29 How To Use Then In Javascript
The if/else statement is a part of JavaScript's "Conditional" Statements, which are used to perform different actions based on different conditions. In JavaScript we have the following conditional statements: Use if to specify a block of code to be executed, if a specified condition is true 27/2/2018 · the .then() function is used for the PROMISE (so for async function ) when you need to KNOW WHEN IT'S FINISHED (and it is finished ok .. or KO ) ..so you have . MYASYNCFUNCTION().then(function(response({ //do what you want when it's finish and everything ok .. with the result }).catch(function(error){ // it's finshed but with error })
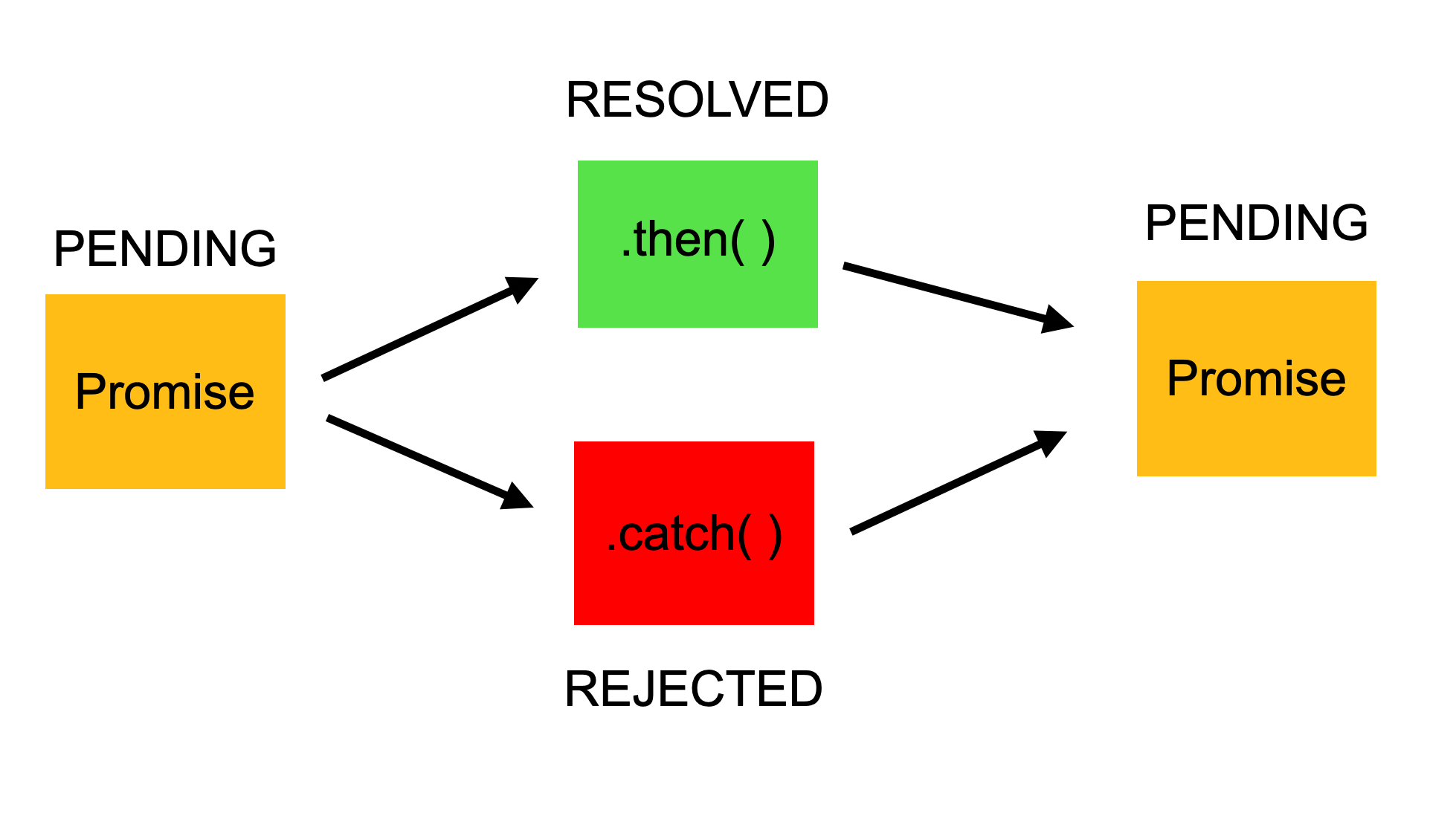 Javascript Promise Tutorial Resolve Reject And Chaining In
Javascript Promise Tutorial Resolve Reject And Chaining In
Promise How To. Here is how to use a Promise: myPromise.then(. function(value) { /* code if successful */ }, function(error) { /* code if some error */ } ); Promise.then () takes two arguments, a callback for success and another for failure. Both are optional, so you can add a callback for success or failure only.

