20 Javascript Async Function Promise
An asyncfunction always returns a promise. That's how it reports the completion of its asynchronous work. If you're using it in another asyncfunction, you can use awaitto wait for its promise to settle, but in a non-asyncfunction (often at the top level or in an event handler), you have to use the promise directly, e.g.: Promises provide a couple of recipes to do that. In this chapter we cover promise chaining. The idea is that the result is passed through the chain of .then handlers. Then the .then handler is called (**). …and so on. As the result is passed along the chain of handlers, we can see a sequence of alert calls: 1 → 2 → 4.

As you can see, both of these async functions return a Promise; and that Promise object resolves to the vanilla String values.. But, we've already identified the first flaw in my mental model.Which is that the above two async functions are different in some way. When, in reality, these two async functions are exactly the same because, according to the Mozilla Developer Network (MDN), any non ...
Javascript async function promise. Your approach using await in an async then callback will work, but it's unnecessarily complex if all you want to do is call the async function and have its result propagate through the chain. But if you are doing other things and want the syntax benefit of async functions, that's fine. I'll come back to that in a moment. async functions returns promises, so you just return the result of ... Because async functions are Promises under the hood, we can run both asyncThing1 () and asyncThing2 () in parallel by calling them without await. Then we can use await and Promise.all, which returns an array of results once all Promises have completed. This allows the Promises to run in parallel again, but still gives us a pleasant-to-use ... 28/3/2017 · In the first function the keyword async is useless, the function test will return a Promise. The second function will return a Promise where you see the keyword await. When the awaited promise will resolved the execution inside the function continue and you can access to result of the promise. EDIT 1.
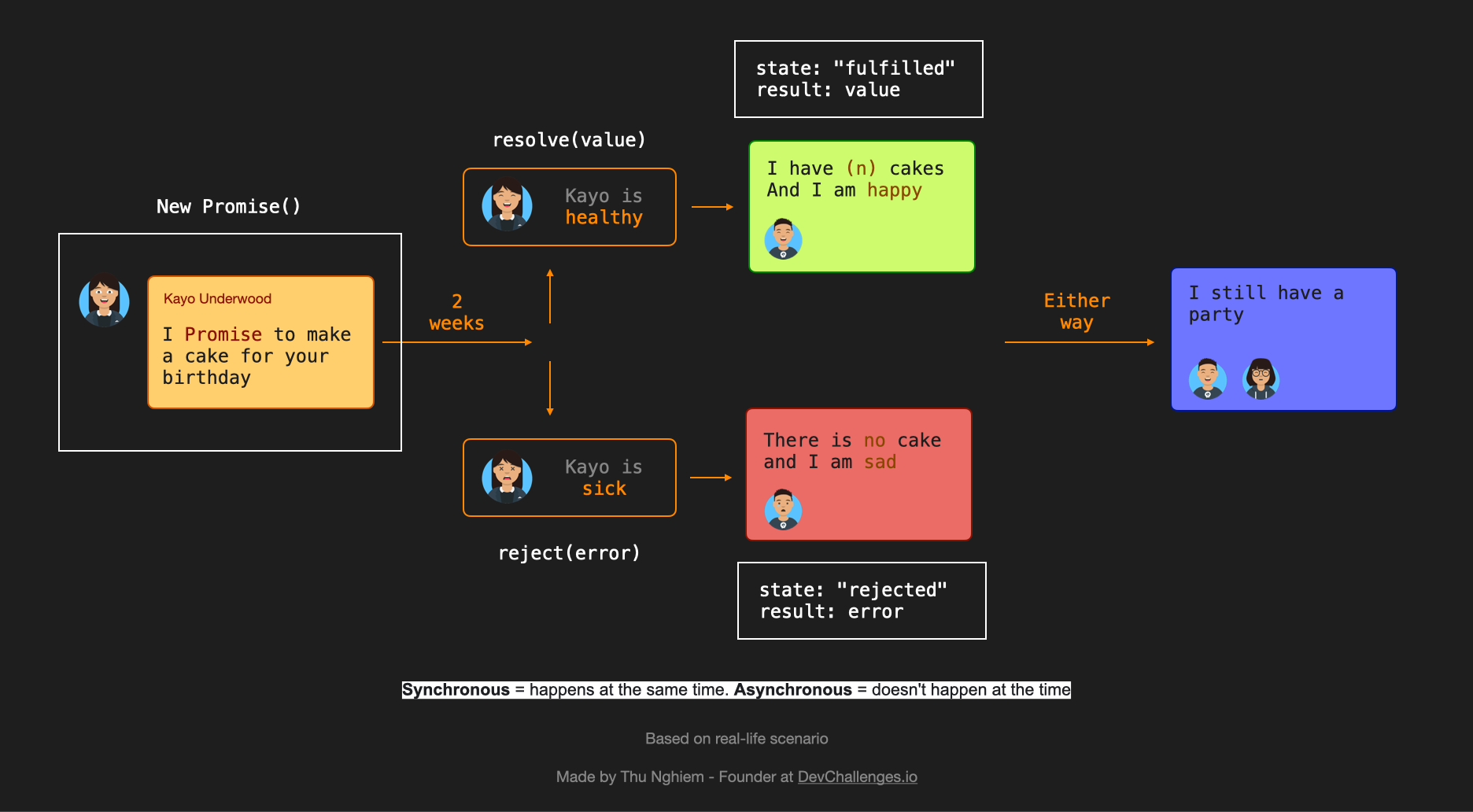
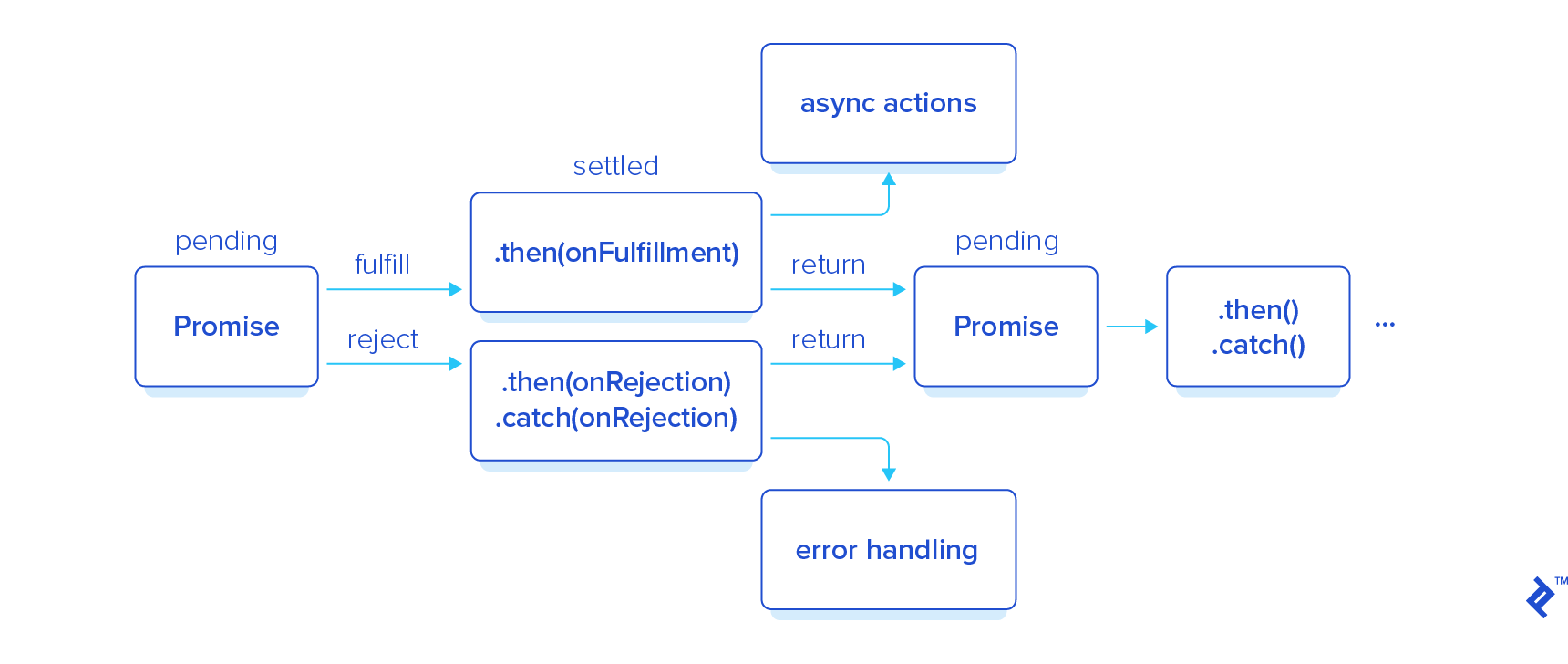
Promise Object Properties. A JavaScript Promise object can be: Pending; Fulfilled; Rejected; The Promise object supports two properties: state and result. While a Promise object is "pending" (working), the result is undefined. When a Promise object is "fulfilled", the result is a value. When a Promise object is "rejected", the result is an ... forEach loop fails in a promise or async function #. If you haven't faced the issue of async-await not working when used within a forEach loop in an async function or a promise block, you might be shocked to learn that the following code will not work as expected.. Click on the "Run" button to see it. Find out how to return the result of an asynchronous function, promise based or callback based, using JavaScript Published Sep 09, 2019 , Last Updated Apr 30, 2020 Say you have this problem: you are making an asynchronous call, and you need the result of that call to be returned from the original function.
