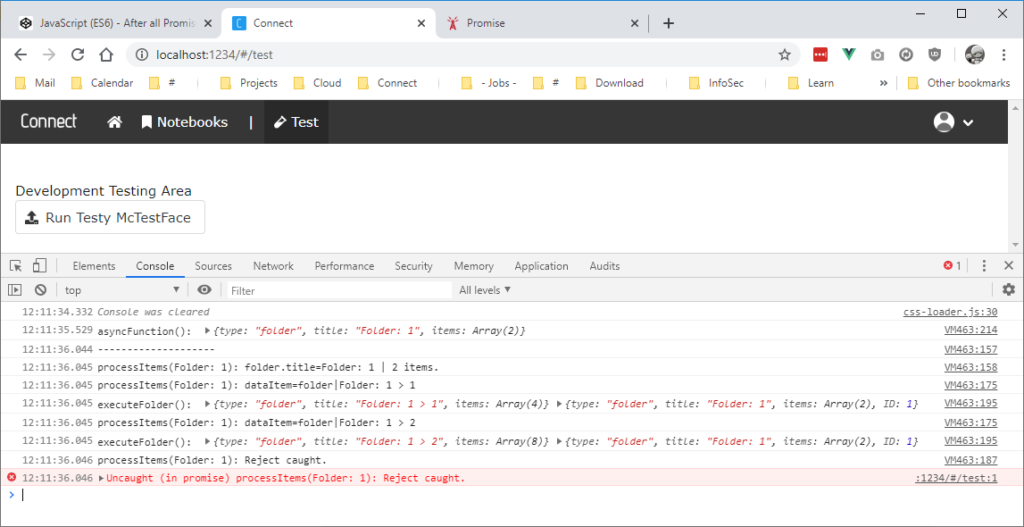
14/2/2018 · // an error thrown inside the promise, triggers .catch() function example {return new Promise ((resolve, reject) => {throw new Error ("test error inside"); resolve (true);});} try {example (). then (r => console. log (`.then(${r})`)). catch (e => console. error (`.catch(${e})`));} catch (e) {console. error (`try/catch(${e})`);} // > Output: // // .catch(Error: test error inside)

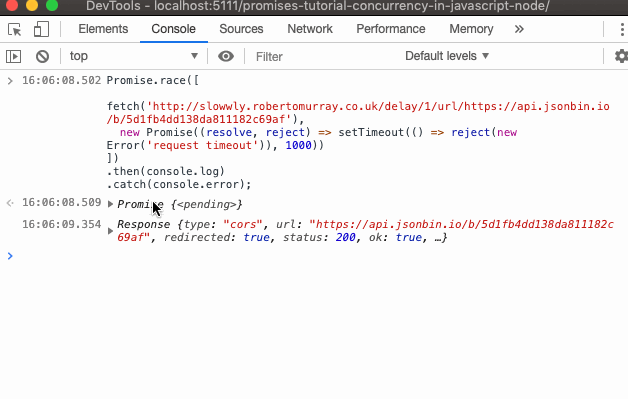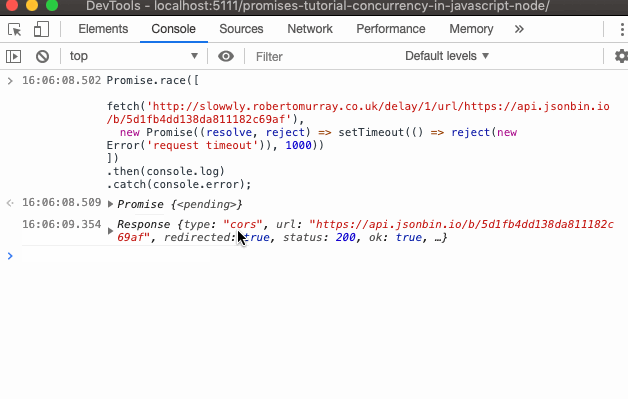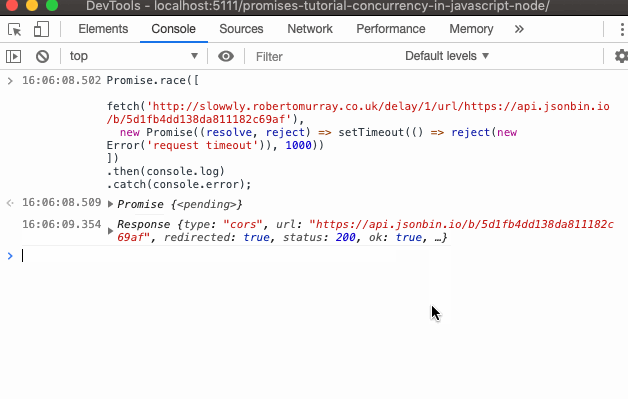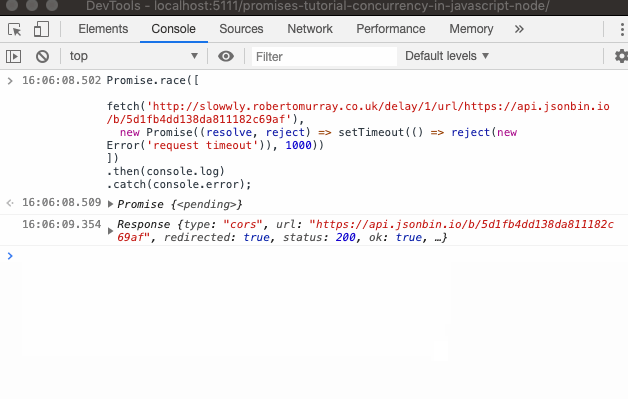
Javascript promise catch error. JavaScript Promise Error Handling Promise chains are good at error handling. When a promise rejects, the control jumps to the closest rejection function. Errors thrown from promises are handled by the second parameter (reject) passed to then () or by the handler passed to catch() Promise.race (promises) - waits for the first promise to settle, and its result/error becomes the outcome. Promise.any (promises) (recently added method) - waits for the first promise to fulfill, and its result becomes the outcome. If all of the given promises are rejected, AggregateError becomes the error of Promise.any. Promise でのエラーハンドリング. 非同期アクションは失敗する可能性があります: エラーの場合、対応する promise は reject されます。. 例えば、リモートサーバが利用不可で fetch が失敗する場合です。. エラー (拒否/reject)を扱うには .catch を使います。. promise ...
