34 Javascript Async Function Return Promise
async functions return promises. you need to do const data = await getData () -- unless you intend to set data at the top level of the code, in which case you can't await on getData and need to console.log from inside getData, or log from a different function that calls await getData () inside it. async function getData () { return await axios.get ('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode /posts'); } (async () => { console.log (await getData ()) }) ()
 Comparing Callbacks Promises And Async Await In Typescript
Comparing Callbacks Promises And Async Await In Typescript
We can also declare an async function which allows us to use the await keyword instead of then and returns a Promise, so we can chain then and catch to the call of the function:

Javascript async function return promise. To declare an async class method, just prepend it with async: class Waiter { async wait() { return await Promise.resolve(1); } } new Waiter() .wait() .then( alert); The meaning is the same: it ensures that the returned value is a promise and enables await. Compared with vanilla Javascript, the main difference of using Promise is async call is acting like any other functions: They return values, too! But what these functions return is a special type ... The code inside the function body is async and promise-based, therefore in effect, the entire function acts like a promise — convenient. Next, we call our function three times to begin the process of fetching and decoding the images and text and store each of the returned promises in a variable. Add the following below your previous code:
When, in reality, these two async functions are exactly the same because, according to the Mozilla Developer Network (MDN), any non- Promise return value is implicitly wrapped in a Promise.resolve () call: The return value of an async function is implicitly wrapped in Promise.resolve - if it's not already a promise itself (as in this example). If you do not return a promise explicitly from an async function, JavaScript automatically wraps the value in a Promise and returns it. The await keyword is for making the JavaScript function execution wait until a promise is settled (either resolved or rejected) and value/error is returned/thrown. Putting the keyword async before a function tells the function to return a Promise. If the code returns something that is not a Promise, then JavaScript automatically wraps it into a resolved promise with that value e.g when it returns an AsyncFunction object:
An async function simply implies that a promise will be returned and if a promise is not returned, JavaScript will automatically wrap it in a resolved promise with the return value in that function. That would look like writing return Promise.resolve ('hello'). Using async before a function definition makes the function return a promise that resolves to the function's return value, rather than returning normally. Using await before an asynchronous function call suspends the current function until the promise that it returns is resolved. Since the return value of an async function is always wrapped in Promise.resolve, return await doesn't actually do anything except add extra time before the overarching Promise resolves or rejects. The only valid exception is if return await is used in a try/catch statement to catch errors from another Promise-based function.
Note that async functions all return Promises, so when you use return you are just resolving the Promise. Wrapping up. Next time you need to convert a callback-based function to a Promise-based one or an async/await-based versions, use the visual diagrams from this post to quickly and easily do so. And if you need some code to play around with ... Our function has an async keyword on its definition (which says that this function will be an Async function, of course). It also has an await keyword, which we use to "wait for" a Promise. 9/2/2016 · The return value will always be a promise. If you don't explicitly return a promise, the value you return will automatically be wrapped in a promise. async function increment(num) { return num + 1; } // Even though you returned a number, the value is // automatically wrapped in a promise, so we call // `then` on it to access the returned value.
async functions return a promise. async functions use an implicit Promise to return results. Even if you don't return a promise explicitly, the async function makes sure that your code is passed through a promise. await blocks the code execution within the async function, of which it (await statement) is a part. If you want to build projects efficiently, then this concept is for you. The theory of async JavaScript helps you break down big complex projects into smaller tasks. Then you can use any of these three techniques - callbacks, promises or Async/await - to run those small tasks in a way that you get the best results. Find out how to return the result of an asynchronous function, promise based or callback based, using JavaScript Published Sep 09, 2019 , Last Updated Apr 30, 2020 Say you have this problem: you are making an asynchronous call, and you need the result of that call to be returned from the original function.
