29 Javascript Define Class Prototype
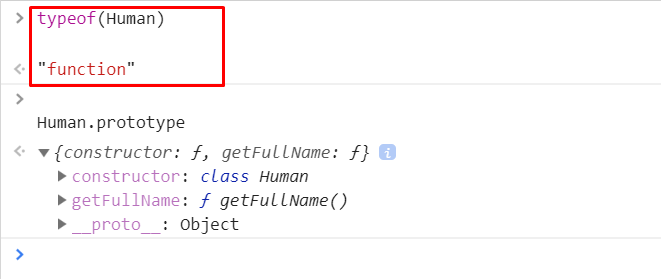
Inheritance in JS is three lines: call the super class, set the prototype to the superclass and reset the constructor back to the child class. The End. Writing methods like this is a complete waste of time. Javascript is a prototype-based language, When we create a function using JavaScript, the engine adds a prototype property inside a function and the prototype basically is an object. Also, it is called a prototype object.
A value stored on the prototype provides a default value for that property. If you subsequently write a value to that property, the instance will acquire that new value, hiding the value that's on the prototype, which will be left intact. In the context of the code you've now added to the question: MyCircle.prototype.radius; does absolutely ...

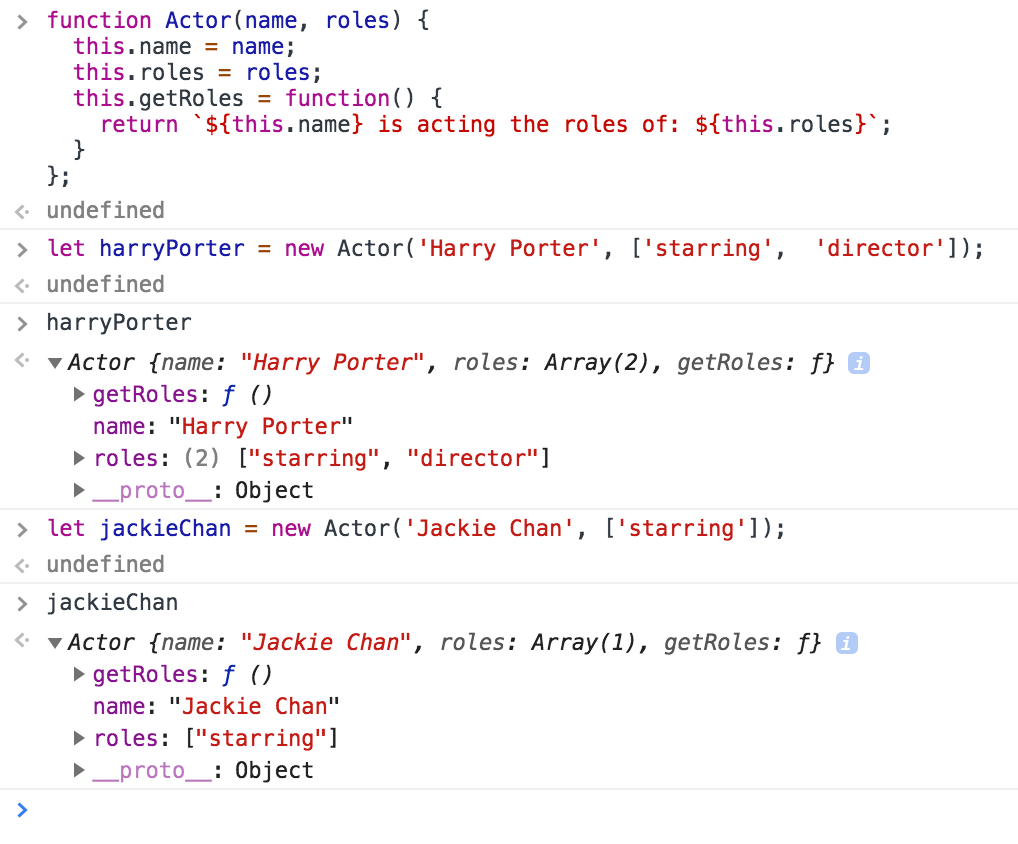
Javascript define class prototype. A JavaScript class is not an object. It is a template for JavaScript objects. JavaScript is often described as a prototype-based language — to provide inheritance, objects can have a prototype object, which acts as a template object that it inherits methods and properties from. An object's prototype object may also have a prototype object, which it inherits methods and properties from, and so on. In JavaScript, a prototype can be used to add properties and methods to a constructor function. And objects inherit properties and methods from a prototype. For example, // constructor function function Person () { this.name = 'John', this.age = 23 } // creating objects const person1 = new Person (); const person2 = new Person (); // adding ...