In JavaScript, we can create a new Promise with new Promise(), which takes in a function as an argument: (resolve, reject) => {}. In this function, resolve and reject are callback functions that are provided by default in JavaScript. Let's take a closer look at the code above. When we run the onMyBirthday function, after 2000ms: 27/3/2017 · "Async functions always returns a promise. If we explicitly return a value at the end of our async function, the promise will be resolved with that value; otherwise, it resolves with undefined." Just to help you better grasp the underpinnings of the async function pattern, lets see how the above code would look like using Promises only: 1 All you have to do is write the word async before any regular function and it becomes a promise. But first, take a break. Let's have a look:👇. Promises vs Async/Await in JavaScript. Before async/await, to make a promise we wrote this: function order(){ return new Promise( (resolve, reject) =>{ // Write code here } ) }
An async function is a function declared with the async keyword, and the await keyword is permitted within them. The async and await keywords enable asynchronous, promise-based behavior to be written in a cleaner style, avoiding the need to explicitly configure promise chains. Async functions may also be defined as expressions. Promises are objects that asynchronously function to return a value sometime in the future. Following this, with ES 2017, the Javascript community sprinkled some syntactic sugar and sparkle over the Promises API to introduce the async/await syntax. A promise is NOT A FUNCTION. A promise is an OBJECT. To create a promise, we pass in an "executor" function into JavaScript's constructor function using the "new" keyword. The "executor" is just a...
The word "async" before a function means one simple thing: a function always returns a promise. Other values are wrapped in a resolved promise automatically. For instance, this function returns a resolved promise with the result of 1; let's test it: 29/5/2017 · This is the code using await/async. function create_section(sections,course_ID,i) { return new Promise( async function resolve() { var s_duration = 0; var sname = sections[i].name; var s_obj = { //some obj } var section_id; DB.section.create(s_obj,function (err, data_s) { if (err) return next(err); section_id = data_s._id; var lesson = sections[i].lessons; var arr = await add_lessons(lesson,section_id,i) resolve(arr); }); } ); }; Async/Await Basics in JavaScript. There are two parts to using async/await in your code. First of all, we have the async keyword, which you put in front of a function declaration to turn it into an async function. An async function is a function that knows to expect the possibility that you'll use the await keyword to invoke asynchronous code.
The async function returns a promise. The converse is also true. Every function that returns a promise can be considered as async function. await is used for calling an async function and waits for it to resolve or reject. await blocks the execution of the code within the async function in which it is located. Async operations like promises are put into an event queue, which runs after the main thread has finished processing so that they do not block subsequent JavaScript code from running. The queued operations will complete as soon as possible then return their results to the JavaScript environment. We want to make this open-source project available for people all around the world. Help to translate the content of this tutorial to your language!
