26 How To Get Promise Value Javascript
This is also the same for promises in JavaScript. When we define a promise in JavaScript, it will be resolved when the time comes, or it will get rejected. Promises in JavaScript. First of all, a Promise is an object. There are 3 states of the Promise object: Pending: Initial State, before the Promise succeeds or fails; Resolved: Completed ... The function getProjectName returns a promise, not the resolved value of that promise. You should render your UI with render () from this.state and this.props, and if you have data that has to be loaded asynchronously, you can assign the data to i.e. this.props.relatedTo using the componentDidMount () function, something in the line of
Jul 20, 2021 - The Promise.resolve() method returns a Promise object that is resolved with a given value. If the value is a promise, that promise is returned; if the value is a thenable (i.e. has a "then" method), the returned promise will "follow" that thenable, adopting its eventual state; otherwise the ...

How to get promise value javascript. The Promise.resolve() method returns a Promise object that is resolved with a given value. If the value is a promise, that promise is returned; if the value is a thenable (i.e. has a "then" method), the returned promise will "follow" that thenable, adopting its eventual state; otherwise the returned promise will be fulfilled with the value. Now you are able to return data from JavaScript promise. Return Data From Promise using ES6 Async/Await. JavaScript ES6 provides a new feature called async/await which can used as an alternative to Promise.then. Using async/await you can write the above code in synchronous manner without any .then. Oct 05, 2018 - Promises are better than callbacks, but the logic flow is just as hard to understand. Async /await Let’s you write async code that looks synchronous. Also, you don’t get a result from a promise. You get a promise of a result. This means you will get undefined as the return value of apiGetAll.
Jun 22, 2020 - In this tutorial, you will learn how to use the Promise.all() method to aggregate results from multiple asynchronous operations. pixelbits answer is correct and you should always use.then () to access the value of a promise in production code. However, there is a way to access the promise's value directly after it has been resolved by using the following unsupported internal node.js binding: process.binding ('util').getPromiseDetails (myPromise) // using a resolved promise, the 'then' block will be triggered instantly, // but its handlers will be triggered asynchronously as demonstrated by the console.logs const resolvedProm = Promise. resolve (33); let thenProm = resolvedProm. then (value => {console. log ("this gets called after the end of the main stack. the value received and returned is: "+ value); return value;}); // instantly ...
Promise Object Properties. A JavaScript Promise object can be: Pending; Fulfilled; Rejected; The Promise object supports two properties: state and result. While a Promise object is "pending" (working), the result is undefined. When a Promise object is "fulfilled", the result is a value. When a Promise object is "rejected", the result is an ... Understanding JavaScript Promises. In JavaScript, a promise is an object that returns a value which you hope to receive in the future, but not now. Because the value will be returned by the promise in the future, the promise is very well-suited for handling asynchronous operations. The solution is surprisingly simple. Even if you're a little uncomfortable with the idea of promises in JavaScript, you will love how you can solve this issue using them. As pointed out by Erop and Robin in the comments, Nodejs version 8 and above now support turning callback functions into promises using the built-in util module.
The roommate promising to find the résumé and texting back is synonymous with how we define a promise in JavaScript. The code does not directly or immediately return a value. Instead, it returns a promise that it will eventually provide the value at a later time. Promises are a comparatively new feature of the JavaScript language that allow you to defer further actions until after a previous action has completed, or respond to its failure. This is useful for setting up a sequence of async operations to work correctly. This article shows you how promises work, how you'll see them in use with web APIs, and how to write your own.Promises are a ... This second promise (promise2) represents the completion not just of doSomething(), but also of the successCallback or failureCallback you passed in, which can be other asynchronous functions returning a promise.When that's the case, any callbacks added to promise2 get queued behind the promise returned by either successCallback or failureCallback. ...
A Promise is an object representing the eventual completion or failure of an asynchronous operation. Since most people are consumers of already-created promises, this guide will explain consumption of returned promises before explaining how to create them. Jun 19, 2021 - For example, the loadCached function below fetches a URL and remembers (caches) its content. For future calls with the same URL it immediately gets the previous content from cache, but uses Promise.resolve to make a promise of it, so the returned value is always a promise: Well, you seem to understand the creation of the Promise sufficiently well. To simplify a bit, you create a promise of some sort: [code]const wait = ( value, delay = 1000 ) => new Promise( resolve => setTimeout( => resolve( value ), delay ) ); ...