As you know we can define getters and setters in JS using defineProperty().I've been stuck when trying to extend my class using defineProperty().. Here is an example code: I have an array of fields which must be added to a object Prototype JavaScript Framework | Defining classes and inheritance Defining classes and inheritance In early versions of Prototype, the framework came with basic support for class creation: the Class.create () method. Until now the only feature of classes defined this way was that the constructor called a … To define a class in JS, you use a function (Figure 1) and in the context of object creation, we call this function a constructor. ... Once Javascript's prototype search reaches null, ...
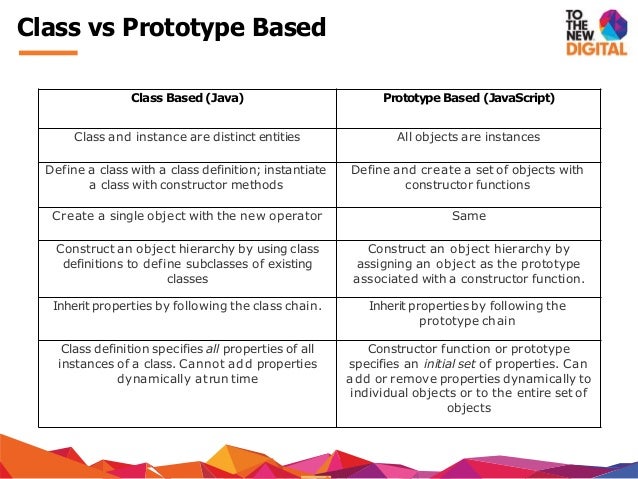
With the ES6 syntax, JavaScript has been provided the feature to create classes. However, the concept of true classes does not exist in JavaScript but it is emulated through prototype and the class syntax is just syntactic sugar around it. Therefore, understanding this behavior is important to realize the convenience and limitations of ES6 classes. 4/4/2018 · Let’s begin by a reminder of the definition of class in Javascript according to MDN : J avaScript classes, introduced in ECMAScript 2015, are primarily syntactical sugar over JavaScript’s existing... We want to make this open-source project available for people all around the world. Help to translate the content of this tutorial to your language!
This tutorial discusses the differences in syntax between creating objects in javascript with the class keyword or with the prototype methods.Examples are gi... Classes. The concept of classes was introduced in JavaScript in ES6 (ECMA2015). In the object-oriented programming paradigm, a class is a blueprint for creating objects with properties and methods while encapsulating the implementation details from the user. However, the concept of true classes does not exist in JavaScript. Every JavaScript function has prototype property. You could call this the function's prototype, although some would say that's confusing. In any case, every object that is constructed through the function using new syntax will have a [ [Prototype]] linking to the function's prototype property. // PascalCase is just a convention
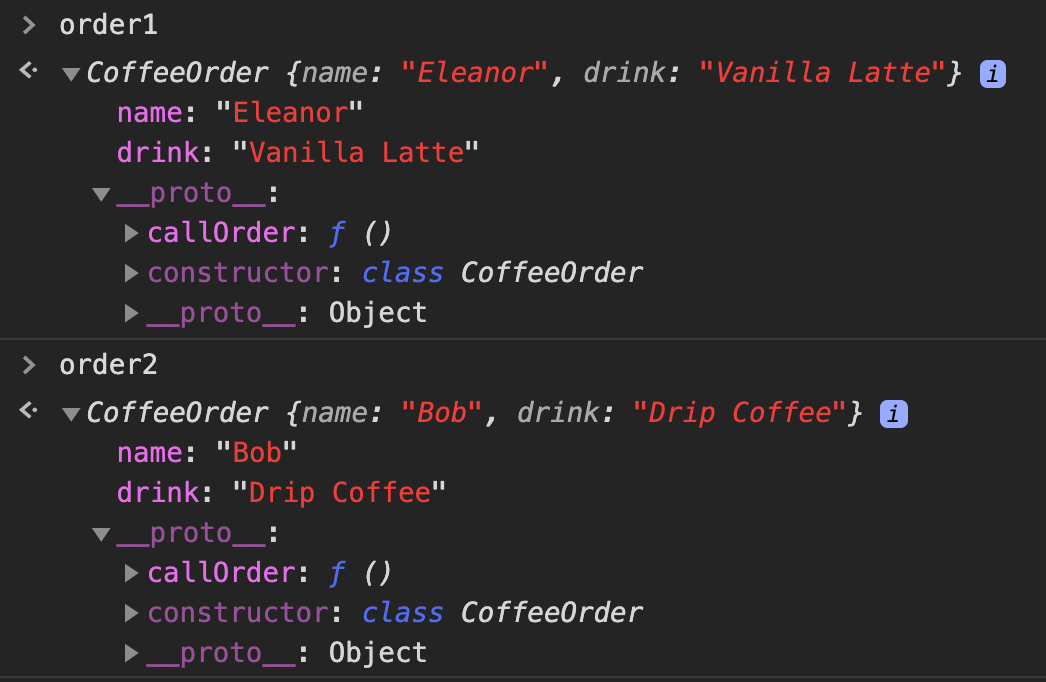