How to use then in javascript. You should not specify a semicolon after the then () method if you are using catch (). This will tell JavaScript that then () and catch () are separate, and so an error will be returned in your code. If our promise is rejected, the contents of the catch () statement will run. Let's see what happens when we run our code: Callbacks added with then () will never be invoked before the completion of the current run of the JavaScript event loop. These callbacks will be invoked even if they were added after the success or failure of the asynchronous operation that the promise represents. Multiple callbacks may be added by calling then () several times. // using a resolved promise, the 'then' block will be triggered instantly, // but its handlers will be triggered asynchronously as demonstrated by the console.logs const resolvedProm = Promise. resolve (33); let thenProm = resolvedProm. then (value => {console. log ("this gets called after the end of the main stack. the value received and returned is: "+ value); return value;}); // instantly ...
How To Write Conditional Statements in JavaScript describes how to use the if, else, and else if keywords to control the flow of a program based on different conditions, which in JavaScript are often the result of user input. In addition to if...else, JavaScript has a feature known as a switch statement. 2 weeks ago - Promises are one of the ways we can deal with asynchronous operations in JavaScript. Many people struggle with understanding how Promises work, so in this post I will try to explain them as simply as I can. Promises are a broad topic so I can't go into every detail in Dec 02, 2019 - The spec also uses the term thenable to describe an object that is promise-like, in that it has a then method. This term reminds me of ex-England Football Manager Terry Venables so I'll be using it as little as possible. ... The above and JavaScript promises share a common, standardized behaviour ...
In JavaScript, 0 is considered 'falsy', while numbers greater or lesser than 0 are considered 'truthy'. As a result, one has to write the correct code like this. As a result, one has to ... Output: Success, You are a GEEK; Promise Consumers. Promises can be consumed by registering functions using .then and .catch methods.. then() then() is invoked when a promise is either resolved or rejected. Parameters: then() method takes two functions as parameters. promise.then( null, (error) => { console.log(error) } ); However, you can handle errors in a better way using the .catch() method that we will see in a minute. Let's look at a couple of examples of handling results and errors using the .then and .catch handlers. We will make this learning a bit more fun with a few real asynchronous requests.
Mar 31, 2021 - For instance, this might happen when we start to do a job but then see that everything has already been completed and cached. That’s fine. We immediately have a resolved promise. ... The properties state and result of the Promise object are internal. We can’t directly access them. We can use ... May 14, 2018 - Promises are one of the most exciting additions to JavaScript ES6. For supporting asynchronous programming, JavaScript uses callbacks, among other things. However, callbacks suffer from problems like… Promise How To ... );. Promise.then() takes two arguments, a callback for success and another for failure. Both are optional, so you can add a callback for ...
CodinGame is a challenge-based training platform for programmers where you can play with the hottest programming topics. Solve games, code AI bots, learn from your peers, have fun. JavaScript Promises: then (f,f) vs then (f).catch (f) Posted July 21, 2021. javascript promise. 5 Comments. In JavaScript, you can access the fullfillment value or the rejection reason of a promise in 2 ways. A) Use 2 callbacks on promise.then (fn, fn): promise .then(success, error); B) Or use a chain of promise.then (fn).catch (fn): Recently in JavaScript, the fetch() API has been used for API requests to URLs. Before this, requests were made using XMLHttpRequest. With ES2017+, using fetch API and async/await, you can make asynchronous requests to URL endpoints, first you'd need to define the function as an async function and await the response in json and then return ...
