33 How Does Javascript Handle Asynchronous Code
Async functions are the subsequent logical step in the evolution of asynchronous programming in JavaScript. They will make your code a lot cleaner and simpler to manage. Declaring a function as async will ensure that it always returns a Promise, so you don't have to be worried about it anymore. Oct 10, 2020 - Whether you set the timeout to ... called by asynchronous code will execute after the synchronous top-level functions. This happens because the JavaScript host environment, in this case the browser, uses a concept called the event loop to handle concurrency, or parallel ...
 Async Await Javascript Tutorial How To Wait For A Function
Async Await Javascript Tutorial How To Wait For A Function
Well, arguably its not true that Javascript is single threaded if you see from the under hood working of browser JS to your JS code, there are thread pools. By single ...
How does javascript handle asynchronous code. Javascript is synchronous "by default". Meaning, the next line of code cannot run until the current one has finished. The next function cannot run until the current one has completed. But blocks of code run in parallel when it comes to asynchronous; Asynchronous functions run independently. ECMAScript 2017 introduced the JavaScript keywords async and await. The following table defines the first browser version with full support for both: Chrome 55. Edge 15. Firefox 52. Safari 11. Opera 42. Graceful asynchronous programming with Promises. Promises are a comparatively new feature of the JavaScript language that allow you to defer further actions until after a previous action has completed, or respond to its failure. This is useful for setting up a sequence of async operations to work correctly.
Asynchronous operations are those that are done in a different order than how they are listed in the program. Javascript has the ability to handle functions this way so that none of them, if... Asynchronous JavaScript: Asynchronous code allows the program to be executed immediately where the synchronous code will block further execution of the remaining code until it finishes the current one. This may not look like a big problem but when you see it in a bigger picture you realize that it may lead to delaying the User Interface. The first and oldest way to write asynchronous JavaScript code is by using callbacks. A callback is an asynchronous function that is passed as argument to other function when you call it. When that function you called finishes its execution it "calls back" the callback function. Until this happens, the callback function is not invoked.
JavaScript can have asynchronous code, but it is generally single-threaded. This is like a restaurant with a single worker who does all of the waiting and cooking. But if this worker works quickly enough and can switch between tasks efficiently enough, then the restaurant seemingly has multiple