21/8/2014 · You may have expected the error handler onRejected in handleData to catch the exception that was thrown from calling the undefined function fetchMoreData. However, that is not the case. The onRejected function in handleData only handles errors or rejected promises returned from the preceding promise, in this case, the promise … It builds on promises, e.g. doSomething() is the same function as before. You can read more about the syntax here. Promises solve a fundamental flaw with the callback pyramid of doom, by catching all errors, even thrown exceptions and programming errors. This is essential for functional composition of asynchronous operations. Javascript Promises are quite simple to start with, but confusions arise when Promises are chained. This tutorial focuses on the return values of then() and catch(), which are crucial to understanding the process.
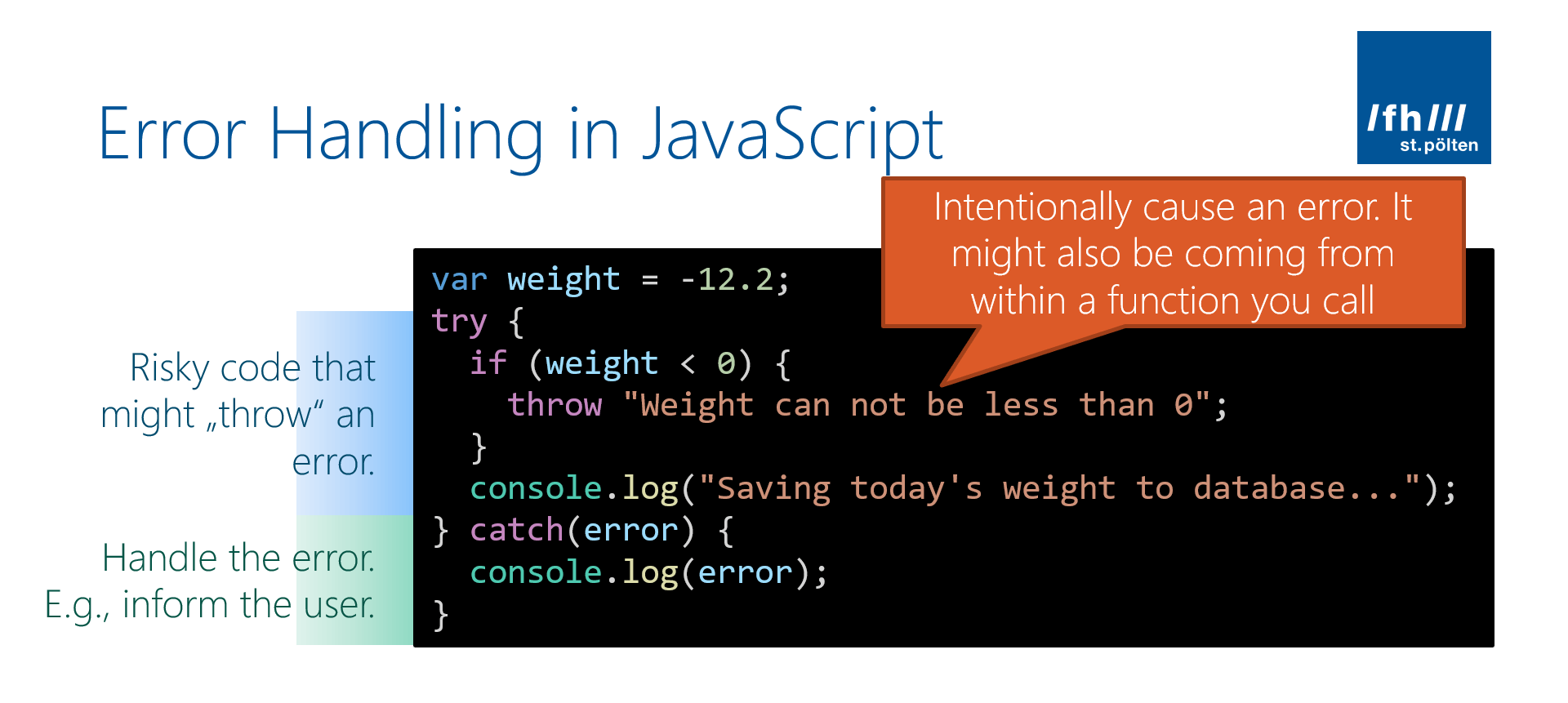
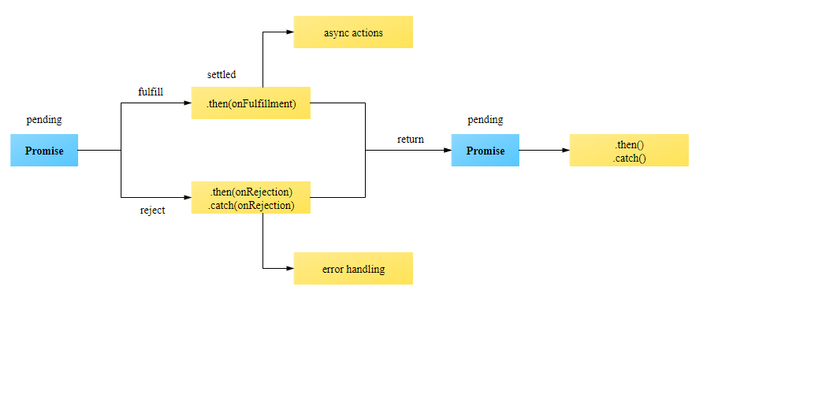
The Promise returned by catch() is rejected if onRejected throws an error or returns a Promise which is itself rejected; otherwise, it is resolved. Return value Internally calls Promise.prototype.then on the object upon which it was called, passing the parameters undefined and the received onRejected handler. Inside the promise, the catch () method will catch the error caused by the throw statement and reject (). If an error occurs and you don't have the catch () method, the JavaScript engine issues a runtime error and stops the program. Was this tutorial helpful ? Error handling in async/await causes a lot of confusion. There are numerous patterns for handling errors in async functions, and even experienced developers sometimes ...
