26 How To Define Callback Function In Javascript
A callback function is a lucky function that gets passed into the enclosing higher-order function: The callback function gets executed (called) inside the higher order function, but not necessarily immediately. It gets "called back" — hence the name — at whatever point serves the code's purpose. May 03, 2020 - Node JS handle all asynchronous calls via callback. Hey wait, what is callback..?? well, callbacks in the general definition are just…
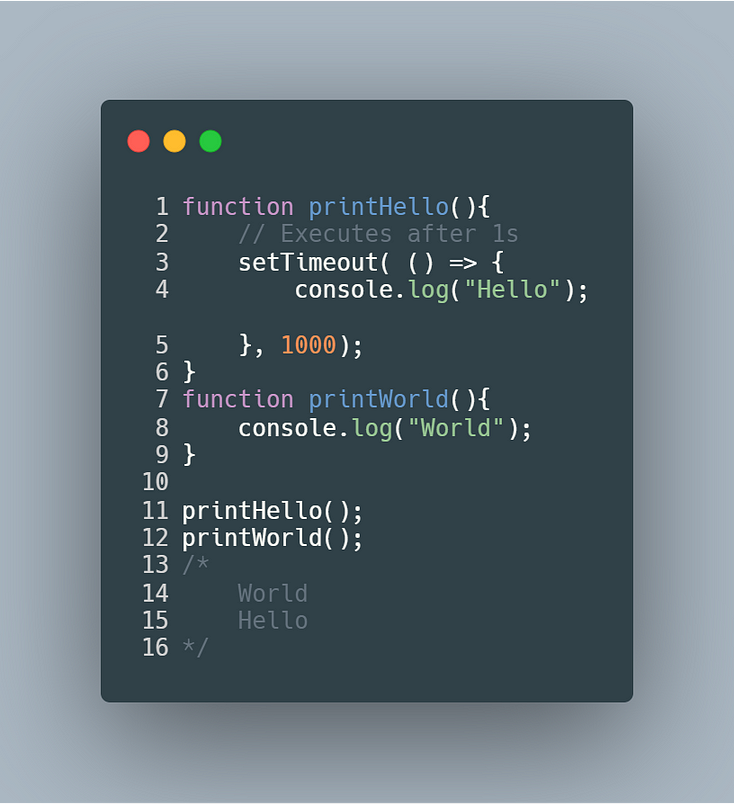 What Is Callback Function In Javascript How It Is Replaced
What Is Callback Function In Javascript How It Is Replaced
To use the arguments inside of ... when defining the function · The variables and arguments must be in expected order. That is, the first argument gets assigned to the first variable. ... The number 100 would be assigned to the variable parameterOne. The number 200 would be assigned to the variable parameterTwo. ... A JavaScript Callback is a function ...

How to define callback function in javascript. Callback Functions A callback function is a function that is passed as an argument to another function, to be "called back" at a later time. A function that accepts other functions as arguments is called a higher-order function, which contains the logic for when the callback function gets executed. Syntax: Above is an example of a callback variable in JavaScript function. "geekOne" accepts an argument and generates an alert with z as the argument. "geekTwo" accepts an argument and a function. "geekTwo" moves the argument it accepted to the function to passed it to. "geekOne" is the callback function in this case. In this tutorial, you will learn about JavaScript callback functions with the help of examples.
Simply put, a callback function is a function that passed as an argument of another function. Later on, it will be involved inside the outer function to complete some kind of action. A higher-order function is a function that takes a function as its argument, or returns a function as a result. Callback function A callback function is a function passed into another function as an argument, which is then invoked inside the outer function to complete some kind of routine or action. Here is a quick example: firstfunction (callbackfunction (param)); That will execute callbackfunction immediately and pass the return value from executing it as the argument to firstfunction which is unlikely what you want.
A callback is a function that is passed as an argument to another function. Usually, the callback is then invoked at some point within the outer function. Note: The outer function that takes in a callback is called a higher-order function. JavaScript Callbacks A callback is a function passed as an argument to another function. Using a callback, you could call the calculator function (myCalculator) with a callback, and let the calculator function run the callback after the calculation is finished: The function receives an array as first argument and a callback function as second argument. While the function itself iterates over the array, it pulls out every item of the array and passed it to the callback function. If the callback function returns true, the item is added to the filtered list.
Feb 02, 2016 - Inside of function two, we run ... we run callback2 with variable 2. Let's take a look at the code in the JavaScript Console to see how it functions. First we start in the browser with the Developer tools open and the JavaScript Console ready to go. ... FunctionOne is defined so that it ... Jul 03, 2020 - Your snippet is the best example to understand how apply works in Javascript Callbacks. ... Checking if it’s defined & a function is an extra, unneeded step. A closure is the combination of a function bundled together (enclosed) with references to its surrounding state (the lexical environment). In other words, a closure gives you access to an outer function's scope from an inner function. In JavaScript, closures are created every time a function is created, at function creation time.