One way to get the value resolved value of a JavaScript promise it to call the then method with a callback that has one parameter. The parameter has the resolved value. For instance, we can write: Promise.resolve (1) Promises are better than callbacks, but the logic flow is just as hard to understand. Async /await Let's you write async code that looks synchronous. Also, you don't get a result from a promise. You get a promise of a result. This means you will get undefined as the return value of apiGetAll. So const api will always equal undefined. Jul 18, 2018 - JS is so powerful because of its ability to handle asynchronous tasks, and with ES2015, there’s a new player on our async team: promises. A Promise is a powerful thing, it lets us elegantly handle…
Jul 07, 2020 - What is a promise? How can we better understand a promise? How does the JS Engine actually process a Promise when it sees it in the wild? A promise describes a placeholder for an asynchronous computation that only returns the value to a given callback if you call .then (callback). You can use this behavior to determine whether a given value is a promise. Because promises implement the .then () method, you can check whether it's a function. It's happening because the Javascript code always executes synchronously, so the console.log () function starts immediately after the fetch () request, not waiting until it is resolved. In the moment when console.log () function starting to run, a Promise that should be returned from a fetch () request is in a pending status.
Promises and asynchronous operations are hard for people to understand. I see questions here daily about promises and not 'getting' it. If non-async way to access promise results would be added to the default promise, I'd imagine that this would be an even larger amount. It's good to try and enforce 'the right way' of doing things. The promise is a placeholder holding the result of an asynchronous operation. If the operation completes successfully, then the promise fulfills with the operation value, but if the operation fails: the promise rejects with the reason of the failure. Promises can also create chains, which are useful in handling multiple dependent async operations. let promise = new Promise(resolve => resolve(value)); The method is used for compatibility, when a function is expected to return a promise. For example, the loadCached function below fetches a URL and remembers (caches) its content.
JavaScript promises are one of the most popular ways of writing asynchronous functions that return a single value on completion or failure of the operation.. What is Promise.all()? The Promise.all() is a static method (part of Promise API) that executes many promises in parallel, and waits until all of them are settled. It takes an array of promises as an input (an iterable) and returns a ... Aug 24, 2020 - A Promise object is widely used in Javascript async programming. And it's sometimes confusing for developers how to use it properly. In this blog post, I've attempted to describe a use case when a developer needs to use a returned value from a Promise object somewhere later in code. You can create a promise using the promise constructor like this: let promise = new Promise (function (resolve, reject) { // Make an asynchronous call and either resolve or reject }); In most cases, a promise may be used for an asynchronous operation. However, technically, you can resolve/reject on both synchronous and asynchronous operations.
Find out how to return the result of an asynchronous function, promise based or callback based, using JavaScript Published Sep 09, 2019 , Last Updated Apr 30, 2020 Say you have this problem: you are making an asynchronous call, and you need the result of that call to be returned from the original function. The return value of each resolved promise in the chain is passed along to the next .then(), while the reason for rejection is passed along to the next rejection-handler function in the chain. The promises of a chain are nested like Russian dolls, but get popped like the top of a stack. Promise.resolve () method in JS returns a Promise object that is resolved with a given value. Any of the three things can happened: If the value is a promise then promise is returned. If the value has a "then" attached to the promise, then the returned promise will follow that "then" to till the final state.
What are promises in JavaScript? A Promise in JavaScript is an object that holds the future value of an asynchronous operation. For example, if we are requesting some data from a server, the promise promises us to get that data that we can use in the future. A promise object can have the following states: What is a promise?A JavaScript promise is an object that represents the completion or failure of an asynchronous task and its resulting value.¹ The end. I'm kidding of course. So, what does that definition even mean? First of all, many things in JavaScript are objects. You can create Oct 07, 2018 - We will get back to that later. ... As we can see PromiseStatus can have three different values. pending resolved or rejected When promise is created PromiseStatuswill be in the pending status and will have PromiseValue as undefined until the promise is either resolved or rejected.
2 weeks ago - Get access to ad-free content, doubt assistance and more! ... The Promise is an object that represents either completion or failure of a user task. A promise in JavaScript can be in three states pending, fulfilled or rejected. The main advantage of using a Promise in JavaScript is that a user ... Use the then function to access the eventual result of a promise (or, if the operation fails, the reason for that failure). Regardless of the state of the promise, the call to then is non-blocking, that is, it returns immediately; so what it does not do is immediately return the result value ... The return value of each resolved promise in the chain is passed along to the next .then(), while the reason for rejection is passed along to the next rejection-handler function in the chain. The promises of a chain are nested like Russian dolls, but get popped like the top of a stack.