Explanation: Async functions in Javascript allow us to stick to conventional programming strategies such as using for, while, and other methods that are otherwise synchronous in nature and cannot be used in Javascript. In this example, we wrap the possible response returned from the HTTP request in a promise. Code language: JavaScript (javascript) With async/await, the catch block will handle parsing errors. As can be seen evidently, this is much more efficient, simple and less complicated. 2. Conditionals. async/await handles conditionals in a much better fashion as compared to using Promises. Promises are a comparatively new feature of the JavaScript language that allow you to defer further actions until after a previous action has completed, or respond to its failure. This is useful for setting up a sequence of async operations to work correctly.
So with asynchronous JavaScript, the JavaScript doesn't wait for responses when executing a function, instead it continues with executing other functions. Let's look at ways of executing asynchronous JavaScript . Methods for writing asynchronous JavaScript. There are two ways of writing asynchronous code in JavaScript, promises and async/await. More recent additions to the JavaScript language are async functions and the await keyword, added in ECMAScript 2017. These features basically act as syntactic sugar on top of promises, making asynchronous code easier to write and to read afterwards. They make async code look more like old-school synchronous code, so they're well worth learning. JavaScript Visualized: Promises & Async/Await. ... The await keyword suspends the async function, whereas the Promise body would've kept on being executed if we would've used then!
The keyword await before a function makes the function wait for a promise: let value = await promise; The await keyword can only be used inside an async function. Async functions always return a promise, whether you use await or not. That promise resolves with whatever the async function returns, or rejects with whatever the async function throws. Async functions Any Async function returns a Promise implicitly, and the resolved value of the Promise will be whatever returns from your function. Our function has an async keyword on its...
 Converting Javascript Callbacks To Promise And Async Await
Converting Javascript Callbacks To Promise And Async Await
 Asynchronous Javascript Async Await Tutorial Toptal
Asynchronous Javascript Async Await Tutorial Toptal
 Await And Async Explained With Diagrams And Examples
Await And Async Explained With Diagrams And Examples
 Migrating From Promise Chains To Async Await
Migrating From Promise Chains To Async Await
 Async Await In Node Js How To Master It Risingstack
Async Await In Node Js How To Master It Risingstack
 The Performance Overhead Of Javascript Promises And Async
The Performance Overhead Of Javascript Promises And Async
 Javascript Callbacks Vs Promises Vs Async Await Vegibit