The class expression is one way to define a class in ECMAScript 2015. Similar to function expressions, class expressions can be named or unnamed. If named, the name of the class is local to the class body only. JavaScript classes use prototype-based inheritance. method() here is a function property added to an another function protype (here Class.prototype). You can either directly access by class name or by an object/instance ( new Class() ). Added advantage - this way of method() definition will create only one copy of method() in the memory and will be shared across all the object's/instance's created from the Class 10/1/2020 · As far as I know, there are two way to define the method, but most of the JavaScript engineer (maybe includes you) will recommend define it via prototype. function Family(){ this.member = { me: "Dennis" }; } Family.prototype.showMe = function(){ console.log(this.member.me); } const family = new Family(); family.showMe(); // Dennis
JavaScript Class v Prototype As noted above, a class in JavaScript is merely syntactic sugar to make things easier for feature developers working in JavaScript. While the approach allows for a... JavaScript is a prototype-based language, and functions differently than the traditional class-based paradigm that many other object-oriented languages use. In this tutorial, we learned how prototypes work in JavaScript, and how to link object properties and methods via the hidden [[Prototype]] property that all objects share. We also learned ... Classes are a template for creating objects. They encapsulate data with code to work on that data. Classes in JS are built on prototypes but also have some syntax and semantics that are not shared with ES5 class-like semantics.
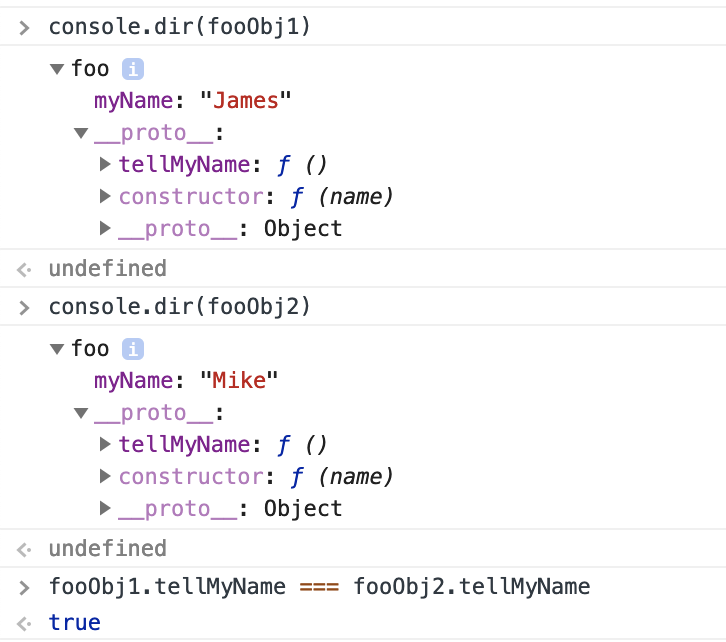
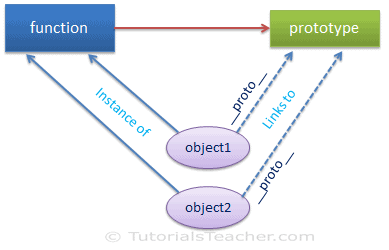
JavaScript objects have a link to a prototype object. When trying to access a property of an object, the property will not only be sought on the object but on the prototype of the object, the prototype of the prototype, and so on until either a property with a matching name is found or the end of the prototype chain is reached. JavaScript classes, introduced in ECMAScript 2015 or ES6, are primarily the syntactical sugar over the JavaScript is an existing prototype-based inheritance. The class syntax does not introduce the new object-oriented inheritance model to JavaScript. Define a class in Javascript. One way to define the class is by using the class declaration. Classes are declared with the class keyword. We will use function expression syntax to initialize a function and class expression syntax to initialize a class. const x = function() {} Copy. const y = class {} Copy. We can access the [ [Prototype]] of an object using the Object.getPrototypeOf () method.