A promise represents the eventual result of an asynchronous operation. The primary way of interacting with a promise is through its then method, which registers callbacks to receive either a promise's eventual value or the reason why the promise cannot be fulfilled. In some cases, you may want to check the status of the promise. The then() method returns a Promise. It takes up to two arguments: callback functions for the success and failure cases of the Promise.
 Get Promise Value In React Component Stack Overflow
Get Promise Value In React Component Stack Overflow
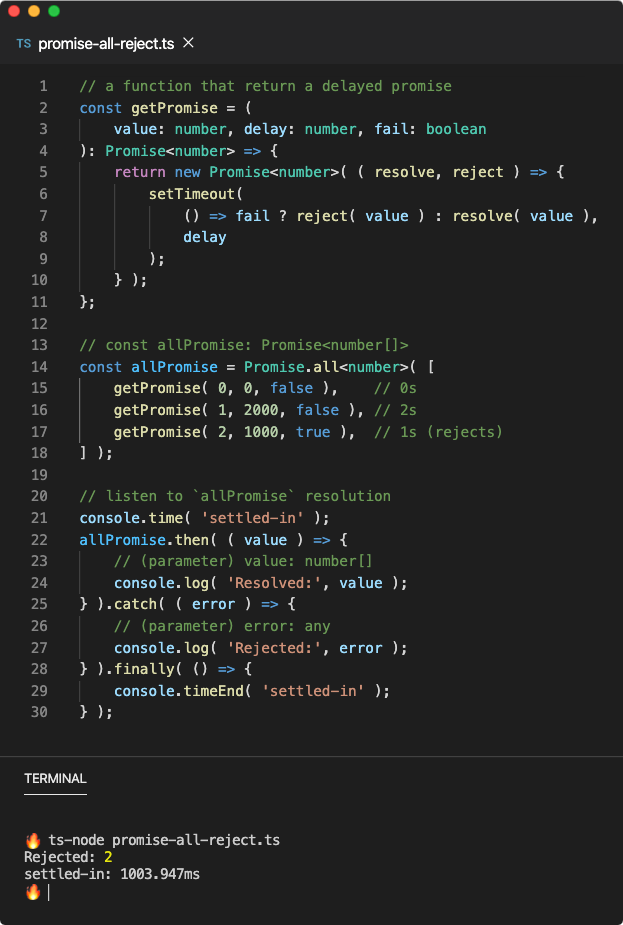 A Quick Introduction To Promises And Async Await With
A Quick Introduction To Promises And Async Await With
 Promises And Async Await Cheatsheet
Promises And Async Await Cheatsheet
 Javascript Promise Resolve Function Complete Guide