Javascript Callbacks Vs Promises Vs Async Await Vegibit
 Async Await The Async Keyword Javascript Codecademy Forums
Async Await The Async Keyword Javascript Codecademy Forums
 How To Learn Javascript Promises And Async Await In 20 Minutes
How To Learn Javascript Promises And Async Await In 20 Minutes
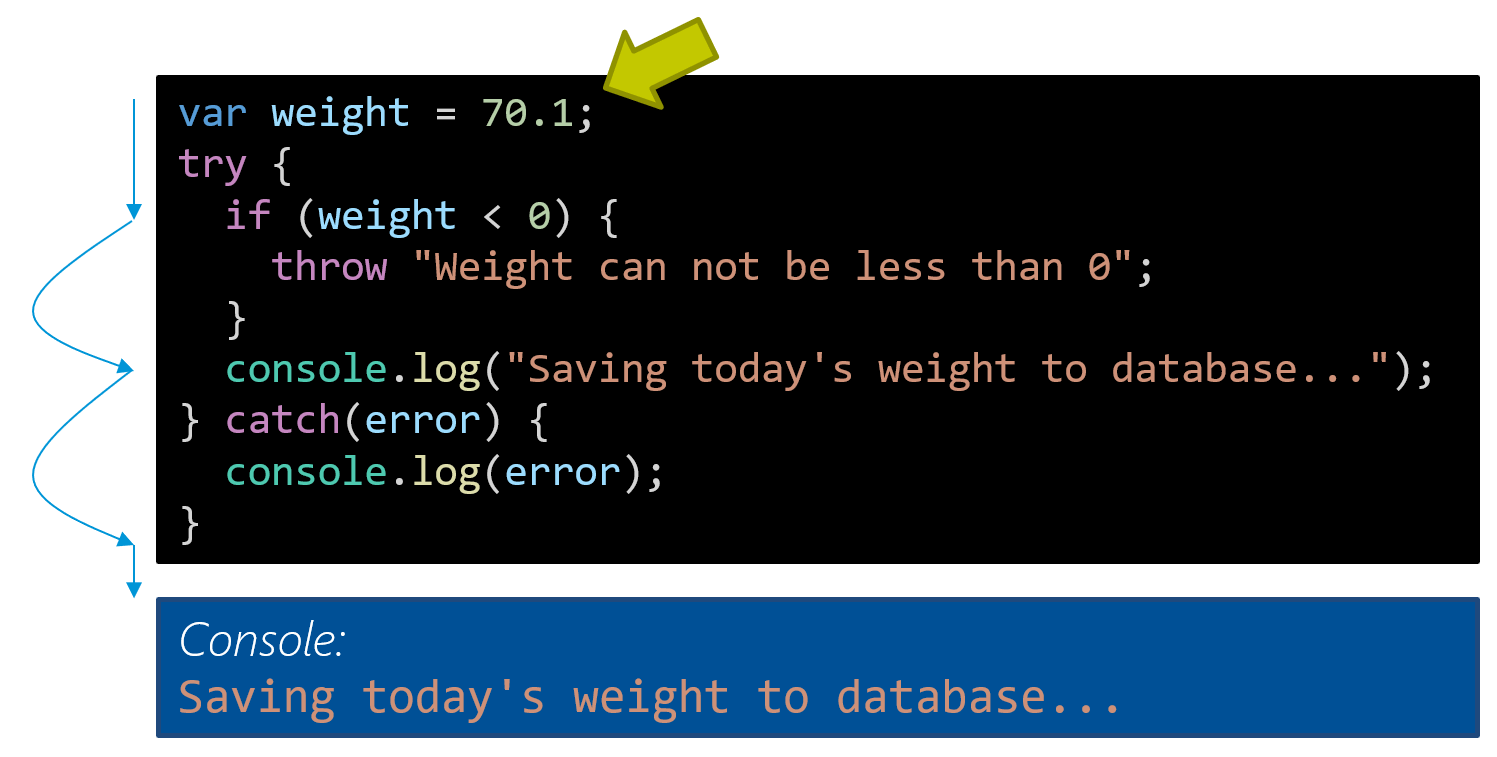 Asynchronous Javascript With Promises Amp Async Await In
Asynchronous Javascript With Promises Amp Async Await In
 How Javascript Async Await Works And How To Use It
How Javascript Async Await Works And How To Use It
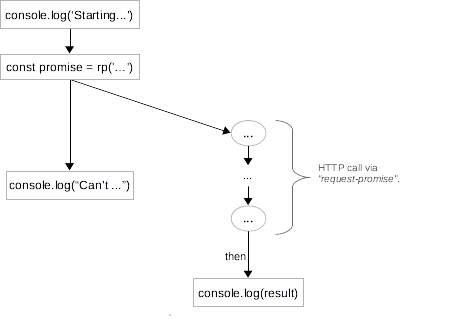 Await And Async Explained With Diagrams And Examples
Await And Async Explained With Diagrams And Examples
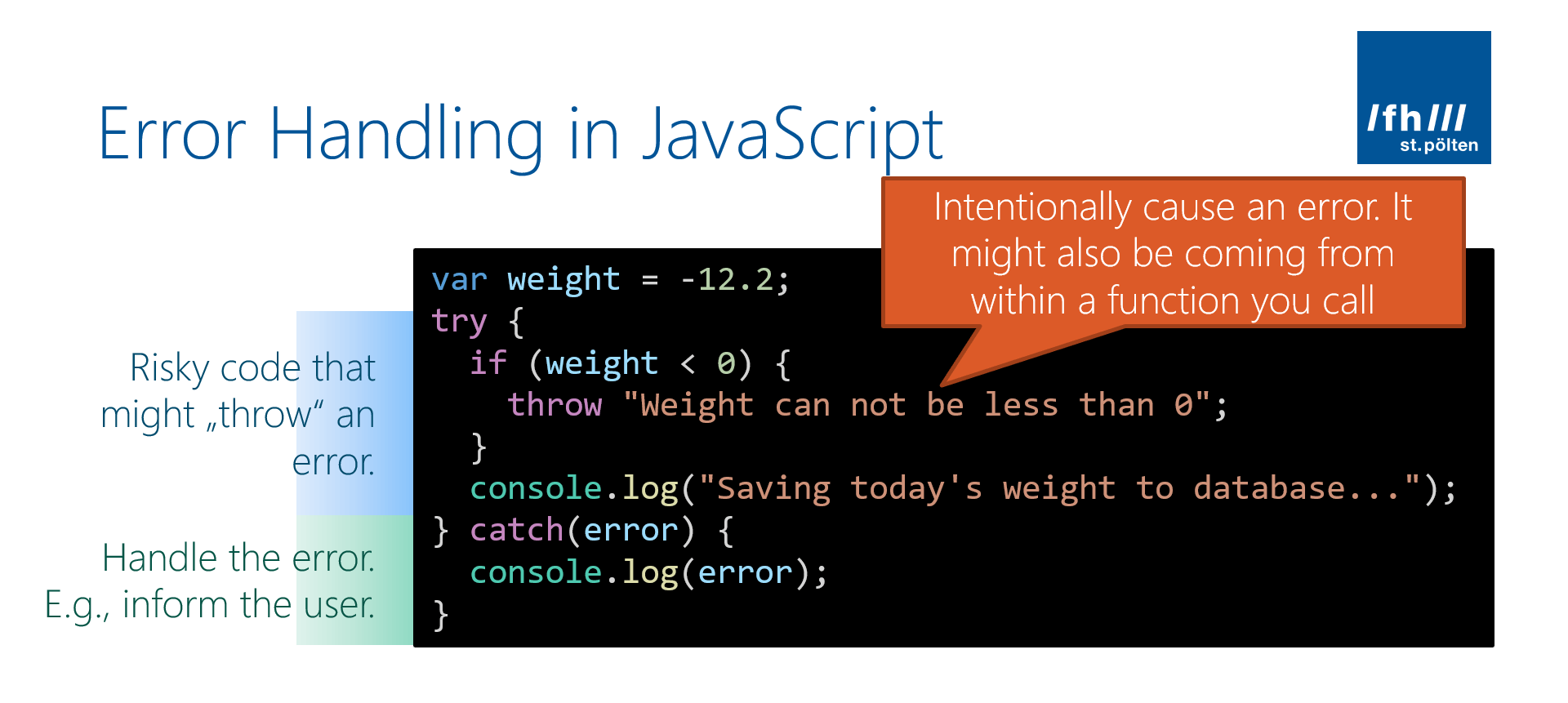 Asynchronous Javascript With Promises Amp Async Await In
Asynchronous Javascript With Promises Amp Async Await In
 Refactor This Redundant Await On A Non Promise Sonarlint
Refactor This Redundant Await On A Non Promise Sonarlint
 Javascript Loops How To Handle Async Await
Javascript Loops How To Handle Async Await
 How To Rewrite A Callback Function In Promise Form And Async
How To Rewrite A Callback Function In Promise Form And Async
Faster Async Functions And Promises V8
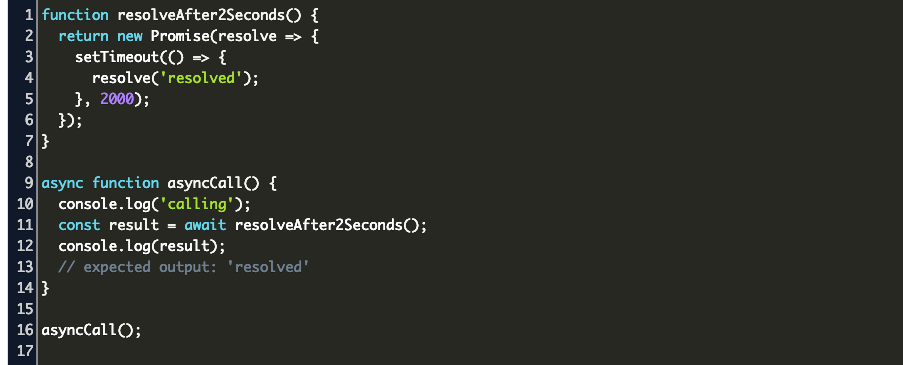 Calling An Async Function From Another Async Function Js Code
Calling An Async Function From Another Async Function Js Code

0 Response to "20 Javascript Async Function Promise"
Post a Comment