It's important to note that there are no classes in JavaScript. Functions can be used to somewhat simulate classes, but in general JavaScript is a class-less language. Everything is an object. And when it comes to inheritance, objects inherit from objects, not classes from classes as in the "class"-ical languages. 1. Using a function All JavaScript objects created by assigning an identifier the value of object literals share the same prototype object. This means that their private prototype property points to the same object in the prototype chain and hence, inherits its properties. This object can be referred to in JavaScript code as Object.prototype. The Object.prototype is on the top of the prototype inheritance chain: Date objects, Array objects, and Person objects inherit from Object.prototype. Adding Properties and Methods to Objects Sometimes you want to add new properties (or methods) to all existing objects of a given type.
JavaScript is an object-based language based on prototypes, rather than being class-based. Because of this different basis, it can be less apparent how JavaScript allows you to create hierarchies of objects and to have inheritance of properties and their values. This chapter attempts to clarify the situation. The answer is Prototype. The prototype is an object that is associated with every functions and objects by default in JavaScript, where function's prototype property is accessible and modifiable and object's prototype property (aka attribute) is not visible. Every function includes prototype object by default. JavaScript classes, introduced in ECMAScript 2015, are primarily syntactical sugar over JavaScript's existing prototype-based inheritance. The class syntax does not introduce a new object-oriented inheritance model to JavaScript.
The result of this definition is about the same. So, there are indeed reasons why class can be considered a syntactic sugar to define a constructor together with its prototype methods.. Still, there are important differences. First, a function created by class is labelled by a special internal property [[IsClassConstructor]]: true.So it's not entirely the same as creating it manually.
 Better Javascript With Es6 Pt Ii A Deep Dive Into Classes
Better Javascript With Es6 Pt Ii A Deep Dive Into Classes
 How To Work With Classes In Typescript Packt Hub
How To Work With Classes In Typescript Packt Hub
 Javascript Prototype Vs Class Let S See How Classes In Js
Javascript Prototype Vs Class Let S See How Classes In Js
 Defining Methods In The Javascript Prototype Object
Defining Methods In The Javascript Prototype Object
 Classical Vs Prototypal Inheritance Dev Community
Classical Vs Prototypal Inheritance Dev Community
 Details Of The Object Model Javascript Mdn
Details Of The Object Model Javascript Mdn
 How Does Javascript Prototype Work Stack Overflow
How Does Javascript Prototype Work Stack Overflow
 Object Prototypes Learn Web Development Mdn
Object Prototypes Learn Web Development Mdn
Three Ways To Create A Javascript Class Learn Web Tutorials
 Javascript A Prototype Based Language By Abhinav Rai Medium
Javascript A Prototype Based Language By Abhinav Rai Medium
 Using Prototype Vs This In A Javascript Class Can Help
Using Prototype Vs This In A Javascript Class Can Help
 The Prototype Pattern Learning Javascript Design Patterns
The Prototype Pattern Learning Javascript Design Patterns
 Getting Started With Modern Javascript Classes Javascript
Getting Started With Modern Javascript Classes Javascript
 Javascript Prototype Vs Class Let S See How Classes In Js
Javascript Prototype Vs Class Let S See How Classes In Js
 Why You Should Use Prototype To Create Class Methods In
Why You Should Use Prototype To Create Class Methods In
Javascript Engine Fundamentals Optimizing Prototypes
 Demystifying Es6 Classes And Prototypal Inheritance Scotch Io
Demystifying Es6 Classes And Prototypal Inheritance Scotch Io

 Object Prototypes Learn Web Development Mdn
Object Prototypes Learn Web Development Mdn
 The Complete Guide To Javascript Classes
The Complete Guide To Javascript Classes
0 Response to "29 Javascript Define Class Prototype"
Post a Comment