workers. To handle these operations in JavaScript, a developer must use asynchronous programming techniques. Since JavaScript is a single-threaded programming language with a synchronous execution model that proccesses one operation after another, it can only process one statement at a time. Feb 10, 2021 - Welcome to post # 4 of the series dedicated to exploring JavaScript and its building components. In the process of identifying and describing the core elements, we also share some rules of thumb we…
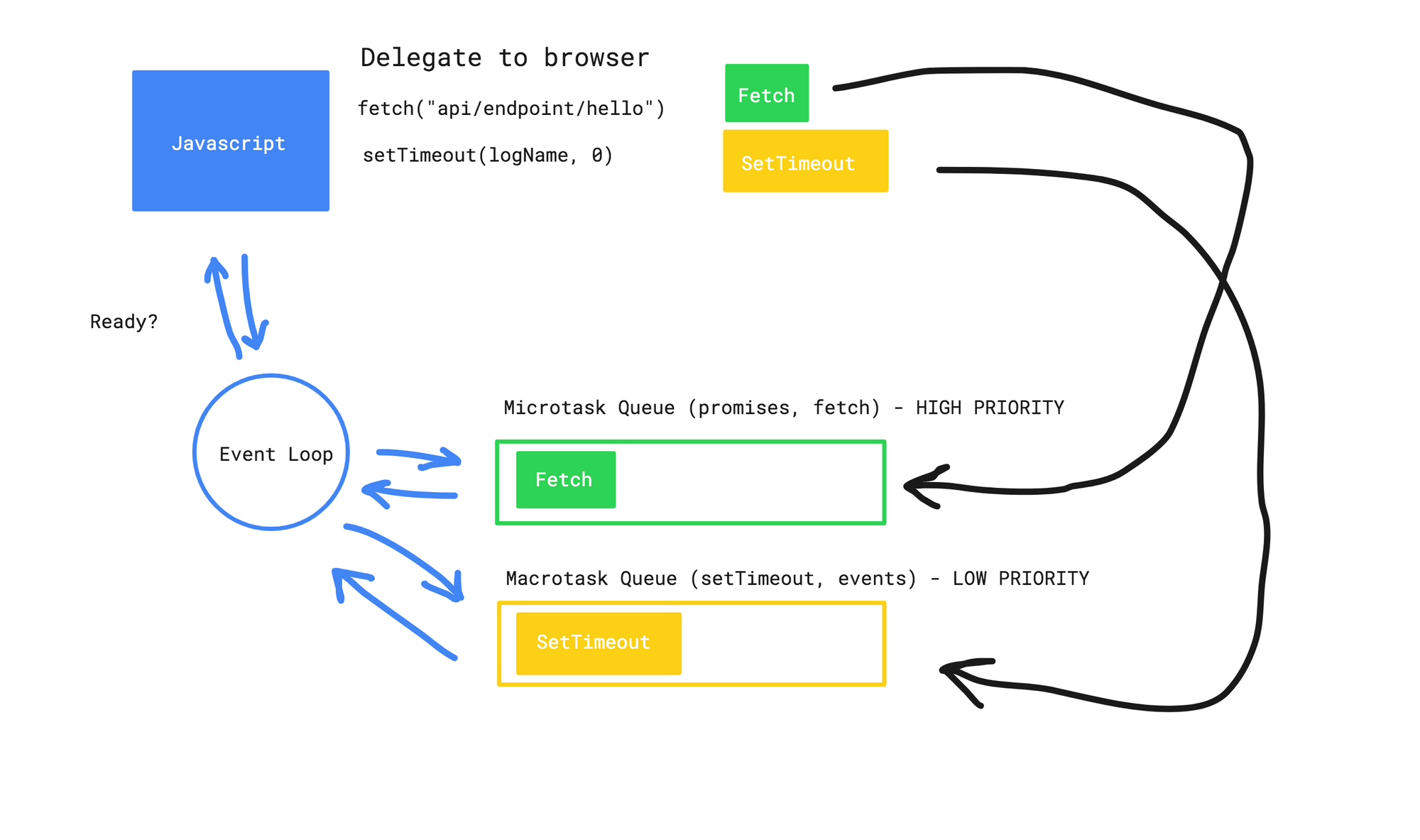
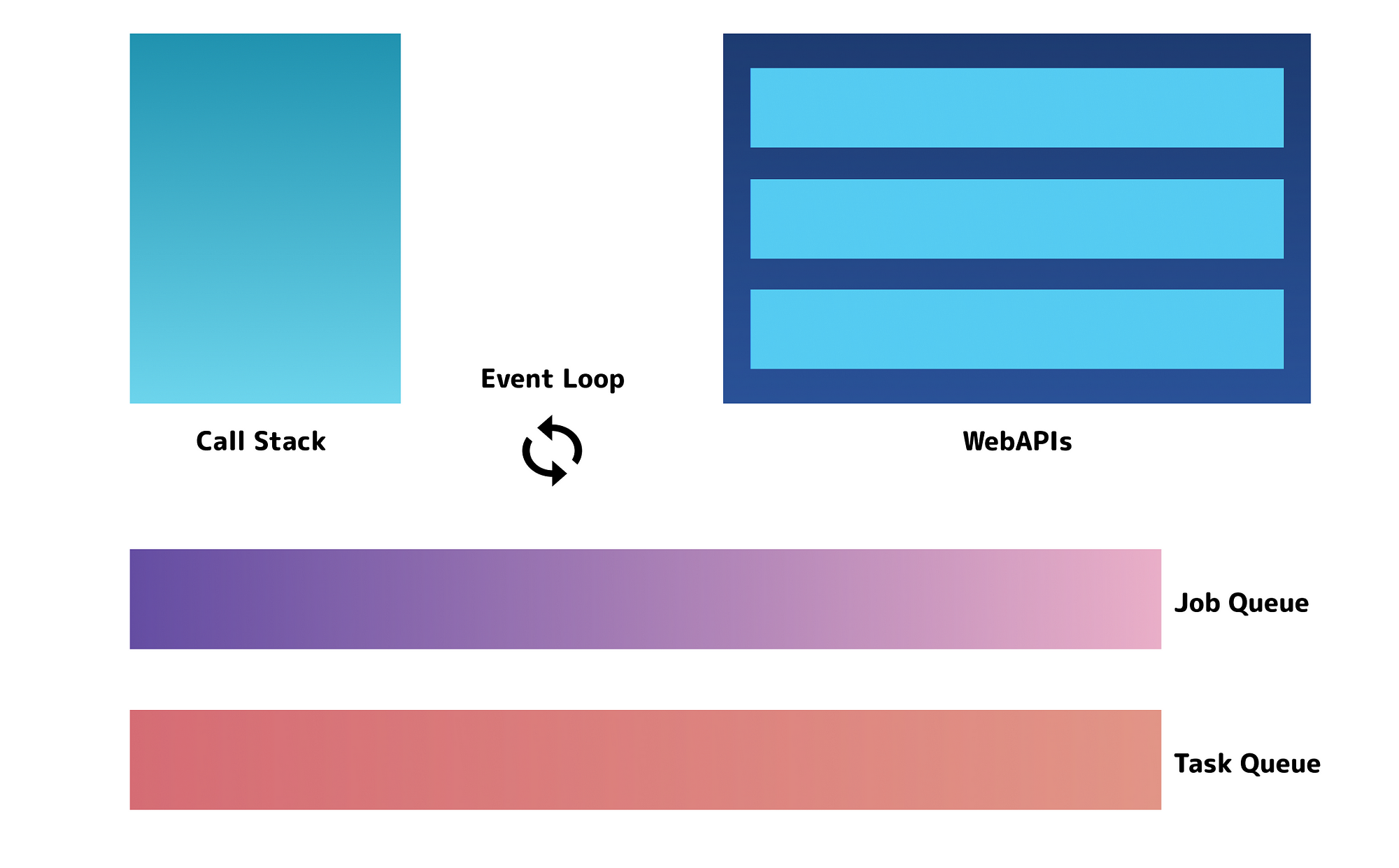
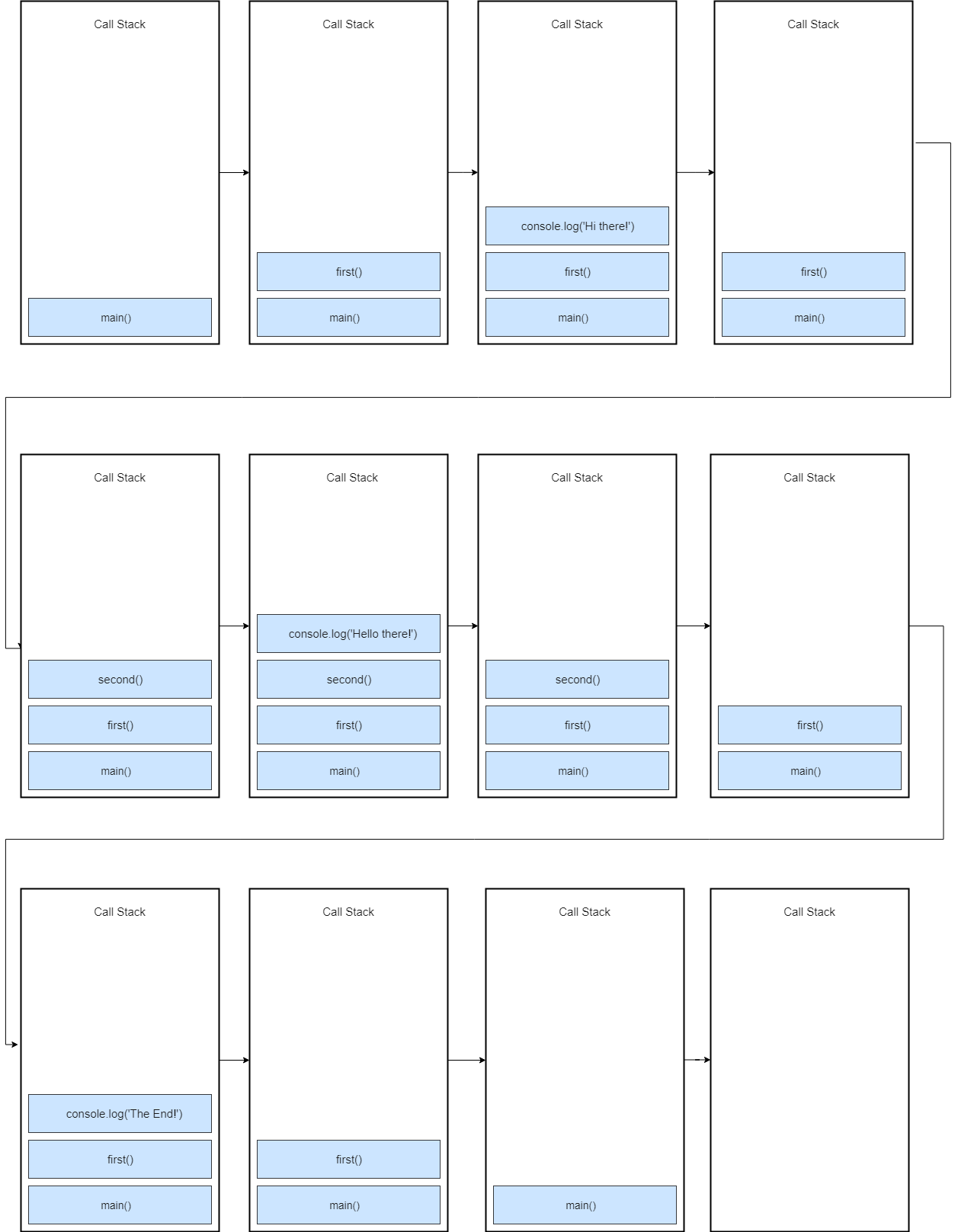
The "Event Loop" checks on the job queues and, whenever the call stack is empty, pops the code from them and pushes it onto the call stack to be executed. The two queues to handle asynchronous code: The callback queue. The micro-task queue which is used by promises. Please see more on job queues here. Writing non-blocking, asynchronous code is a staple of Node.js development and the broader JavaScript world. JavaScript itself uses an event loop which makes writing asynchronous functions more difficult by default. Let's look at examples of synchronous and asynchronous code; as well as some methods for programming asynchronously. JavaScript is asynchronous in nature and so is Node. Asynchronous programming is a design pattern which ensures the non-blocking code execution. Non blocking code do not prevent the execution of piece of code.
