28 Javascript Get Precision Of Number
The toPrecision() method in TypeScript is used to return the string representation in exponential or fixed-point to the specified precision.. Syntax: number.toPrecision( [ precision ] ) Parameter: It represents an integer value specifying the number of significant digits. Return Value: The toPrecision() method in TypeScript returns a string representing a Number in fixed-point or exponential ... JavaScript numbers have 64-bit precision, which is also called double precision (type double in some programming languages). ... You get a number in exponential notation: > 1234567890123456789012..toFixed() '1.2345678901234568e+21' > 1234567890123456789012..toString() '1.2345678901234568e+21' ...
Concurrency Model And The Event Loop Javascript Mdn
A Number is a floating point number with a limited precision of 64 bits, about 16 digits. The largest integer number which can be represented by a JavaScript Number is +/- 9007199254740992 ( +/- 2^53 ). Because of the limited precision of floating point numbers round-off errors can occur during calculations. This can be easily demonstrated:

Javascript get precision of number. Unlike many other programming languages, JavaScript does not define different types of numbers, like integers, short, long, floating-point etc. JavaScript numbers are always stored as double precision floating point numbers, following the international IEEE 754 standard. Enough said about limitations, precision, and the cross-browser issue, let's move on to a example, that'll show you how to get a pseudo-random number between 0 and 1. The random number generator is seeded from the current time, as in Java. When it comes to floating values, the JavaScript can handle precision upto 16 decimal units. The smallest number in JavaScript is 5e-324. It is like the smallest block that adds up to make numbers and therefore, we can't reach a perfect floating result when performing floating operations.
IDs in Twitter are 64 bits long. While JSON is a text format and can represent integers of arbitrary size, you lose precision in JavaScript once numbers are parsed: > parseInt("10765432100123456789") 10765432100123458000 Therefore, if you want to preserve the value of an ID in JavaScript, you need to store it in a string. A string representing a Number object in fixed-point or exponential notation rounded to precision significant digits. See the discussion of rounding in the description of the Number.prototype.toFixed () method, which also applies to toPrecision (). If the precision argument is omitted, behaves as Number.prototype.toString (). Difficulty Level : Medium. Last Updated : 13 May, 2021. Given a double value val, the task is to set its precision value to a specific decimal places. Examples: Input: val = 1 Output: 1.0000 Upto 4 decimal places Input : 12.5 Output : 12.500000 Upto 6 decimal places. Approach: Using String.format ()
Once you're all done doing the math, if you need a native JavaScript Number (e.g. to return to a client), you can just instantiate one using the Decimal: const returnValue = { finalAmount: Number (finalAmount) }; As it turns out, the library we're using does this for us when we put a Decimal object into a model slot that expects a Number ... JavaScript Number: Summary. JavaScript number holds the value of numbers in JavaScript. It can be written as hexadecimal. After the decimal point, a number JavaScript can hold up to 17 digits, but only up to 15 until it loses precision. If the number is too big for a JavaScript program to compile, it will return Infinity. JavaScript has built-in methods to format a number to a certain precision. They are toFixed and toPrecision, and are part of the Number object. Any browser that supports ECMAScript version 3 should support toFixed and toPrecision. This roughly equates to Netscape 6.0 and above and IE 5.5 and above.
The toPrecision() method formats a number to a specified length. A decimal point and nulls are added (if needed), to create the specified length. In JavaScript, toPrecision () is a Number method that is used to convert a number to a specified precision ( rounding the result where necessary) and return its value as a string. Because toPrecision () is a method of the Number object, it must be invoked through a particular instance of the Number class. You can't. All Numbers have the standard JavaScript precision. If you had "126.01" and "1.3450" (i.e. Strings), then you could do something like: console.log("The precision of " + str_number + " is " + str_number.split('.')[1].length + " decimal places"); Or use 0 if you want significant figures instead.
Regular numbers in JavaScript are stored in 64-bit format IEEE-754, also known as "double precision floating point numbers". These are numbers that we're using most of the time, and we'll talk about them in this chapter. BigInt numbers, to represent integers of arbitrary length. The toPrecision () method in Javascript is used to format a number to a specific precision or length. If the formatted number requires more digits than the original number then decimals and nulls are also added to create the specified length. In JavaScript, numbers are implemented in double-precision 64-bit binary format IEEE 754 (i.e., a number between ±2^−1022 and ±2^+1023, or about ±10^−308 to ±10^+308, with a numeric precision of 53 bits). Integer values up to ±2^53 − 1 can be represented exactly.
Sometimes you might end up with a number that is stored as a string type, which makes it difficult to perform calculations with it. This most commonly happens when data is entered into a form input, and the input type is text.There is a way to solve this problem — passing the string value into the Number() constructor to return a number version of the same value. Therefore, to get a finer level of precision via decimals, there must be a scheme within the operating bit range to represent such numbers. In the case with JavaScript, the scheme is 64 bit and Figure 2 illustrates how the scheme is divided between the left- and right-hand portions of the decimal point as well as the sign (positive or negative). 18/11/2017 · In Javascript, all numbers are encoded as double precision floating point numbers, following the international IEEE 754 standard. This format stores numbers in 64 bits, where the number, the fraction (AKA mantissa), is stored in bits 0 to 51, the exponent in bits 52 to 62, and the sign in bit 63. Floating-point numbers are represented as binary ...