Async return values Async functions always return a promise, whether you use await or not. That promise resolves with whatever the async function returns, or rejects with whatever the async... To understand why the expression always evaluates to true, recall that async/await is just syntactic sugar for Promises. In JavaScript, an async function actually wraps its return value in a Promise object—even if it seems like the function is directly returning a value, and even if the function does not await anything. JavaScript Promises and Async/Await: As Fast As Possible™. Using promises, we can write asynchronous programs in a more manageable way. Using Async/Await syntax, a promise-based asynchronous ...
Return Data From Promise using ES6 Async/Await JavaScript ES6 provides a new feature called async/await which can used as an alternative to Promise.then. Using async/await you can write the above code in synchronous manner without any.then. javascript promise async 14 Comments When returning from a promise from an asynchronous function, you can wait for that promise to resolve return await promise, or you can return it directly return promise: An async function will return a different reference, whereas Promise.resolve returns the same reference if the given value is a promise. It can be a problem when you want to check the equality of a promise and a return value of an async function.
Async Functions. Async functions are functions that return a promise. You can declare any function as an async function just by adding the 'async' keyword before it. These functions were realized to obviate the need for explicitly instantiating new custom Promises. JavaScript Async Previous Next "async and await make promises easier to write" async makes a function return a Promise. await makes a function wait for a Promise. Async Syntax. The keyword async before a function makes the function return a promise: Example. async function myFunction() { return "Hello"; We need to create a function (method), either a simple function or an arrow function (We are analyzing the facts using arrow functions). Create an asynchronous function and then upon calling that function we should return the output in the form of promise.