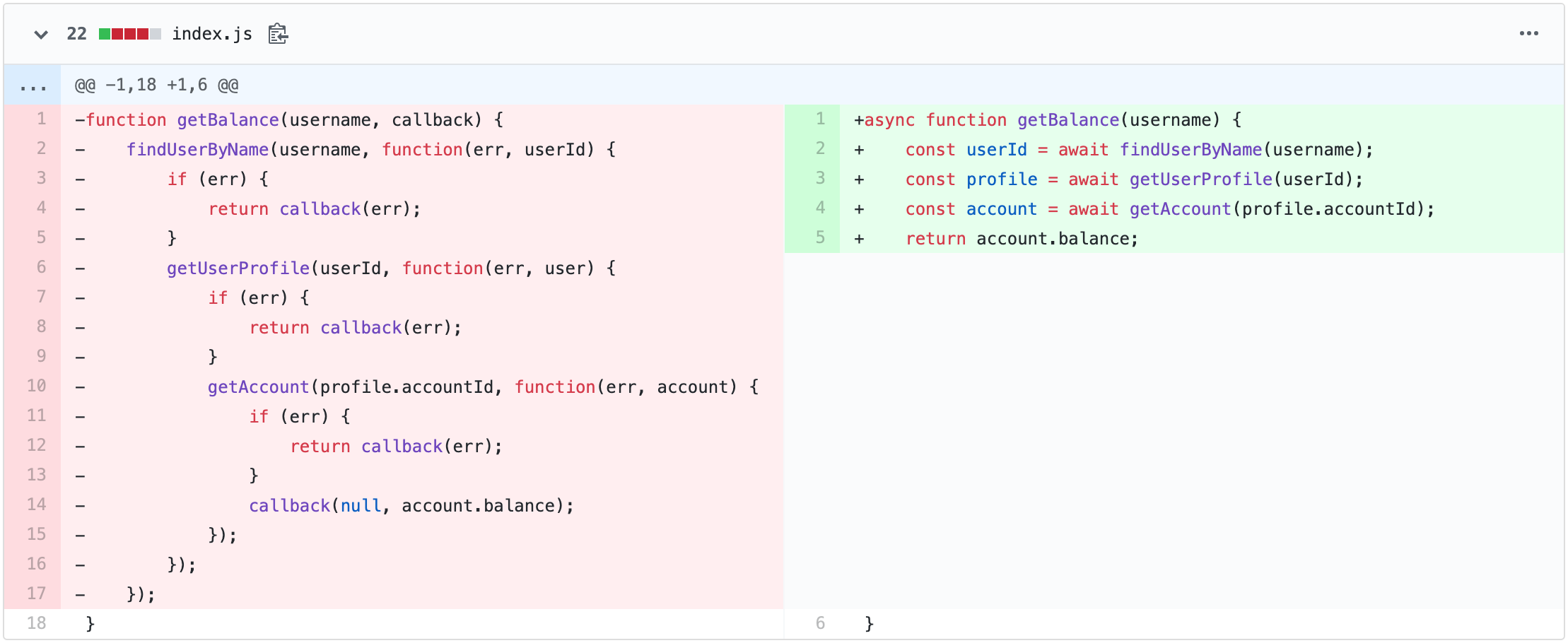
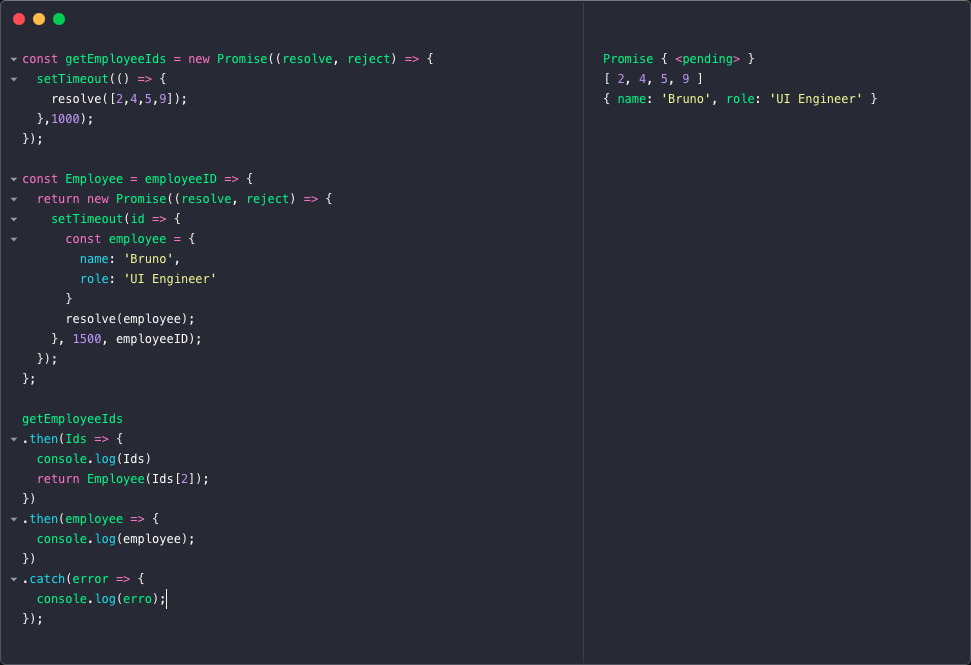
The async function() defines an asynchronous function that returns an AsyncFunction object. This function operates asynchronously via the event loop using an implicit Promise to return a value. C, Java, C#, PHP, Go, Ruby, Swift, and Python are all synchronous by default. Some of them handle async by using threads, spawning a new process. JavaScript. JavaScript is synchronous by default and is single threaded. This means that code cannot create new threads and run in parallel. Lines of code are executed in series, one after another ... Oct 09, 2017 - A promise is used to handle the asynchronous result of an operation. JavaScript is designed to not wait for an asynchrnous block of code to completely execute before other synchronous parts of the code can run. For instance, when making API requests to servers, we have no idea if these servers ...