The Number is a primitive data type used for positive or negative integer, float, binary, octal, hexadecimal, and exponential values in JavaScript. The Number type in JavaScript is double-precision 64 bit binary format like double in C# and Java. It follows the international IEEE 754 standard. For example, Emscripten currently compiles C++ float operations to JavaScript number operations. Technically, Emscripten could use Float32Array loads/stores after every operation to throw away the extra float64 precision, but this would be a big slowdown, so fidelity is sacrificed for performance. Although it's quite rare for this difference to ... Math.abs (): The Math.abs () function in JavaScript is used to return the absolute value of a number. It takes a number as its parameter and returns its absolute value.
The floor () method rounds a number DOWNWARDS to the nearest integer, and returns the result. If the passed argument is an integer, the value will not be rounded. In previous articles I explained jQuery upload images without postback using handler file, JavaScript get whole number division using Math.ceil function, JavaScript limit number characters in multiline textbox, jQuery fixed header on window scroll with example, jQuery currency conversion as per exchange rates and many articles relating to ... Using toFixed () Method: The number of decimal places in float values can be set using the toFixed () method. This method converts the number into a string, keeping the specified number of digits after the point. If no value is passed as a parameter, then it takes 0 as default value i.e. no decimal points are displayed.
The reasoning behind that number is that JavaScript uses double-precision floating-point format numbers as specified in IEEE 754 and can only safely represent integers between - (2^53 - 1) and 2^53 - 1. Safe in this context refers to the ability to represent integers exactly and to correctly compare them. The JavaScript number toPrecision () method returns the string representing a number of specified precision.
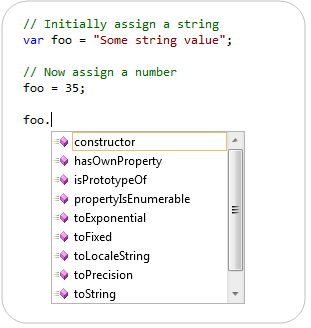 Scottgu S Blog Javascript Intellisense Improvements With Vs
Scottgu S Blog Javascript Intellisense Improvements With Vs
 Javascript Tofixed Learn The Syntax Of Javascript Tofixed