28/3/2017 · In the first function the keyword async is useless, the function test will return a Promise. The second function will return a Promise where you see the keyword await. When the awaited promise will resolved the execution inside the function continue and you can access to result of the promise. EDIT 1. Explanation: Async functions in Javascript allow us to stick to conventional programming strategies such as using for, while, and other methods that are otherwise synchronous in nature and cannot be used in Javascript. In this example, we wrap the possible response returned from the HTTP request in a promise. A common need is to execute two or more asynchronous operations back to back, where each subsequent operation starts when the previous operation succeeds, with the result from the previous step. We accomplish this by creating a promise chain. Here's the magic: the then() function returns a new promise, different from the original:
 Node Js Request Async Await Code Example
Node Js Request Async Await Code Example
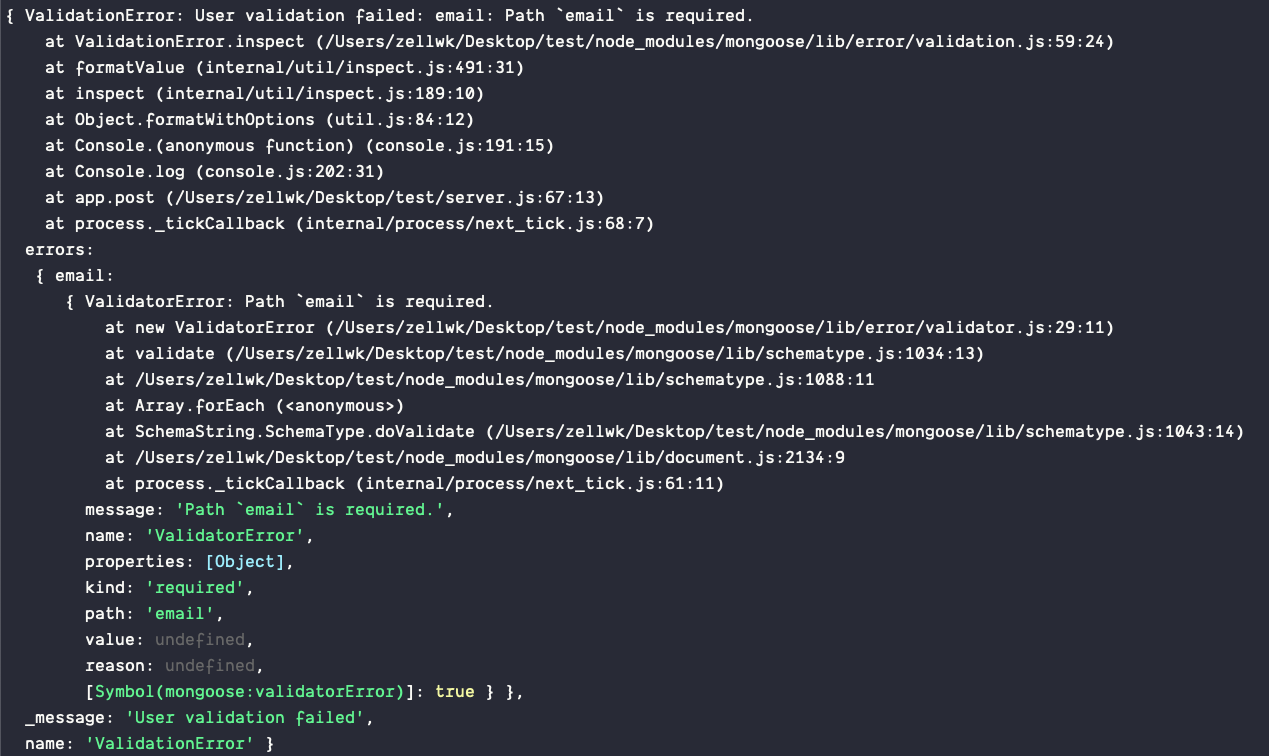 Using Async Await In Express Zell Liew
Using Async Await In Express Zell Liew