The benefit is you should be able to handle errors where you want, rather than having to catch them at every step along the way like errors in node.js-style callbacks - e.g. function (err, result) {} . Errors in that world are often swallowed up, too - because they're not exceptions, they're just a parameter passed to a callback. Promises in JavaScript are an object representation of an asynchronous operation. Promises are like a placeholder for some value that may not have been computed yet. If the async operation failed, JavaScript will reject the promise. The catch () function tells JavaScript what function to call if the promise is rejected: JavaScript catches adddlert as an error, and executes the catch code to handle it. JavaScript try and catch The try statement allows you to define a block of code to be tested for errors while it is being executed.
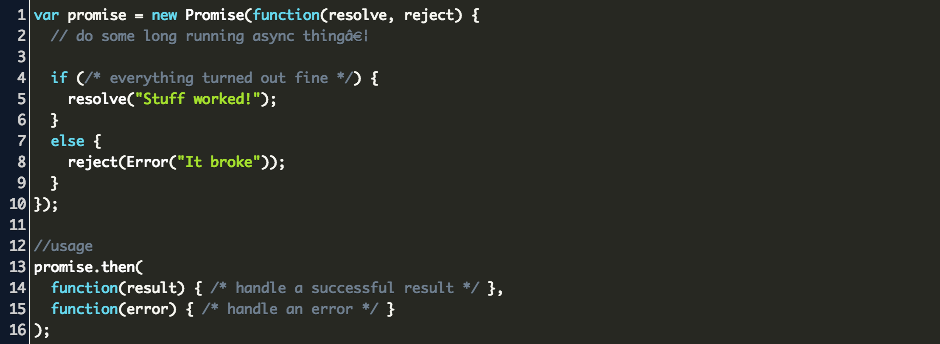
Promise Consumers. Promises can be consumed by registering functions using .then and .catch methods. then() then() is invoked when a promise is either resolved or rejected. Parameters: then() method takes two functions as parameters. 9/7/2021 · Similarly to the rest of Javascript, you can use built-in, Promise-specific methods called .catch() and .finally(). A Promise executes immediately and either resolves to a single value, or rejects... Not using try/catch with async/await could result to (node:11) DeprecationWarning: Unhandled promise rejections are deprecated. In the future, promise rejections that are not handled will terminate the Node.js process with a non-zero exit code. */. Tagged with javascript, webdev, asyncawait, promises.