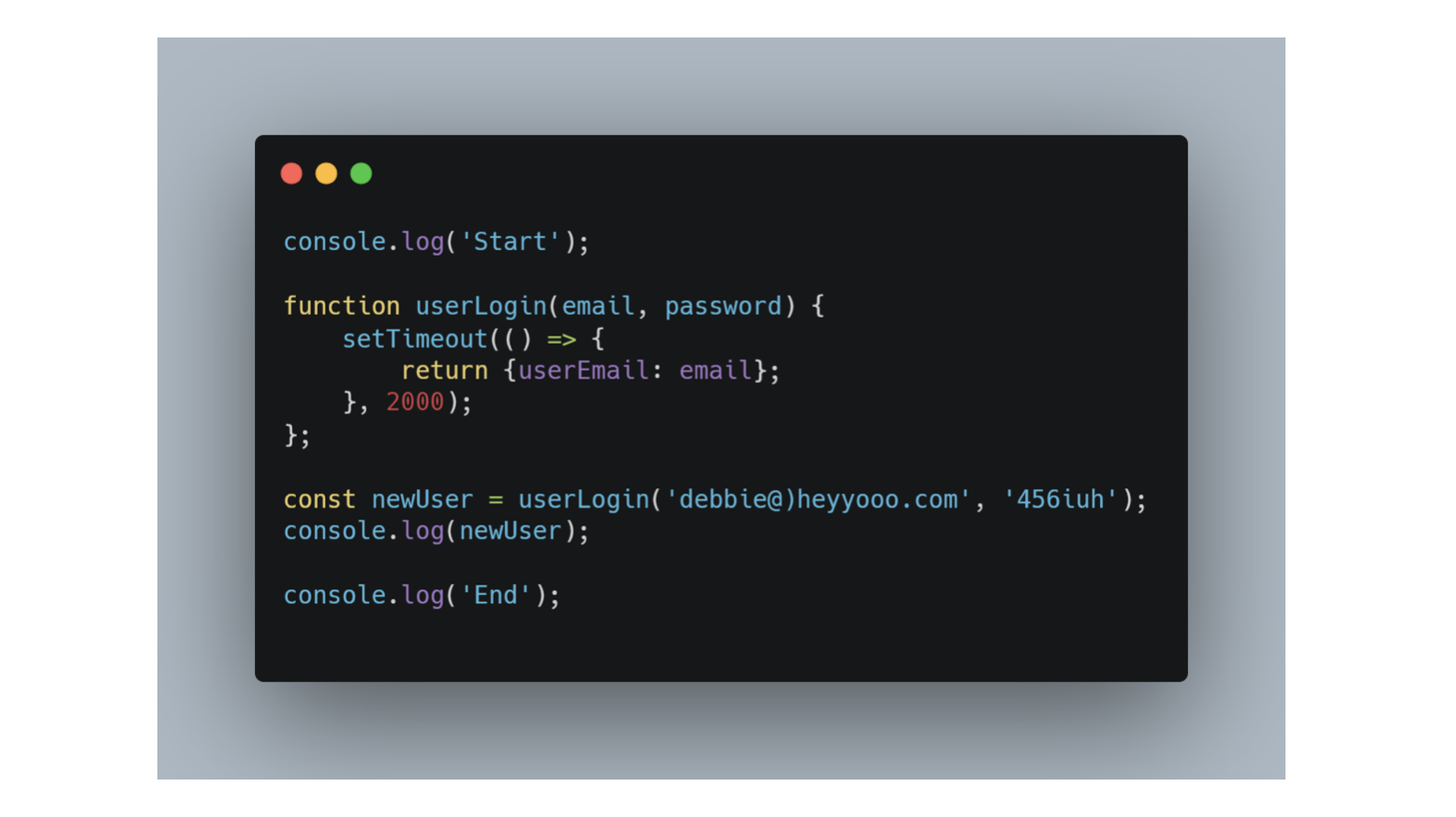
In the real world, callbacks are most often used with asynchronous functions. A typical example is JavaScript setTimeout (). Waiting for a Timeout When using the JavaScript function setTimeout (), you can specify a callback function to be executed on time-out: Jul 07, 2021 - JavaScript is a single-threaded programming language which means only one thing can happen at a time. That is, the JavaScript engine can only process one statement at a time in a single thread. While… JavaScript async/await is a new way to deal with asynchronous operations in JavaScript. It offers you the power to make your code shorter and clearer. Async/await is much more readable and more comfortable to compose, while being non-blocking. What is a callback?