 Async Await Return Values Cmichel
Async Await Return Values Cmichel
 Async Await In Node Js How To Master It Risingstack
Async Await In Node Js How To Master It Risingstack
 Refactor This Redundant Await On A Non Promise Sonarlint
Refactor This Redundant Await On A Non Promise Sonarlint
 Async Await The Async Keyword Javascript Codecademy Forums
Async Await The Async Keyword Javascript Codecademy Forums
 Callback Vs Promises Vs Async Await Loginradius Engineering
Callback Vs Promises Vs Async Await Loginradius Engineering
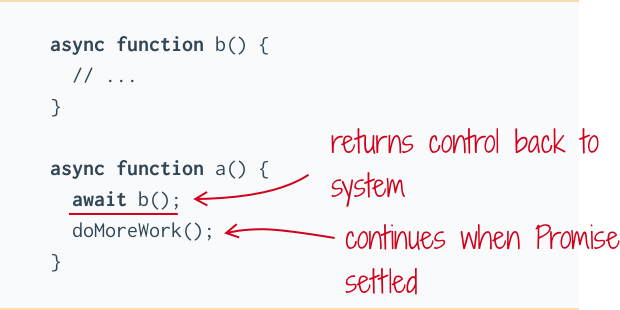 Promises And Async Await Relationship
Promises And Async Await Relationship
 Promises Promise Chain And Async Await Time To Hack
Promises Promise Chain And Async Await Time To Hack
 Amazing Visual Js Dynamic Diagram Demonstrates The Process
Amazing Visual Js Dynamic Diagram Demonstrates The Process
 How Javascript Async Await Works And How To Use It
How Javascript Async Await Works And How To Use It
Faster Async Functions And Promises V8
 Javascript Mapping And Wrapping Classic Callback Functions
Javascript Mapping And Wrapping Classic Callback Functions