Javascript Promise Resolve Function Complete Guide
 Get Value From Promise Object Serverside Into Client Side
Get Value From Promise Object Serverside Into Client Side
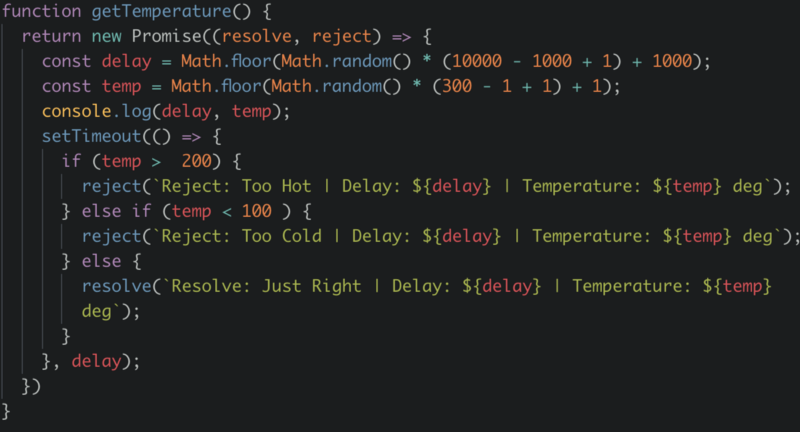 How To Write A Javascript Promise
How To Write A Javascript Promise
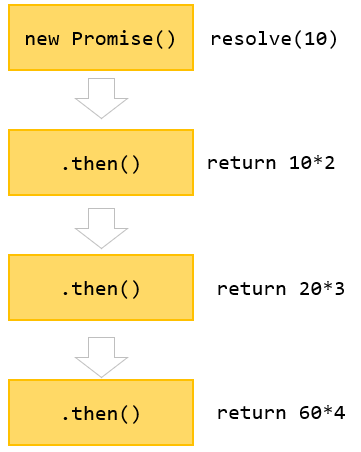 Promise Chaining In Javascript
Promise Chaining In Javascript
 Overview Of Promises In Javascript
Overview Of Promises In Javascript
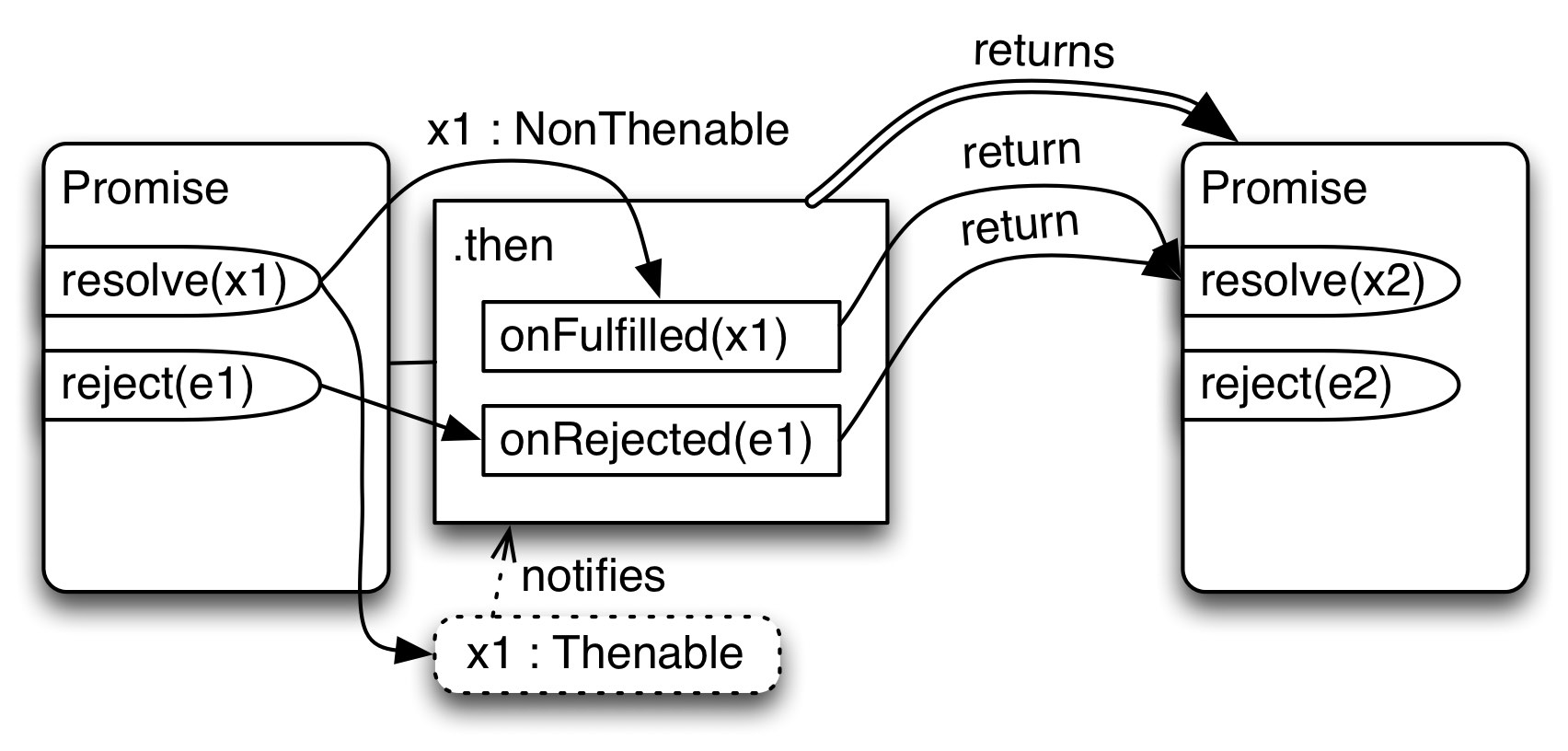 25 Promises For Asynchronous Programming
25 Promises For Asynchronous Programming
 Javascript Promise Tutorial Resolve Reject And Chaining In
Javascript Promise Tutorial Resolve Reject And Chaining In
 Javascript Promise Resolve Example Promise Resolve
Javascript Promise Resolve Example Promise Resolve
 Async Await In Node Js How To Master It Risingstack