console.log ('Starting'); let image; fetch('coffee.jpg').then((response) => { console.log('It worked :)') return response.blob(); }).then((myBlob) => { let objectURL ... Instead, you need your code to wait until the response is returned before it tries to do anything else to it. There are two main types of asynchronous code style you'll come across in JavaScript code, old-style callbacks and newer promise-style code. In the below sections we'll review each of these in turn. JavaScript (in the browser) is entirely single-threaded (with the exception of WebWorkers). The term "asynchronous" doesn't necessarily have anything to do with being multi-threaded. The network fetch likely happens on browser "networking" thread in a higher performance language (c++, rust, etc.), but this means nothing to JavaScript.
Mar 04, 2019 - That is because a JavaScript program is single threaded and all code is executed in a sequence, not in parallel. In JavaScript this is handled by using what is called an “asynchronous non-blocking I/O model”. What that means is that while the execution of JavaScript is blocking, I/O operations ... Nov 25, 2019 - In this article, we are going to explore the evolution of JavaScript around asynchronous execution in the past era and how it changed the way we write and read code. We will start with the beginnings of web development, and go all the way to modern asynchronous pattern examples. In addition to having code that is difficult to maintain, the DRY principle has absolutely no value in this case. Error handling, for example, is repeated in each function and the main callback is called from each nested function. More complex asynchronous JavaScript operations, such as looping ...
Jan 31, 2019 - In general JavaScript is executing asynchronous code in a non-blocking way which is great to ensure responsiveness of the application. However, when dealing with asynchronous code (e.g. reading from the file system, accessing external APIs) we need to handle it in a special way to be able to ... So how do we get asynchronous code with Javascript then? Well, we can thank the Javascript engine (V8, Spidermonkey, JavaScriptCore, etc...) for that, which has Web API that handle these tasks in the background. The call stack recognizes functions of the Web API and hands them off to be handled by the browser. Nov 06, 2020 - In JavaScript operations, it’s advised to wrap your code in a try…catch method in order to handle errors that might be in our function. Lastly, we call the function at the end of the program and log the message This is how to return async JavaScript in our console, this is how we respond to asynchronous ...
Jan 31, 2019 - In general JavaScript is executing asynchronous code in a non-blocking way which is great to ensure responsiveness of the application. However, when dealing with asynchronous code (e.g. reading from the file system, accessing external APIs) we need to handle it in a special way to be able to ... Jul 18, 2018 - Normally, programming languages ... manage asynchronicity, in the language or through libraries. C, Java, C#, PHP, Go, Ruby, Swift, Python, they are all synchronous by default. Some of them handle async by using threads, spawning a new process. ... JavaScript is synchronous by default and is single threaded. This means that code cannot create ... May 28, 2020 - Review the evolution of async programming in JavaScript, from callbacks and promises to async/await, and dive into parallelism with the Web Worker API.
JS is single-threaded and everything on the stack runs to completion, so there will never be any synchronous code that interleaves with the body of execute.But run-to-completion is different than "having concurrency issues" as your title suggests. The operation can deliver its result asynchronously: Some operations, such as downloads, can be performed concurrently to the JavaScript process. The JavaScript code triggering such an operation registers a callback, which is invoked with the result once the operation is finished. The invocation is handled ... This is why understanding JavaScript callbacks is essential to understanding asynchronous programming in JavaScript. In the client browser callbacks enable JavaScript code to make a call that might take a long time to respond, like a web service API call, without "freezing" the web page while it waits for a response.
Cooperative asynchronous JavaScript: Timeouts and intervals. Here we look at the traditional methods JavaScript has available for running code asynchronously after a set time period has elapsed, or at a regular interval (e.g. a set number of times per second), talk about what they are useful for, and look at their inherent issues. Asynchronous behavior happens on its own empty function call stack. This is one of the reasons that, without promises, managing exceptions across asynchronous code is hard. Since each callback starts with a mostly empty stack, your catch handlers won’t be on the stack when they throw an exception. Async/Await Basics in JavaScript. There are two parts to using async/await in your code. First of all, we have the async keyword, which you put in front of a function declaration to turn it into an async function. An async function is a function that knows to expect the possibility that you'll use the await keyword to invoke asynchronous code.