How to handle Error in JavaScript Promise.all such that it doesn't stop execution of other promises if one fails ? Well the answer is a simple one. You need to handle error or add a catch block to each of the promises in the array so that it doesn't break the Promise.all execution. Now we have the classic problem, thisThrows returns a rejecting promise, so the regular try...catch is not able to catch the error. As thisThrows () is async, so when we call it, it dispatches a promise, the code does not wait, so the finally block is executed first and then the promise executes, which then rejects. Promises are important building blocks for asynchronous operations in JavaScript. You may think that promises are not so easy to understand, learn, and work with. And trust me, you are not alone! Promises are challenging for many web developers, even after spending years working with them. In this article, I
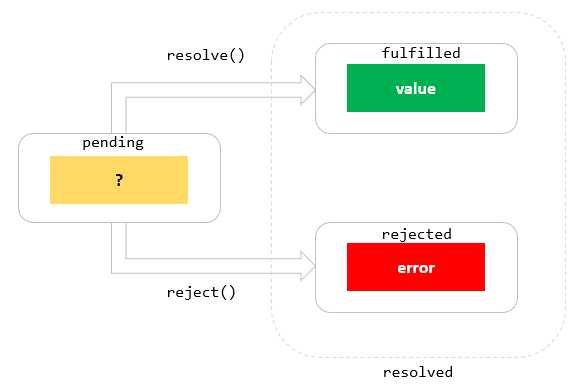
The promise might call reject (), and some code might come along 10 minutes later and call.catch (() => {}) on that promise, in which case the error will be handled. For this reason, the global error handler in Promise libraries like Q and Bluebird has been named onPossiblyUnhandledRejection, which is a fitting name. Promise.resolve ('Zzz!').then (rejectSuccess).catch (error) calls rejectSuccess because the promise is resolved. But rejectSuccess returns a rejected promise, — it is caugth by.catch (error) and the error callback is invoked. As you can see, we now get a JavaScript error because the fetch API cannot connect to that host. [00:26] As a result, the promise that is returned by the fetch call is rejected, and our two fulfillment handlers are never called.
JavaScript promises, mastering the asynchronous. Magus. 287.3K views. 01 What is asynchronous in JavaScript. 02 Why do we need asynchronous? 03 Quick quiz. 04 Some pratice. 05 The challenges of the asynchronous. ... var promise = request(); promise.catch(function (error) { displayError(error); }); ... We will see, how to handle fetch API errors using promises and async await syntax in JavaScript Our courses website is live at jsmates Learn with Param { P } .catch handles errors in promises of all kinds: be it a reject () call, or an error thrown in a handler. We should place.catch exactly in places where we want to handle errors and know how to handle them. The handler should analyze errors (custom error classes help) and rethrow unknown ones (maybe they are programming mistakes).
The handleError function returned a function which handled the error for that specific step on the Promise chain. It then would set a property (break) on the error object — which gets passed down... Promises already solve this problem and provide throw safety. You can simply omit the promise.catch, in fact, the whole code above can be refactored to Promise.reject("oh no") (although you should always reject with errors). Then you can do Promise.reject("oh no").catch(function(e){ console.log(e); }); which logs "Oh no". Throw safety is in ... Most promise implementations don't currently provide the type of functionality you are referring to, but a number of 3rd-party promise libraries (including Q and bluebird) provide a done() method that will catch and rethrow any uncaught errors, thus outputting them to the console.