Introduction to JavaScript Callback Function JavaScript Callback function are the most special and important function of JavaScript whose main aim is to pass another function as a parameter where the callback function runs which means one function when infused into another function with the parameters is again called as per the requirement. A JavaScript Promise object contains both the producing code and calls to the consuming code: Promise Syntax let myPromise = new Promise(function(myResolve, myReject) { A callback is a term that refers to a coding design pattern where you can pass a function to another function. So that within the called function, it can "call back" the function you passed to it. Do you use a callback in JavaScript before ?!. Often seen in many scenarios.
Jun 10, 2020 - As we can see, the callback function here has no name and a function definition without a name in JavaScript is called as an “anonymous function”. This does exactly the same task as the example above. ... If you prefer, you can also write the same callback function as an ES6 arrow function, ... Callback functions in JavaScript Callback functions are frequently used in JavaScript programming. These can be functions that are called when a button is clicked or content that is set on a time delay with the setTimeout () function. A simple example of a callback function in JavaScript is an ordinary button: As we know, in JavaScript, functions are objects. Because of this, functions can take functions as arguments, and other functions can also return it. Functions that take the additional function as a parameter are called higher-order functions, and the function which passes as an argument is called a callback function
Sep 12, 2018 - Let us try to understand a callback function in depth and how to go about using the same in our JavaScript code.What is a callback function?There is no standard definition of what a callback function is. But, callback functions are very common in asynchronous programming. Any function that is passed as an argument and subsequently called by the function that receives it, is called a callback function. That's a lot of words. Lets look at some examples to break ... Defining the interface for a Function or Callback is actually very similar to this; in fact, all you do is omit the "new" keyword, leaving in the callback signature and the return type. For example, here's the interface for a typical Node.js-style callback that accepts an error and / or a result:
In JavaScript, functions are objects; that is, functions are of the type Object and they can be used in a manner like any other object since they are in fact objects themselves. They can be stored in variables, passed as arguments to functions, created within functions, and returned from functions. More complexly put: In JavaScript, functions are objects. Because of this, functions can take functions as arguments, and can be returned by other functions. Functions that do this are called higher-order functions. Any function that is passed as an argument is called a callback function. When calling the callback function, we could use it like below: consumingFunction(callbackFunctionName) Example: // Callback function only know the action, // but don't know what's the data. function callbackFunction(unknown) { console.log(unknown); } // This is a consuming function. function getInfo(thenCallback) { // When we define the function we only know the data but not // the action.
A callback is a function called at the completion of a given task; this prevents any blocking, and allows other code to be run in the meantime. The Node.js way to deal with the above would look a bit more like this: Apr 28, 2021 - This article gives a brief introduction to the concept and usage of callback functions in the JavaScript programming language. Functions are ObjectsThe first thing we need to know is that in Javascript, functions are first-class objects. As such, we can work with them in the same way we work with What are callbacks In JavaScript, a callback is a function passed into another function as an argument to be executed later. Suppose that you the following numbers array: let numbers = [ 1, 2, 4, 7, 3, 5, 6 ];
Well organized and easy to understand Web building tutorials with lots of examples of how to use HTML, CSS, JavaScript, SQL, Python, PHP, Bootstrap, Java, XML and more. A callback is a function that is invoked after a function has finished its execution. As JavaScript is an event-driven language, it does not wait for a function to finish its execution before moving on to the next one. Callbacks make it possible to make a function execute only after another function has finished executing. Dec 02, 2014 - This is my favourite javascript site 🙂 Keep it up with the good work! ... Great article. Thanks you. ... Fantastic writeup! This concise article has really helped me understand how important callback functions are. I shall definitely be coming back here on a regular basis.
The function keyword can be used to define a function inside an expression. ... Synchronous callback function runs like normal JavaScript one by one in order while the Asynchronous callback ... The callback function as the name implies is the function that gets executed after the other function has finished executing. A callback is a function that is passed as a parameter into another function to be executed later to perform some operation. The callback function is executed asynchronously. When to use callback functions in JavaScript? In order to use a callback function, we need to perform some sort of task that will not be able to display results immediately. To emulate this behavior, we are using javascript's setTimeout () function. That function will take 2 seconds to display the message "Hi, there" to the console window.
The callback function is a function that is passed as an argument to another JavaScript function. That callback function is executed inside of the function it was passed into. Using an arrow function in render creates a new function each time the component renders, which may break optimizations based on strict identity comparison. Is it OK to use arrow functions in render methods? Generally speaking, yes, it is OK, and it is often the easiest way to pass parameters to callback functions.