 Javascript Promises Or Async Await Dev Community
Javascript Promises Or Async Await Dev Community
 How To Rewrite A Callback Function In Promise Form And Async
How To Rewrite A Callback Function In Promise Form And Async
 The Performance Overhead Of Javascript Promises And Async
The Performance Overhead Of Javascript Promises And Async
 Javascript Loops How To Handle Async Await
Javascript Loops How To Handle Async Await
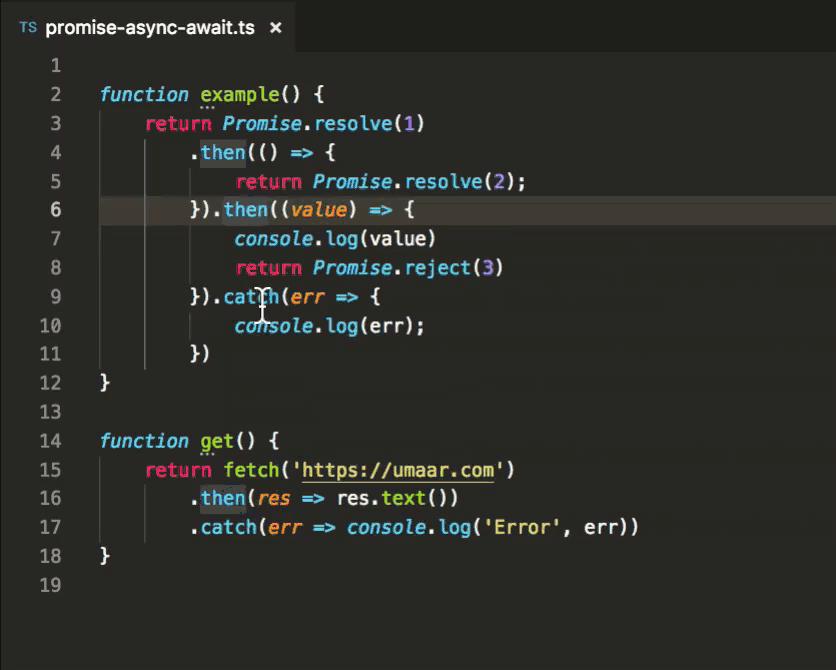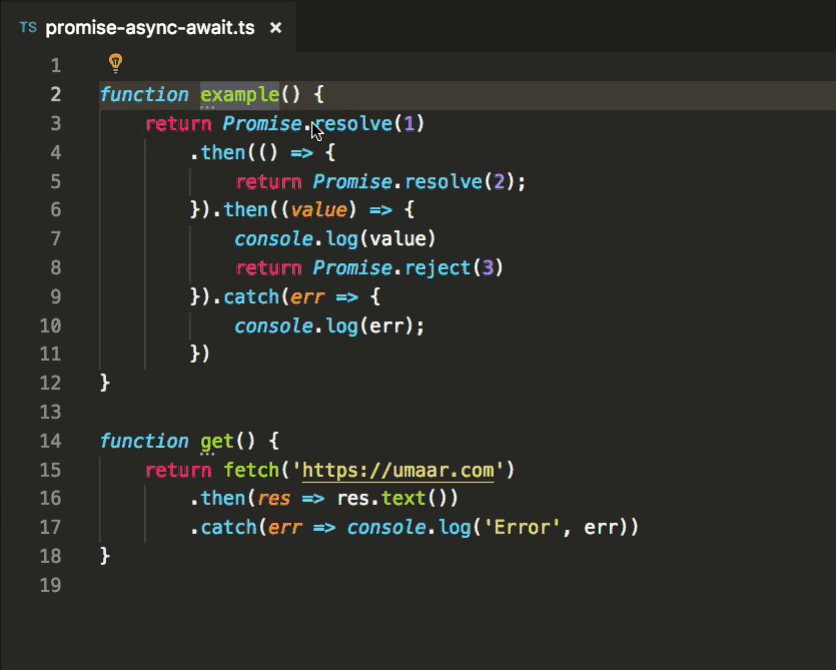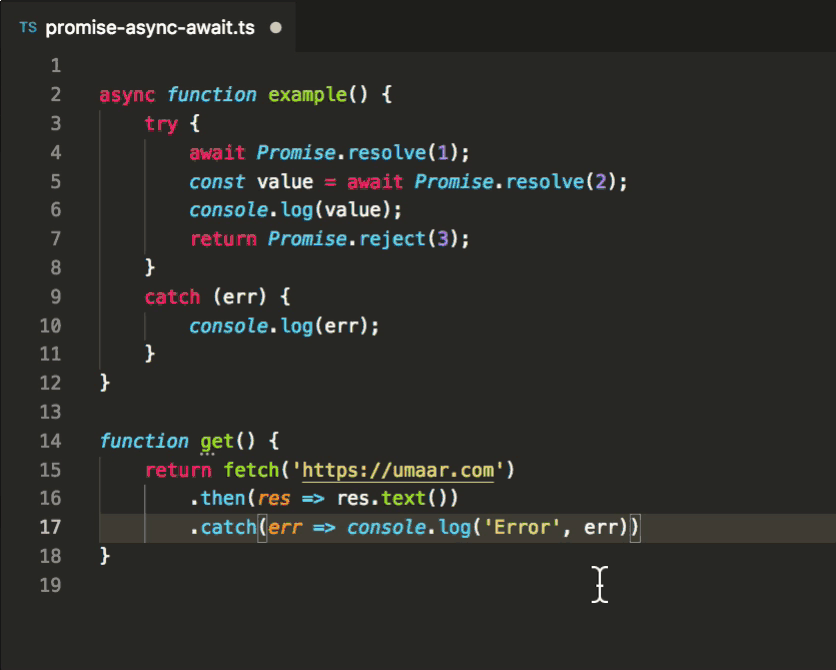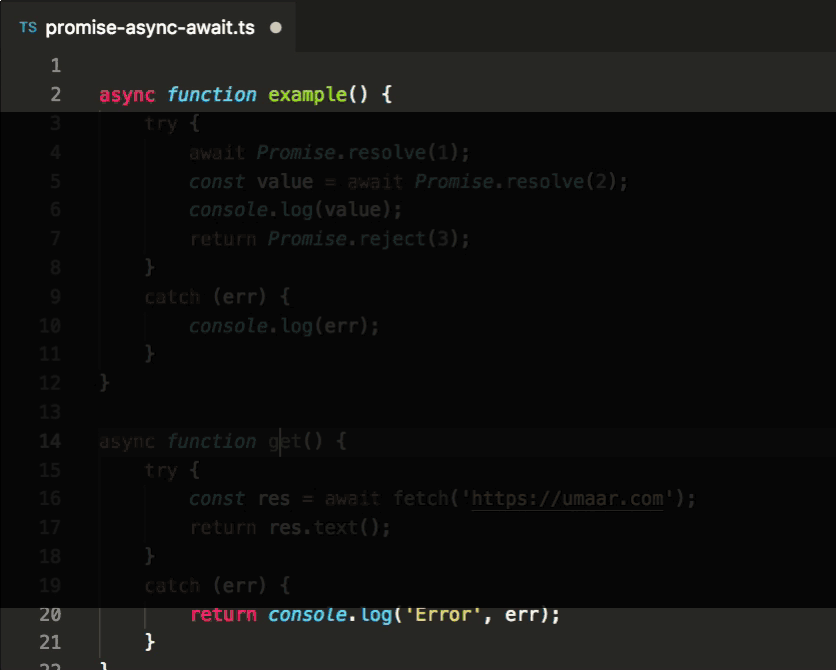 Automatically Convert Promise Then Into Async Await Vs
Automatically Convert Promise Then Into Async Await Vs
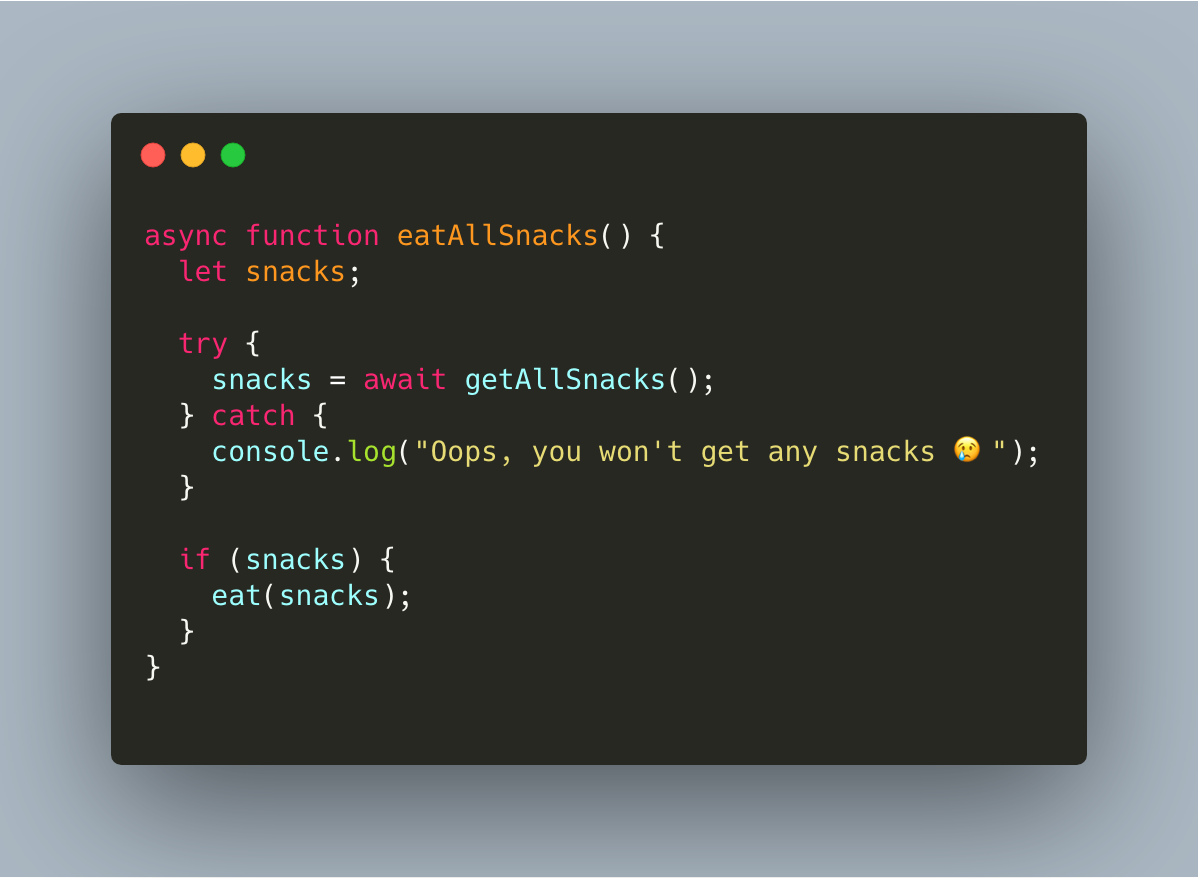 Async Await Without Try Catch In Javascript By Dzmitry
Async Await Without Try Catch In Javascript By Dzmitry
 Async Constructor Functions In Typescript Stack Overflow
Async Constructor Functions In Typescript Stack Overflow
 How To Use Async Await To Properly Link Multiple Functions In
How To Use Async Await To Properly Link Multiple Functions In
 How To Use Fetch With Async Await