27/8/2021 · How to use then in javascript. What Why And How Of Typescript For Javascript Developers Javascript Variable Targeting Optimize Resource Hub Validate Javascript How To Use Try Catch And Settimeout With Async Await Implement Copy On Click Using Javascript By Javascript Jeep Javascript Promises 101 Dev Community The End Of Javascript It operates asynchronously via the event-loop. Async functions will always return a value. Using async simply implies that a promise will be returned, and if a promise is not returned, JavaScript automatically wraps it in a resolved promise with its value. async function firstAsync() {return 27;} firstAsync().then(alert); // 27 Sep 25, 2019 - Q: How to use then() and how to return a promise from a function and use then() ? A: then() is a method in the Promise prototype that returns a promise and accepts two callback functions. One function is for the success and the other is for the failure case of the promise. If both arguments
then () function is related to "Javascript promises" that are used in some libraries or frameworks like jQuery or AngularJS. A promise is a pattern for handling asynchronous operations. The promise allows you to call a method called "then" that lets you specify the function (s) to use as the callbacks. Oct 06, 2019 - Building software that does what you want is great. Building robust software which pre-empts potential issues and can recover enough to give you (as a developer or a user) feedback is even better… The JavaScript += operator can merge two strings together. This operator is more convenient than the long-form "variable = x + y" syntax. For instance, say you have a user's forename and the surname in two strings. You could use the += operator to merge these values into one string.
Jan 17, 2020 - 👉 This article has been updated and republished, read the latest version here A JavaScript library is a bunch of code that was written by someone to provide functionality by using JavaScript but then got packaged up separately (because otherwise, JavaScript would be far too massive to put on everyone's devices). Nov 11, 2019 - Promises in JavaScript are an object representation of an asynchronous computation. You can think of a promise as a placeholder for a value that hasn't been computed yet. However, there's no way to get a promise's value from the promise directly - you need to call the then() function to register ...
It turns out that the way we farm out work in JavaScript is to use environment-specific functions and APIs. And this is a source of great confusion in JavaScript. JavaScript always runs in an environment. Often, that environment is the browser. But it can also be on the server with NodeJS. But what on earth is the difference? Aug 05, 2019 - One of the most important questions I faced in interviews was how promises are implemented. Since async/await is becoming more popular, you need to understand promises. What is a Promise?A promise is an object which represents the result of an asynchronous operation which is either resolved ... JavaScript Promise then () is an inbuilt function that returns a Promise. The then () method takes up to two arguments: callback functions for the success and failure cases of the Promise. Promises in JavaScript are an object representation of an asynchronous computation.
In JavaScript we have the following conditional statements: Use if to specify a block of code to be executed, if a specified condition is true. Use else to specify a block of code to be executed, if the same condition is false. Use else if to specify a new condition to test, if the first condition is false. The JavaScript prompt asks the user for his name and then displays the result in the "welcome" div. You can also use this same code to display the result in the span element using the same code except change the div tag to a span opening and closing tag. 7 days ago — Promise.resolve(undefined).then(bound); // this still works, because we use the youngest // realm (the incumbent) on the stack </script>
3 weeks ago - Here the first .then shows 1 and ... second .then. That handler is in the line (**), it shows 2 and does the same thing. So the output is the same as in the previous example: 1 → 2 → 4, but now with 1 second delay between alert calls. Returning promises allows us to build chains of asynchronous actions. ... Let’s use this feature ... Jan 18, 2021 - The spec also uses the term thenable to describe an object that is promise-like, in that it has a then method. This term reminds me of ex-England Football Manager Terry Venables so I'll be using it as little as possible. ... The above and JavaScript promises share a common, standardized behaviour ... Nov 14, 2016 - It's probably trying to say that you're supposed to do resolve([genre1, genre2, ...]); inside the promise implementation. ... It sounds like you aren't understanding how promises are used. You return a promise. Then, later when your code resolves the promise, it resolves it with a result and ...
Jul 30, 2020 - Get access to ad-free content, doubt assistance and more! ... The then() method in JavaScript has been defined in the Promise API and is used to deal with asynchronous tasks such as an API call. Previously, callback functions were used instead of this function which made the code difficult ... Your approach using await in an async then callback will work, but it's unnecessarily complex if all you want to do is call the async function and have its result propagate through the chain. But if you are doing other things and want the syntax benefit of async functions, that's fine. I'll come back to that in a moment. async functions returns promises, so you just return the result of ... Note that unlike all of the other constructs in JavaScript, the for statement uses semicolons, rather than commas, to separate its arguments. This is in keeping with the syntax used in C, C++, and ...
See Work with tables using the Excel JavaScript API for more information. Data protection. Your add-in can control a user's ability to edit data in a worksheet. The worksheet's protection property is a WorksheetProtection object with a protect() method. The following example shows a basic scenario toggling the complete protection of the active ... Key Takeaways. Promises can handle the asynchronous calls in JavaScript. A promise will be "pending" when executed and will result in "resolved" or "rejected", depending on the response of the asynchronous call. Promises avoid the problem of "callback hell", which happens due to nested callback functions. Conditional statements inject logic into your program, and their application are limitless. If you're still new to JavaScript, mastering how to use the "if-else" statement lets you specifically instruct your program on how it should function. Using conditions in JavaScript is easy.