 Mastering This In Javascript Callbacks And Bind Apply
Mastering This In Javascript Callbacks And Bind Apply
 Callback Functions In Javascript
Callback Functions In Javascript
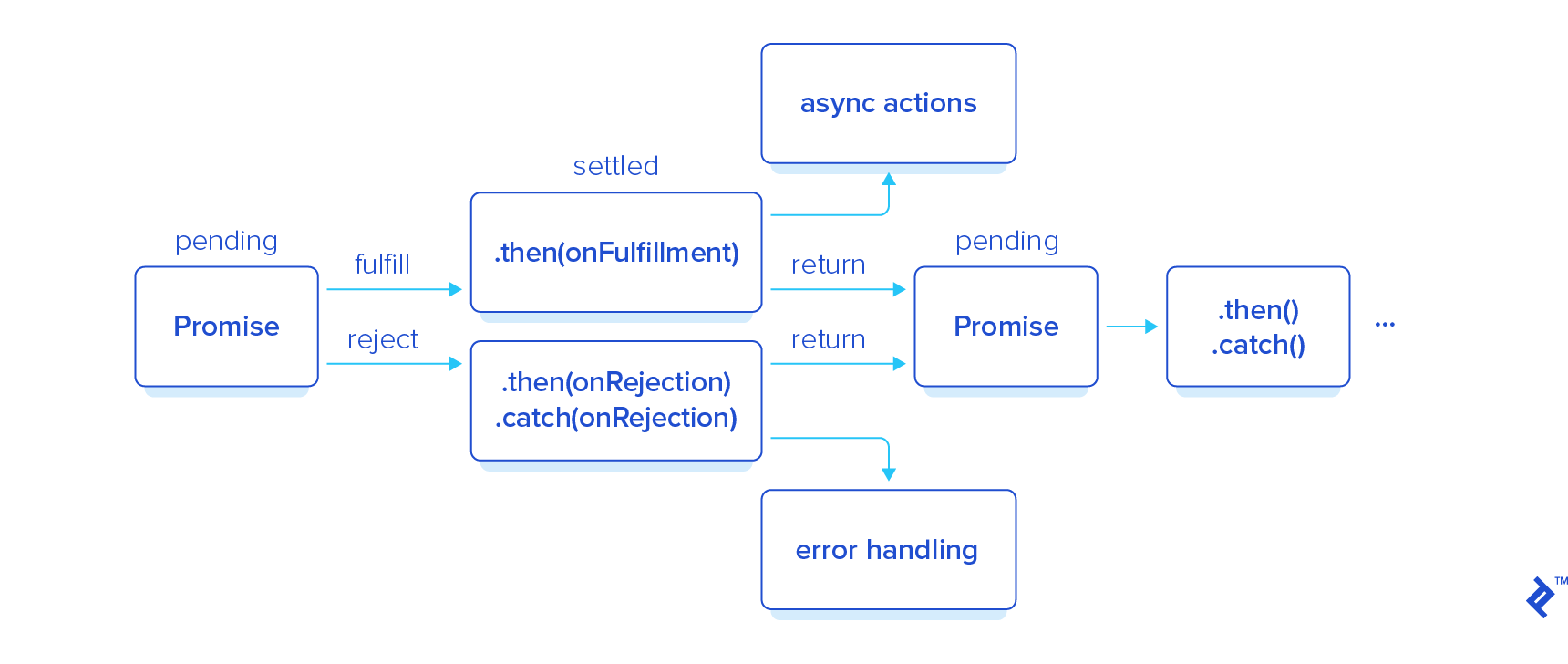 Asynchronous Javascript Async Await Tutorial Toptal
Asynchronous Javascript Async Await Tutorial Toptal
 Javascript What The Heck Is A Callback By Brandon Morelli
Javascript What The Heck Is A Callback By Brandon Morelli
 Exploring Client Callback Code Wala
Exploring Client Callback Code Wala
 Javascript Callback Functions What Are Callbacks In Js And
Javascript Callback Functions What Are Callbacks In Js And
 What Is A Callback Function In Javascript
What Is A Callback Function In Javascript
 Understand Javascript Callback Functions And Call By Value
Understand Javascript Callback Functions And Call By Value
 Resolving Unhandled Rejection Typeerror Callback Is Not A
Resolving Unhandled Rejection Typeerror Callback Is Not A
 Callback Function For The Api Link Is Not Defined Stack
Callback Function For The Api Link Is Not Defined Stack
 How Does Callback Work In Javascript Scotch Io
How Does Callback Work In Javascript Scotch Io
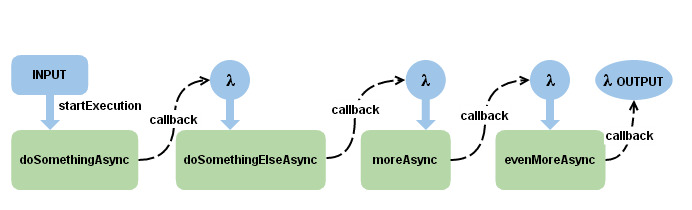 The Callback Syndrome In Node Js
The Callback Syndrome In Node Js
 A Practical Guide To Es6 Arrow Functions By Arfat Salman
A Practical Guide To Es6 Arrow Functions By Arfat Salman