How To Use Fetch With Async Await
 Asynchronous Javascript Using Async Await Scotch Io
Asynchronous Javascript Using Async Await Scotch Io
 Be Careful Of Passing An Async Function As A Parameter In
Be Careful Of Passing An Async Function As A Parameter In

 Javascript Asynchronous Method Comparison Callbacks
Javascript Asynchronous Method Comparison Callbacks
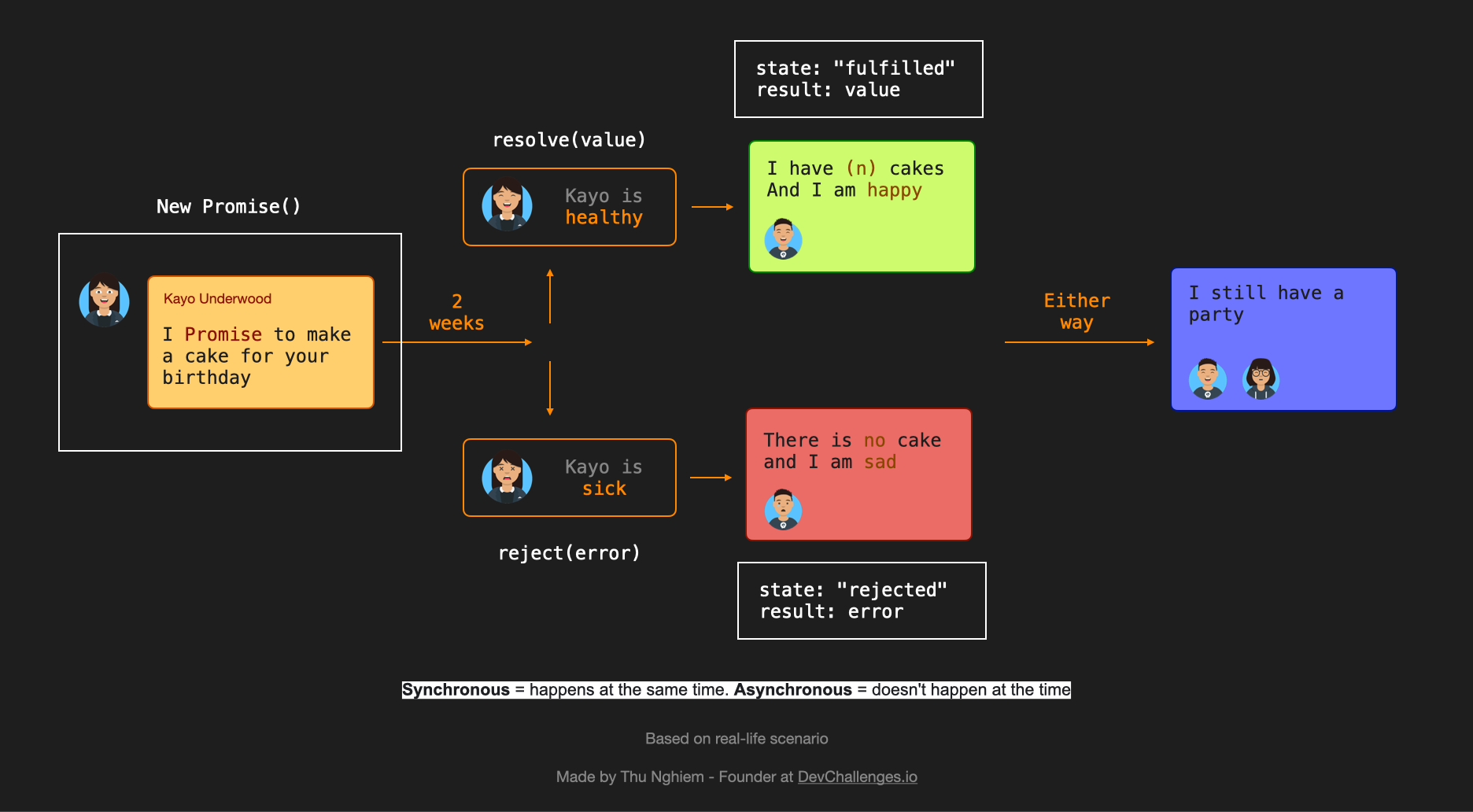 How To Learn Javascript Promises And Async Await In 20 Minutes
How To Learn Javascript Promises And Async Await In 20 Minutes
Unneeded Async Await Usage Throughout The Library Issue
Faster Async Functions And Promises V8
 Why Does Axios With Async Await Return A Full Promise
Why Does Axios With Async Await Return A Full Promise
 Async Await Vs Promises A Guide And Cheat Sheet By Kait
Async Await Vs Promises A Guide And Cheat Sheet By Kait
How To Run Async Javascript Functions In Sequence Or Parallel
 How To Get Promiseresult From Async Await Funcation Code Example
How To Get Promiseresult From Async Await Funcation Code Example
0 Response to "34 Javascript Async Function Return Promise"
Post a Comment