20 Jul 2021 — Use of async and await enables the use of ordinary try / catch blocks ... function foo() { return Promise.resolve(1).then(() => undefined) }. 9/7/2021 · It is common practice to learn the .then() method with Promises. .then takes a callback function and returns another Promise (!) and you can do nifty things like console.log out the returned value,... Here a JavaScript expression is evaluated. If the resulting value is true, the given statement(s) are executed. If the expression is false, then no statement would be not executed. Most of the times, you will use comparison operators while making decisions. Example. Try the following example to understand how the if statement works.
The async/await keywords introduced by ES7 is definitely an improvement to JavaScript asynchronous programming. It can make code easier to read and debug. However in order to use them correctly, one must completely understand promises, since they are no more than syntactic sugar, and the underlying technique is still promises. To achieve all of these objectives and more, JavaScript comes with the built in Date object and related methods. This tutorial will go over how to format and use date and time in JavaScript. The Date Object. The Date object is a built-in object in JavaScript that stores the date and time. It provides a number of built-in methods for formatting ... Aug 05, 2019 - One of the most important questions I faced in interviews was how promises are implemented. Since async/await is becoming more popular, you need to understand promises. What is a Promise?A promise is an object which represents the result of an asynchronous operation which is either resolved ...
 What Is Javascript Learn Web Development Mdn
What Is Javascript Learn Web Development Mdn
 When And How To Use Async Await
When And How To Use Async Await
 How To Integrate Babel For Javascript In Vs Code The
How To Integrate Babel For Javascript In Vs Code The
 Javascript Promise Resolve Method Geeksforgeeks
Javascript Promise Resolve Method Geeksforgeeks