Well organized and easy to understand Web building tutorials with lots of examples of how to use HTML, CSS, JavaScript, SQL, Python, PHP, Bootstrap, Java, XML and more. As you can see, Async / Await is a really simple and clean syntax to handle asynchronous code in JavaScript. However, if you want to work smoothly with this new method, there is no way around Promises since they build the foundation of it. Therefore, learning them too is highly recommended. If you are a Javascript developer, you have to deal with asynchronous code. If you are a Javascript developer working with Node.js, asynchronous code is your all in a day's work. Let's see how to properly deal with asynchronous code, avoiding one of the most common mistake.
 Explaining Async Await In 200 Lines Of Code Ivan Velichko
Explaining Async Await In 200 Lines Of Code Ivan Velichko
 Async Await In Node Js How To Master It Risingstack
Async Await In Node Js How To Master It Risingstack
 How To Use Fetch With Async Await
How To Use Fetch With Async Await
 Demystifying Asynchronous Javascript Event Loop Call Stack
Demystifying Asynchronous Javascript Event Loop Call Stack
 Async Javascript Callbacks Promises And Async Await By
Async Javascript Callbacks Promises And Async Await By
 Understanding Asynchronous Javascript By Sukhjinder Arora
Understanding Asynchronous Javascript By Sukhjinder Arora

 Callback Hell Promises And Async Await
Callback Hell Promises And Async Await
 Async Await For Beginners Understanding Asynchronous Code In
Async Await For Beginners Understanding Asynchronous Code In
 Javascript Asynchronous Tutorial
Javascript Asynchronous Tutorial
 Using Async Await With A Foreach Loop Stack Overflow
Using Async Await With A Foreach Loop Stack Overflow
 Node Js Async Await Tutorial With Asynchronous Javascript
Node Js Async Await Tutorial With Asynchronous Javascript
 Async Programming With Javascript Callbacks Promises And
Async Programming With Javascript Callbacks Promises And
 Callback Vs Promises Vs Async Await Loginradius Engineering
Callback Vs Promises Vs Async Await Loginradius Engineering