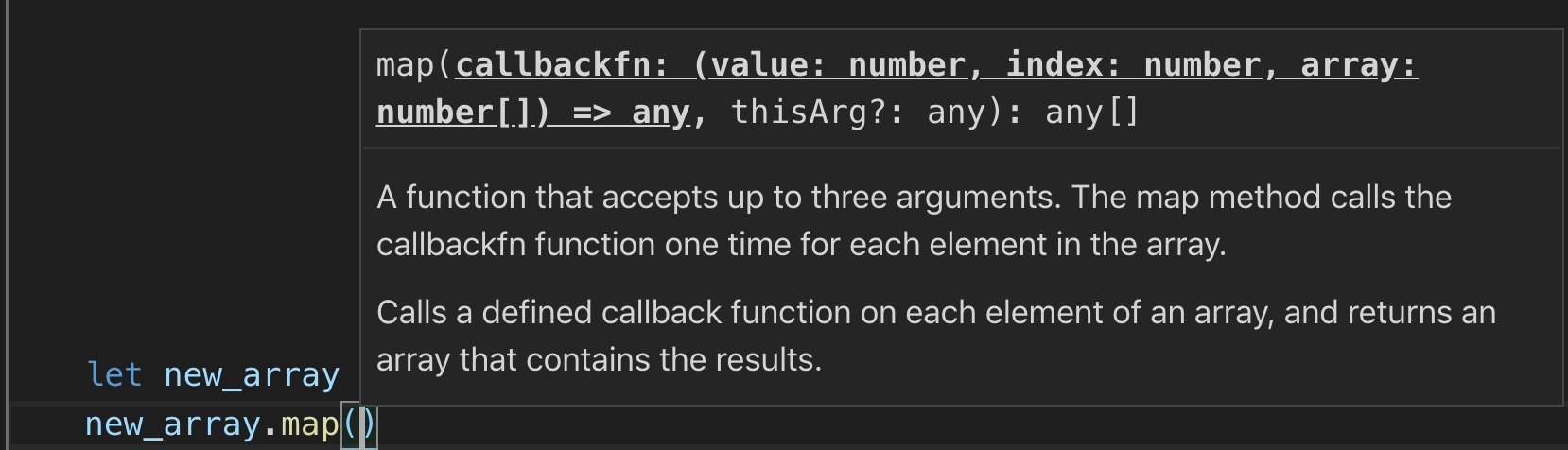 What Are Callbacks A Beginner S Guide By Chris Truong
What Are Callbacks A Beginner S Guide By Chris Truong
 Callback Hell Bmc Software Blogs
Callback Hell Bmc Software Blogs
 Callback Vs Promises Vs Async Await Loginradius Engineering
Callback Vs Promises Vs Async Await Loginradius Engineering
 How To Explain Callbacks In Plain English How Are They
How To Explain Callbacks In Plain English How Are They
 Access The Original Calling Context In A Callback Function In
Access The Original Calling Context In A Callback Function In
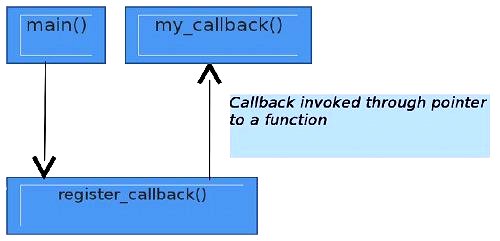 Function Pointers And Callbacks In C An Odyssey
Function Pointers And Callbacks In C An Odyssey
 Defining A Callback Function To Display Values In Labels
Defining A Callback Function To Display Values In Labels
 Mastering This In Javascript Callbacks And Bind Apply
Mastering This In Javascript Callbacks And Bind Apply
 Tools Qa What Are Callback Functions In Javascript And How
Tools Qa What Are Callback Functions In Javascript And How
 Understand Callback Functions In Javascript Through Examples
Understand Callback Functions In Javascript Through Examples
 Tools Qa What Are Callback Functions In Javascript And How
Tools Qa What Are Callback Functions In Javascript And How
0 Response to "26 How To Define Callback Function In Javascript"
Post a Comment