 Asynchronous Javascript With Promises Amp Async Await In
Asynchronous Javascript With Promises Amp Async Await In
 Javascript Promise Code Example
Javascript Promise Code Example
 Understanding Javascript Promises Digitalocean
Understanding Javascript Promises Digitalocean
The Catch Method Javascript Promises Mastering The
 Using Then Catch Finally To Handle Errors In
Using Then Catch Finally To Handle Errors In
 When Is Then Success Fail Considered An Antipattern For
When Is Then Success Fail Considered An Antipattern For
 The Definitive Guide To The Javascript Promises
The Definitive Guide To The Javascript Promises
Promise Catch Func Throws A Syntax Error In Process Update
 Async Await Vs Promises A Guide And Cheat Sheet By Kait
Async Await Vs Promises A Guide And Cheat Sheet By Kait
 16 16 Try Catch With Promises Topics Of Javascript Es6
16 16 Try Catch With Promises Topics Of Javascript Es6
 Javascript Es2015 Promise Error Uncaught In Promise
Javascript Es2015 Promise Error Uncaught In Promise
 How To Rewrite A Callback Function In Promise Form And Async
How To Rewrite A Callback Function In Promise Form And Async
 Promises In Javascript Background Concept Hashnode
Promises In Javascript Background Concept Hashnode
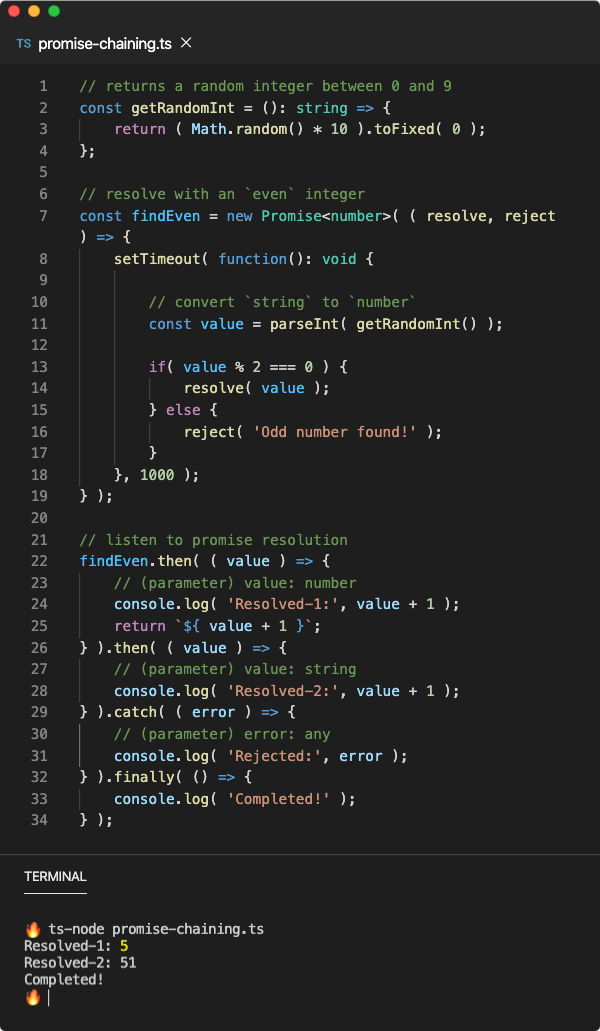
 Finally In Promises Amp Try Catch Dev Community
Finally In Promises Amp Try Catch Dev Community
 A Quick Introduction To Promises And Async Await With
A Quick Introduction To Promises And Async Await With
 Angular Logs Error To Console Before Raising Promise Catch
Angular Logs Error To Console Before Raising Promise Catch
Javascript Promises Tutorial How To Use Them Ictshore Com