 How To Externalize And Minify Javascript
How To Externalize And Minify Javascript
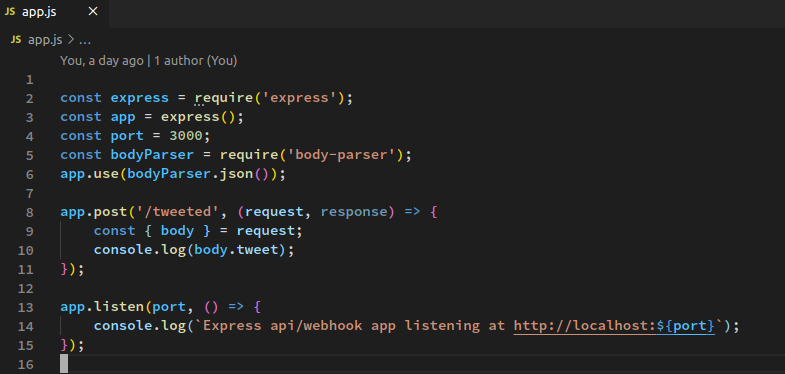 Webhooks Explained With Node Js Ifttt And Twitter By
Webhooks Explained With Node Js Ifttt And Twitter By
 Run Javascript In The Console Chrome Developers
Run Javascript In The Console Chrome Developers
 The Easiest Way To Add Javascript To Your Wordpress Site
The Easiest Way To Add Javascript To Your Wordpress Site
 Pick Group And Rank Questions In Javascript Qualtrics
Pick Group And Rank Questions In Javascript Qualtrics
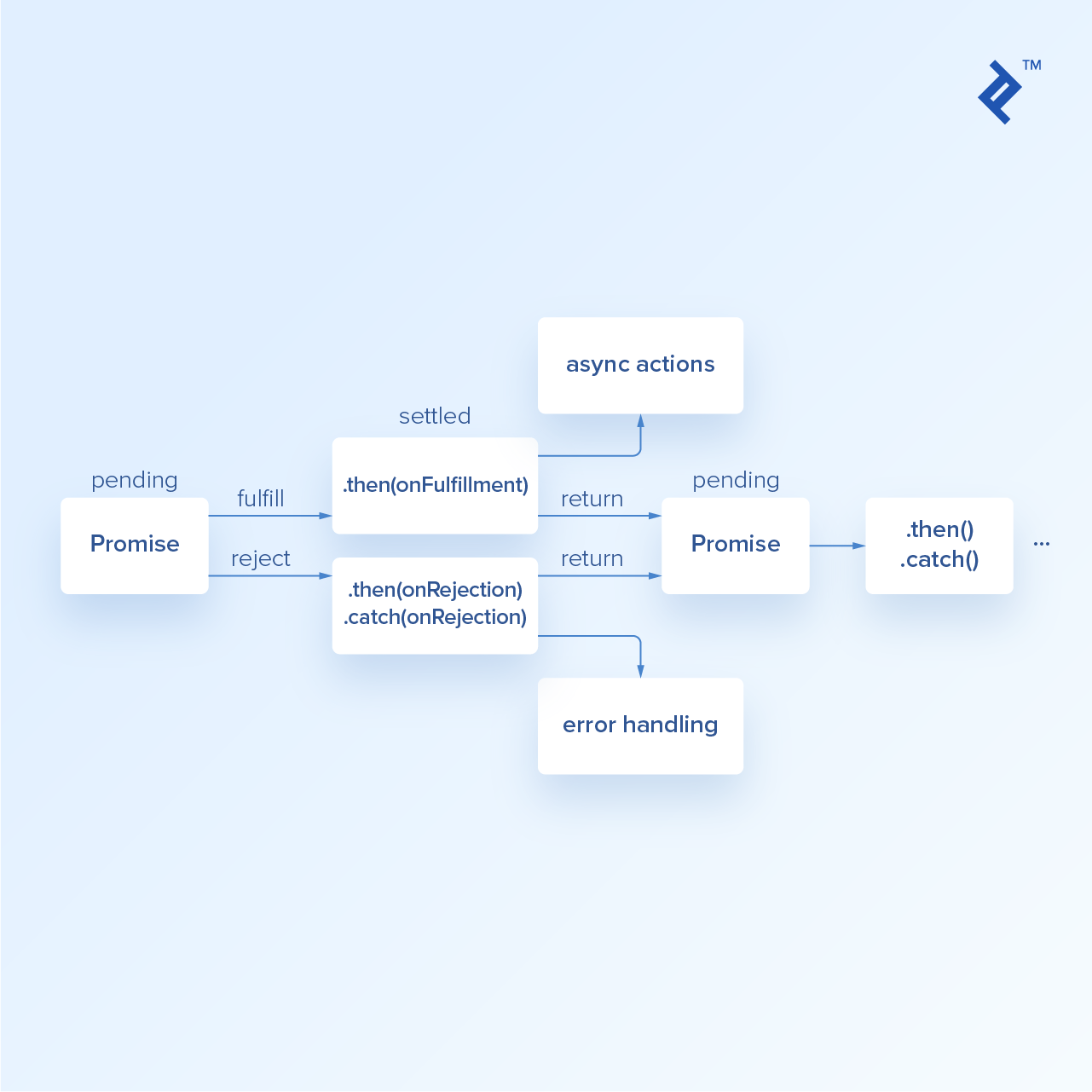 Asynchronous Javascript From Callback Hell To Async And
Asynchronous Javascript From Callback Hell To Async And
 How To Add Javascripts Necessary To Use Bootstrap Templates
How To Add Javascripts Necessary To Use Bootstrap Templates
 Passing Different Values In A Javascript Code Execution
Passing Different Values In A Javascript Code Execution
 A Simple Explanation Of Javascript Closures
A Simple Explanation Of Javascript Closures
 Javascript Promise Tutorial Resolve Reject And Chaining In
Javascript Promise Tutorial Resolve Reject And Chaining In
Asynchronous Javascript The Event Loop Callbacks Promises
 Javascript Functions Studytonight
Javascript Functions Studytonight
 6 Creating A Webassembly Module That Talks To Javascript
6 Creating A Webassembly Module That Talks To Javascript
 How To Use Fetch To Make Ajax Calls In Javascript Dev Community
How To Use Fetch To Make Ajax Calls In Javascript Dev Community
 Unable To Enable Javascript On Ios Device Ciaops
Unable To Enable Javascript On Ios Device Ciaops
 Javascript Promise Tutorial Resolve Reject And Chaining In
Javascript Promise Tutorial Resolve Reject And Chaining In
Pre Processing Documents Prior To Splitting Using Acrobat

 Compare Two Dates With Javascript Stack Overflow
Compare Two Dates With Javascript Stack Overflow
 Tip The Order Of Then And Catch Matters 30 Seconds Of Code
Tip The Order Of Then And Catch Matters 30 Seconds Of Code

0 Response to "29 How To Use Then In Javascript"
Post a Comment