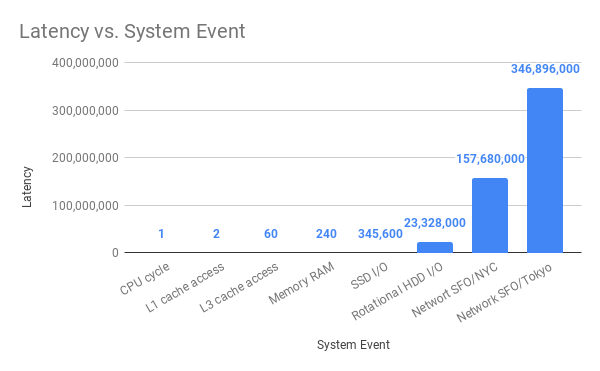 What Every Programmer Should Know About Synchronous Vs
What Every Programmer Should Know About Synchronous Vs
 Async Programming With Javascript Callbacks Promises
Async Programming With Javascript Callbacks Promises
 From Javascript Promises To Async Await Why Bother
From Javascript Promises To Async Await Why Bother
 Asynchronous Javascript Understanding Callbacks
Asynchronous Javascript Understanding Callbacks
 Asynchronous Error Handling In Javascript Ruben Verborgh
Asynchronous Error Handling In Javascript Ruben Verborgh
 The History And Future Of Asynchronous Javascript Okta
The History And Future Of Asynchronous Javascript Okta
 Node Js Event Loop How Even Quick Node Js Async Functions
Node Js Event Loop How Even Quick Node Js Async Functions
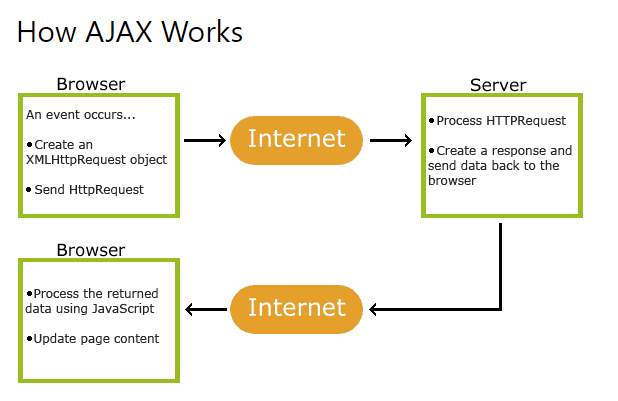 How To Return Ajax Response From Asynchronous Javascript Call
How To Return Ajax Response From Asynchronous Javascript Call
 Javascript Asynchronous Programming And Callbacks
Javascript Asynchronous Programming And Callbacks
 Javascript Promises And Why Async Await Wins The Battle
Javascript Promises And Why Async Await Wins The Battle

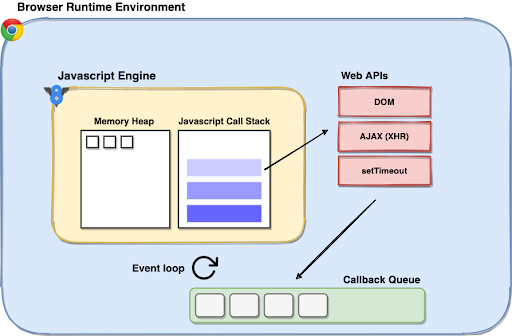
 Deeply Understanding Javascript Async And Await With Examples
Deeply Understanding Javascript Async And Await With Examples
 Async Functions In Javascript Www Thecodebarbarian Com
Async Functions In Javascript Www Thecodebarbarian Com
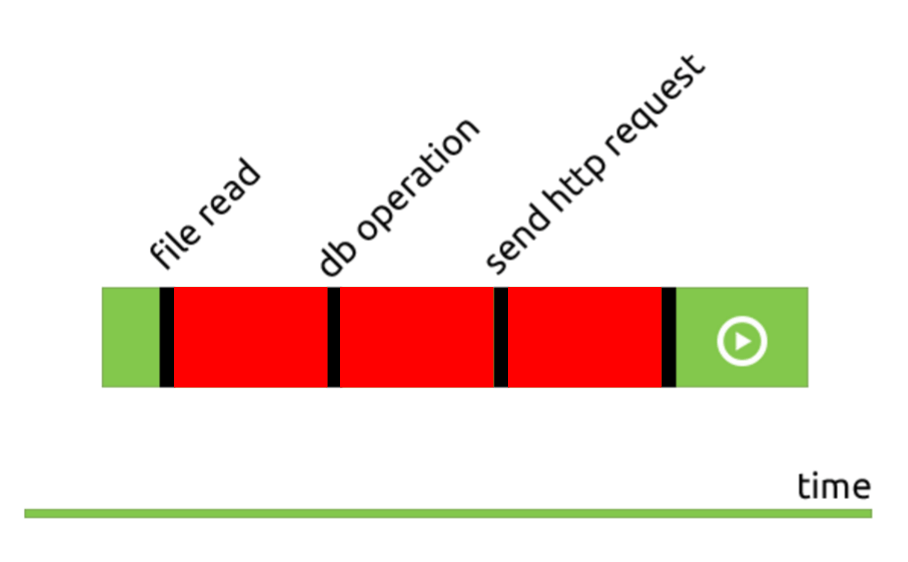 Node Hero Understanding Async Programming In Node Js
Node Hero Understanding Async Programming In Node Js
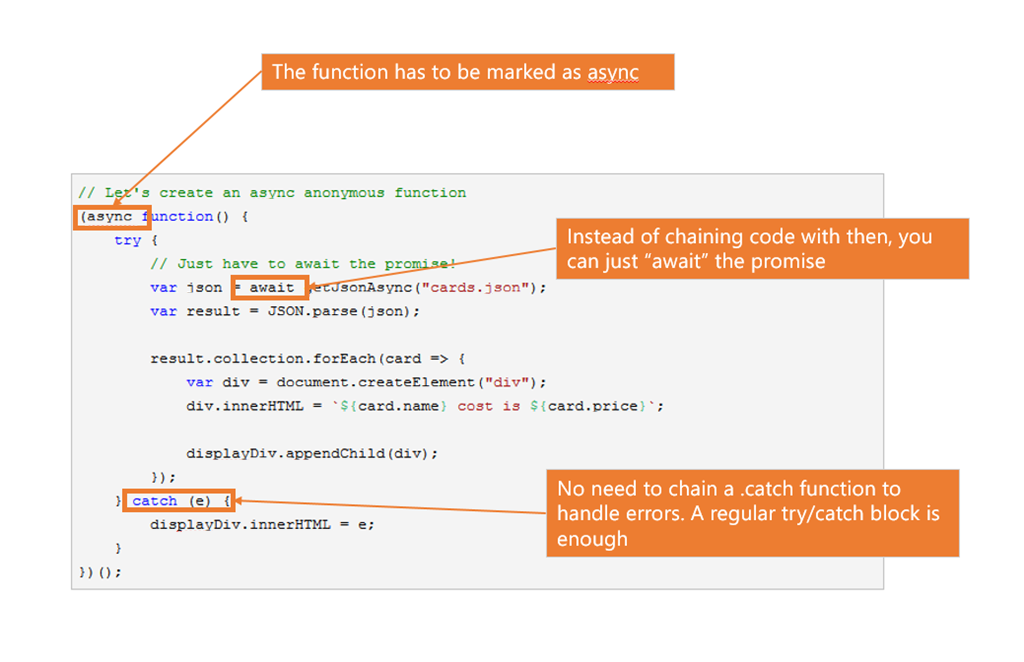 Javascript Goes Asynchronous And It S Awesome Sitepoint
Javascript Goes Asynchronous And It S Awesome Sitepoint
 Javascript Promises And Async Await Cheatsheet Beginner To
Javascript Promises And Async Await Cheatsheet Beginner To
 The Evolution Of Asynchronous Programming In Javascript
The Evolution Of Asynchronous Programming In Javascript
0 Response to "33 How Does Javascript Handle Asynchronous Code"
Post a Comment