 The Javascript Promise Tutorial Adrian Mejia Blog
The Javascript Promise Tutorial Adrian Mejia Blog
 Asynchronous Javascript Using Promises With Rest Apis In Node Js
Asynchronous Javascript Using Promises With Rest Apis In Node Js
 What Exceptions Cannot Be Caught By Try Catch By Bytefish
What Exceptions Cannot Be Caught By Try Catch By Bytefish
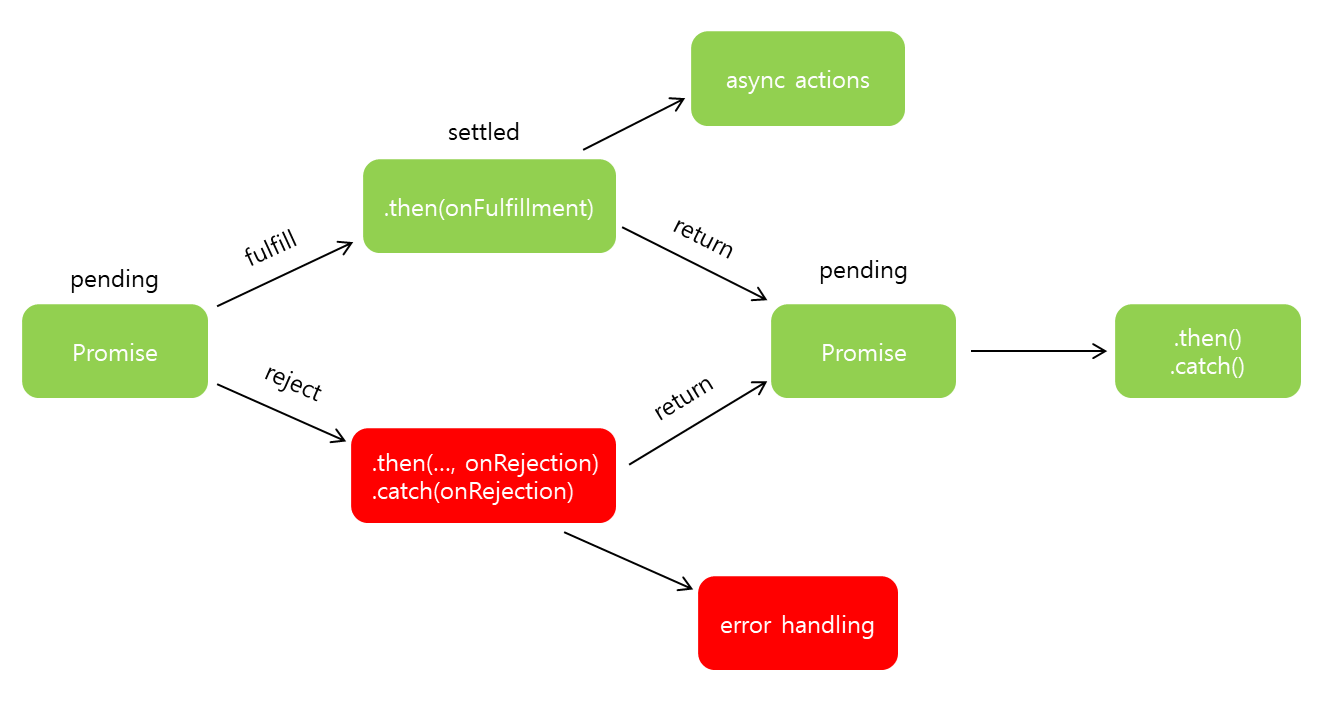 Rsvp Js Javascript Promise Compatible Module In Ie
Rsvp Js Javascript Promise Compatible Module In Ie
All You Need To Know About Javascript Promises
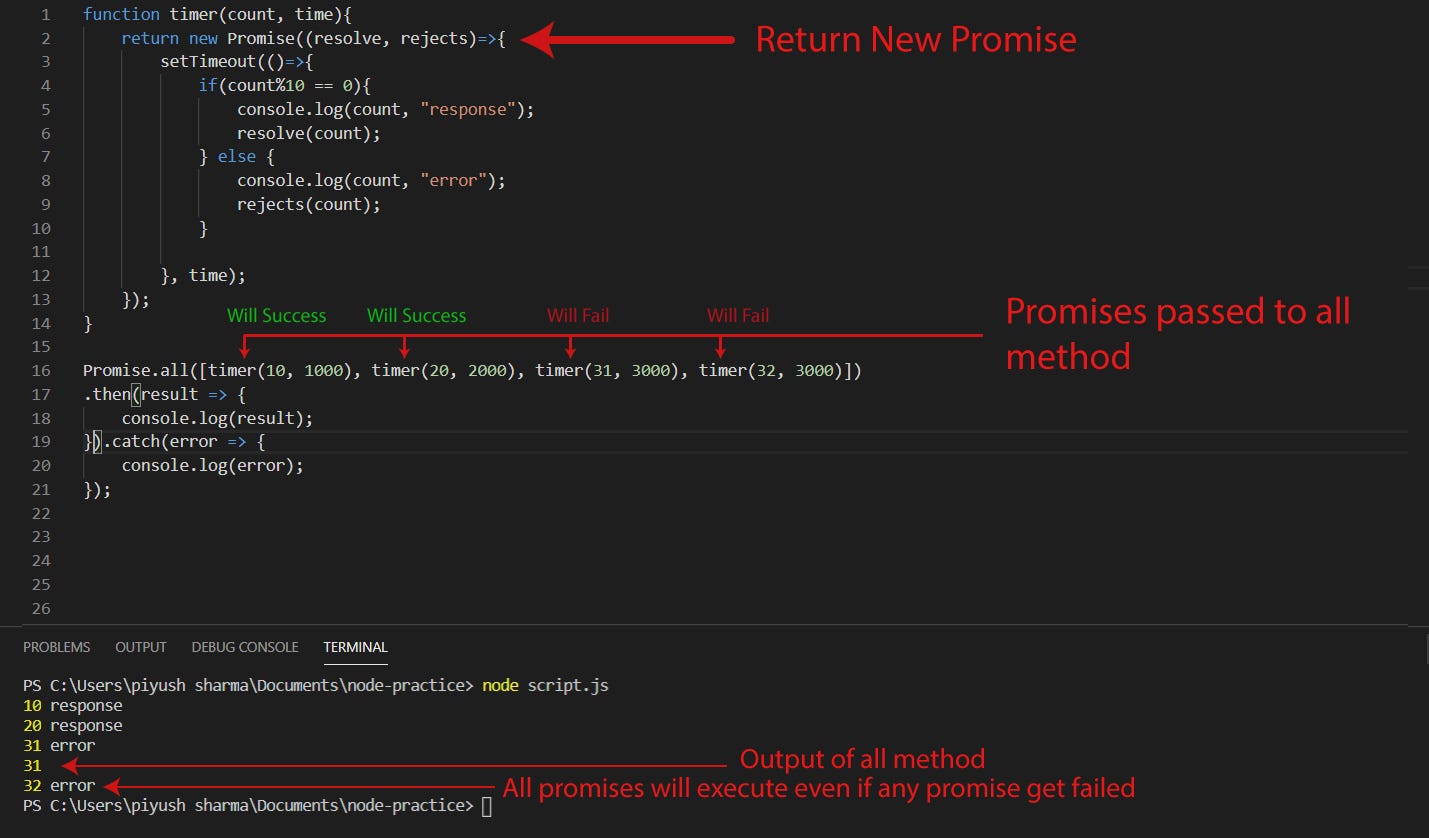 Javascript Promises In 5 Concepts By Piyush Sharma Codeburst
Javascript Promises In 5 Concepts By Piyush Sharma Codeburst
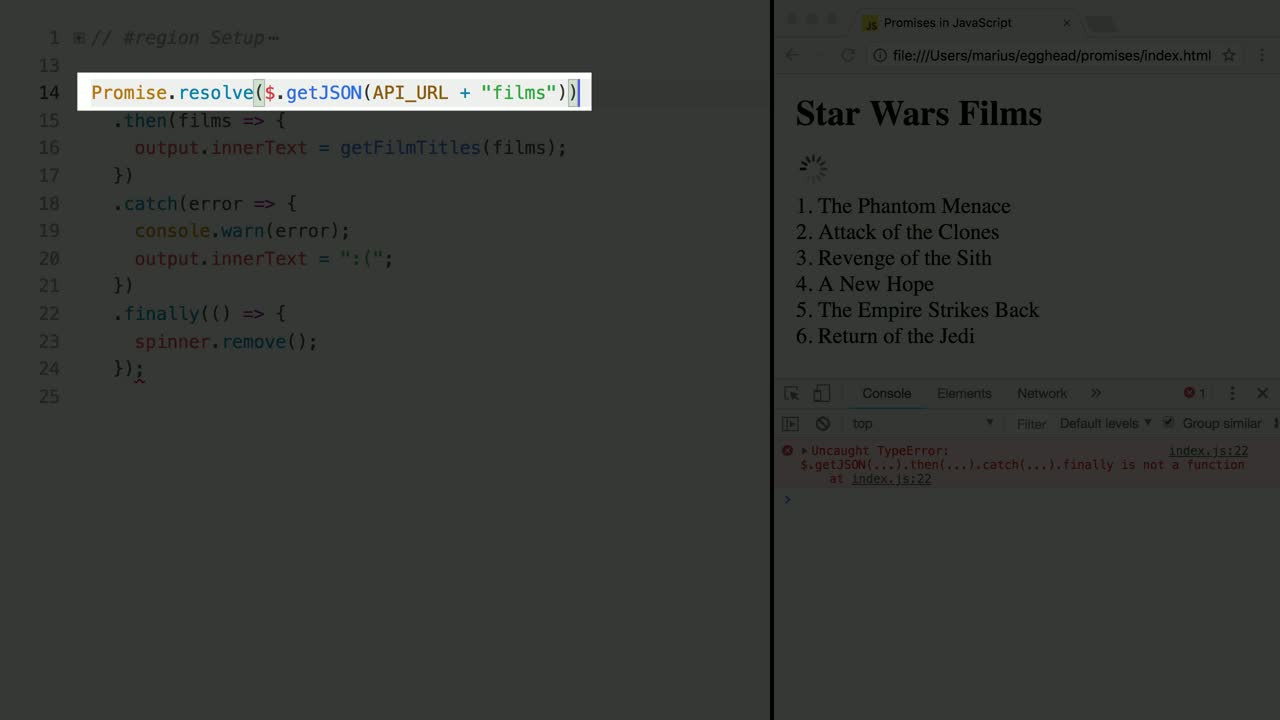 Introduction To Javascript Promises In Depth
Introduction To Javascript Promises In Depth