Javascript Tofixed Learn The Syntax Of Javascript Tofixed
Javascript Return Number Types With Precision
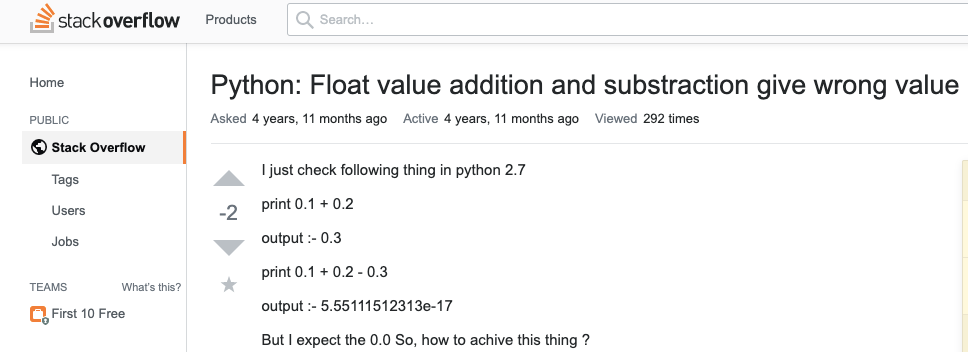 Why Is 0 1 0 2 Not Equal To 0 3 In Most Programming
Why Is 0 1 0 2 Not Equal To 0 3 In Most Programming
 Write A Javascript Function Sigloss X Y That Chegg Com
Write A Javascript Function Sigloss X Y That Chegg Com
 Mastering Javascript Fundamentals Isstring And String
Mastering Javascript Fundamentals Isstring And String
 Javascript Number Format Simple Method Used For Js Number
Javascript Number Format Simple Method Used For Js Number
.png) Mathematical Functions And Converting Data Types In Groovy
Mathematical Functions And Converting Data Types In Groovy
 Rounding A Number To A Specific Precision In Javascript
Rounding A Number To A Specific Precision In Javascript
 Let S Talk About Big Numbers In Javascript By Rolando
Let S Talk About Big Numbers In Javascript By Rolando
Losing Precision In Converting Timestamp And Int64 To
 Inserting Javascript Code Using The Javascript Step
Inserting Javascript Code Using The Javascript Step
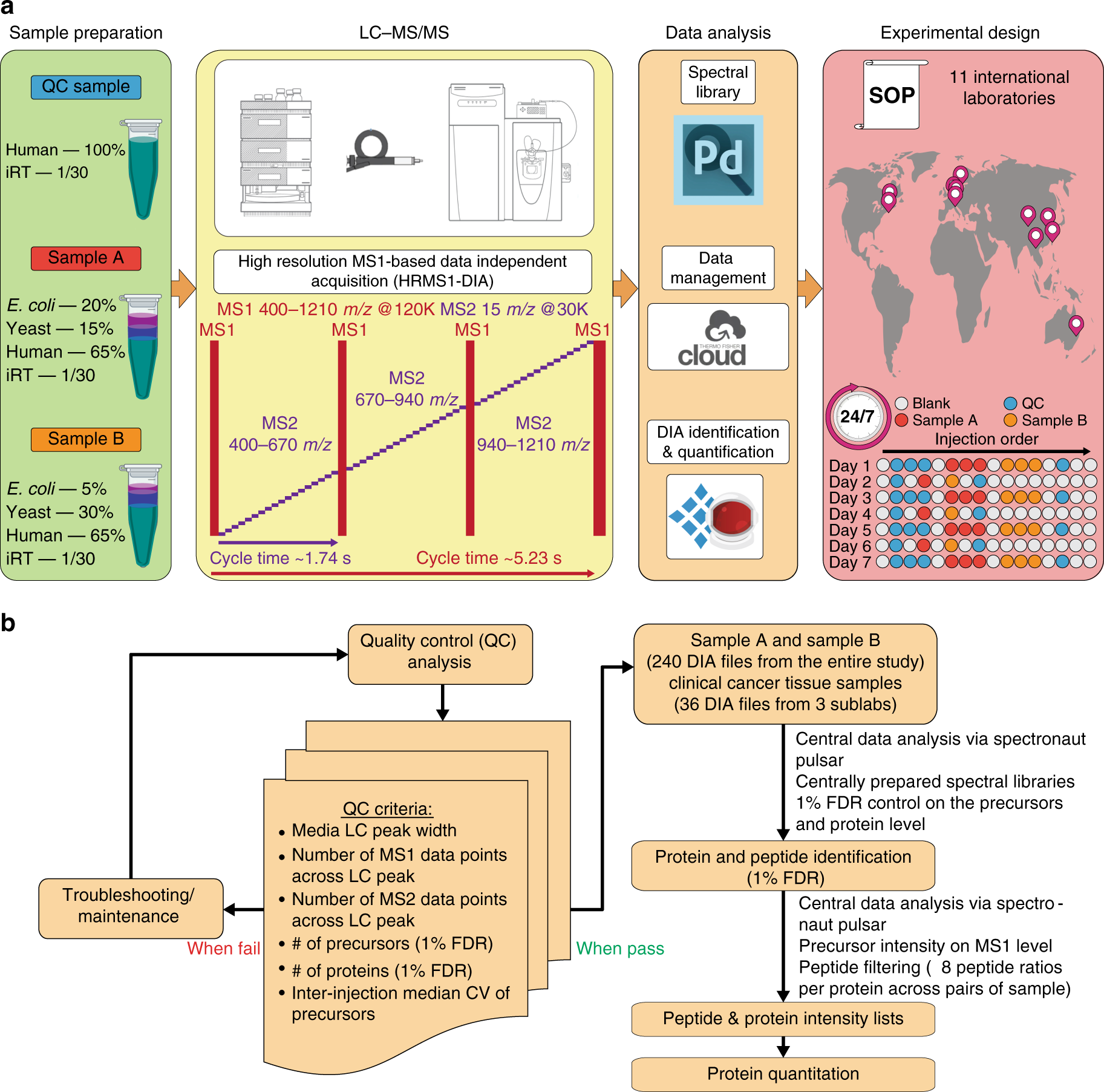 Standardization And Harmonization Of Distributed Multi Center
Standardization And Harmonization Of Distributed Multi Center
Bigint Arbitrary Precision Integers In Javascript V8
 4 Ways To Calculate Precision Wikihow
4 Ways To Calculate Precision Wikihow
 4 Ways To Calculate Precision Wikihow
4 Ways To Calculate Precision Wikihow
 Precision Recall Amp Confusion Matrices In Machine Learning
Precision Recall Amp Confusion Matrices In Machine Learning
 Mastering Javascript Fundamentals Accountingjs Better
Mastering Javascript Fundamentals Accountingjs Better
Javascript Return Number Types With Precision
 Javascript Length Of Number Html Example Code
Javascript Length Of Number Html Example Code
 Overcoming Javascript Numeric Precision Issues
Overcoming Javascript Numeric Precision Issues
 Javascript Rangeerror Precision Is Out Of Range Geeksforgeeks
Javascript Rangeerror Precision Is Out Of Range Geeksforgeeks
 How To Round To A Certain Number Of Decimal Places In
How To Round To A Certain Number Of Decimal Places In
 Javascript Number Issafeinteger Method Geeksforgeeks
Javascript Number Issafeinteger Method Geeksforgeeks


0 Response to "28 Javascript Get Precision Of Number"
Post a Comment