Async Await In Node Js How To Master It Risingstack
Faster Async Functions And Promises V8
 A Quick Introduction To Promises And Async Await With
A Quick Introduction To Promises And Async Await With
 Asynchronous Javascript Using Promises With Rest Apis In Node Js
Asynchronous Javascript Using Promises With Rest Apis In Node Js
 Javascript Promises And Async Await As Fast As Possible
Javascript Promises And Async Await As Fast As Possible
 Promises In Javascript Lets Understand Them By Krishankant
Promises In Javascript Lets Understand Them By Krishankant
 Promise All Function In Javascript The Complete Guide
Promise All Function In Javascript The Complete Guide
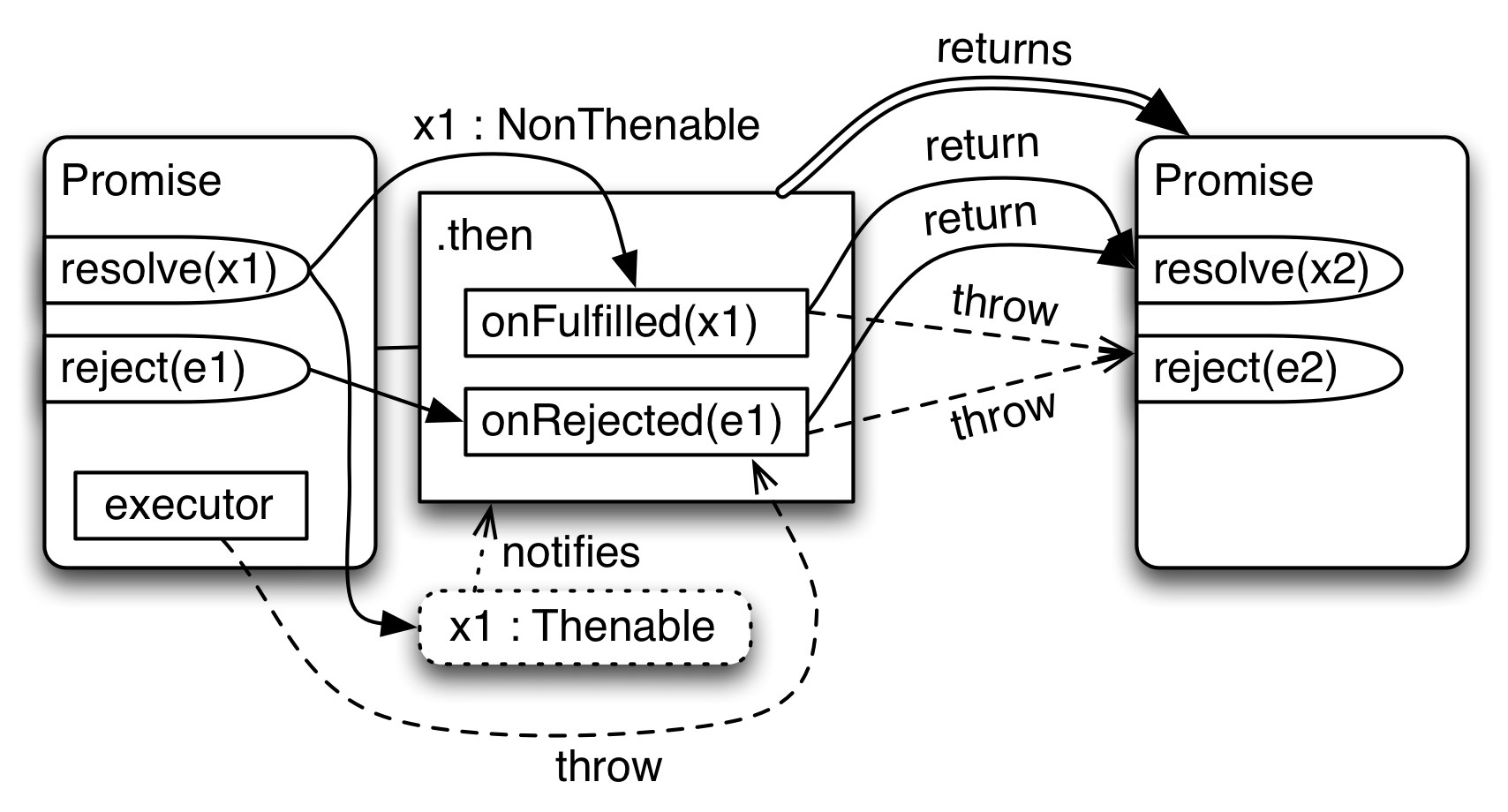 25 Promises For Asynchronous Programming
25 Promises For Asynchronous Programming




0 Response to "26 How To Get Promise Value Javascript"
Post a Comment