 6 Proven Methods For Handling Errors In Javascript Promises Async Await Decorators Rxjs
6 Proven Methods For Handling Errors In Javascript Promises Async Await Decorators Rxjs
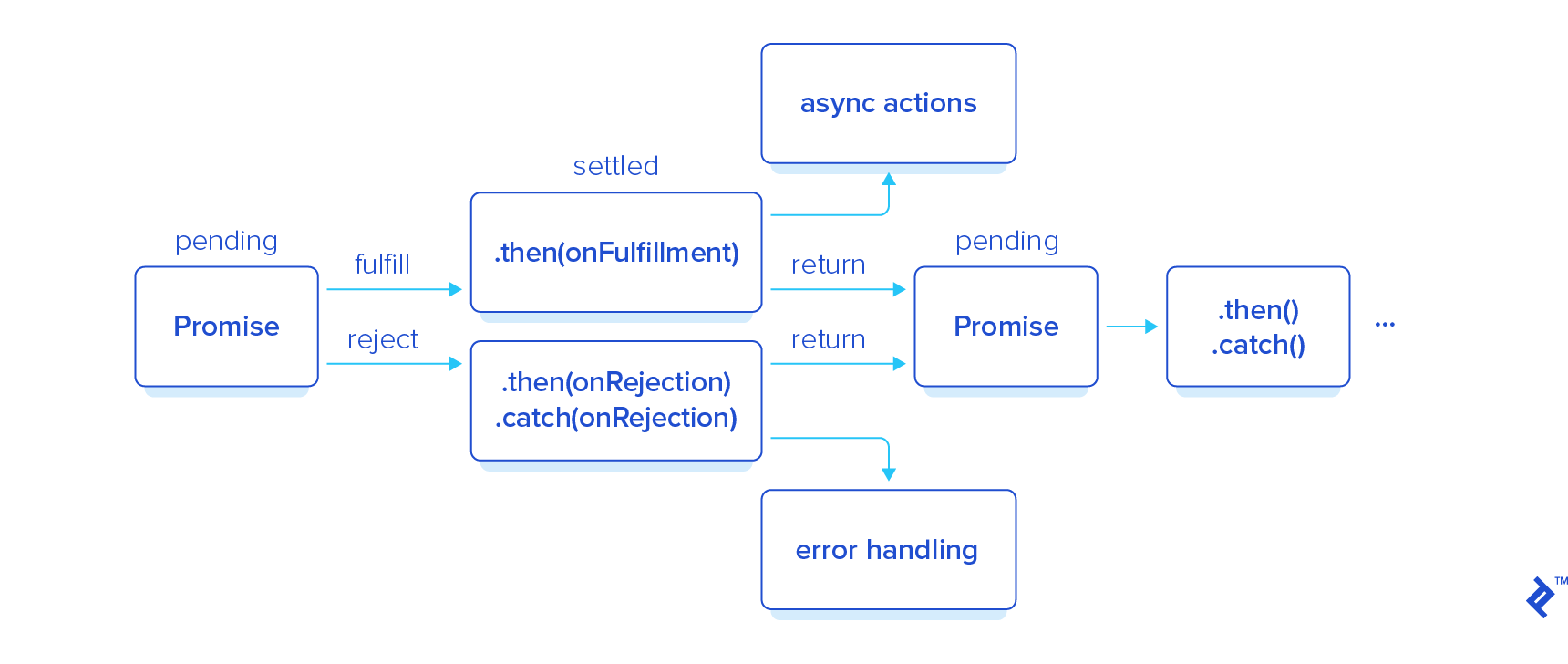 Asynchronous Javascript Async Await Tutorial Toptal
Asynchronous Javascript Async Await Tutorial Toptal
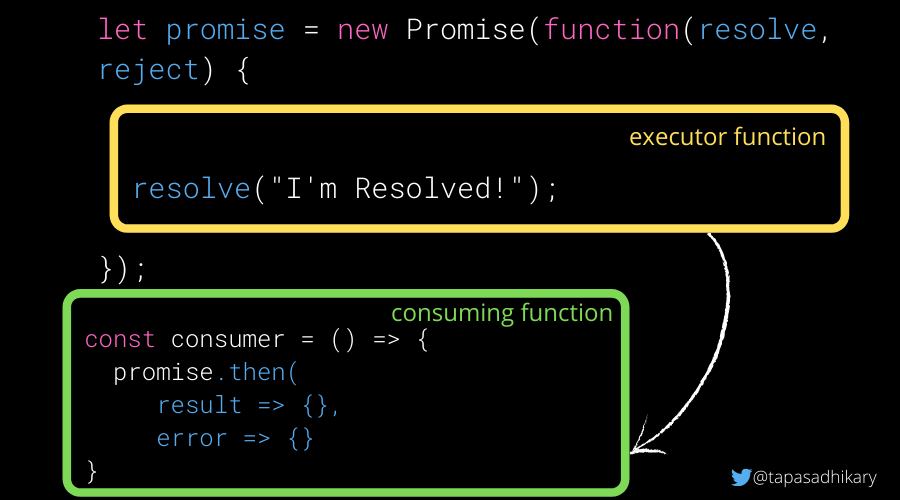 Javascript Promise Tutorial How To Resolve Or Reject
Javascript Promise Tutorial How To Resolve Or Reject
 Javascript Promises In 5 Concepts By Piyush Sharma Codeburst
Javascript Promises In 5 Concepts By Piyush Sharma Codeburst
 Javascript Interview Question 27 Handling Errors In
Javascript Interview Question 27 Handling Errors In
 The Promise Then Function In Javascript Mastering Js
The Promise Then Function In Javascript Mastering Js


0 Response to "33 Javascript Promise Catch Error"
Post a Comment