22 Javascript Try Catch Syntax
You can catch programmer-generated and runtime exceptions but you cannot catch JavaScript syntax errors, though you may handle them in some browsers using window.onerror. This is taken from the book JavaScript- The Complete Reference by Thomas-Powell which I like very much. You can refer to the code examples in that book. This will ultimately help you to create programs which are robust, reliable and efficient. One simple way of handling errors is through try…catch statements. A try…catch statement is a programming mechanism which enables you to test your code for possible errors, and carry out certain actions ...
 Can I Catch Warnings In Try Catch Block In Javascript Code
Can I Catch Warnings In Try Catch Block In Javascript Code
Nov 22, 2017 - Errors are inevitable. They happen. In this article we’ll explore basic error handling in JavaScript with try and catch. We’ll start off by taking a look at the try and catch syntax. Essentially we…
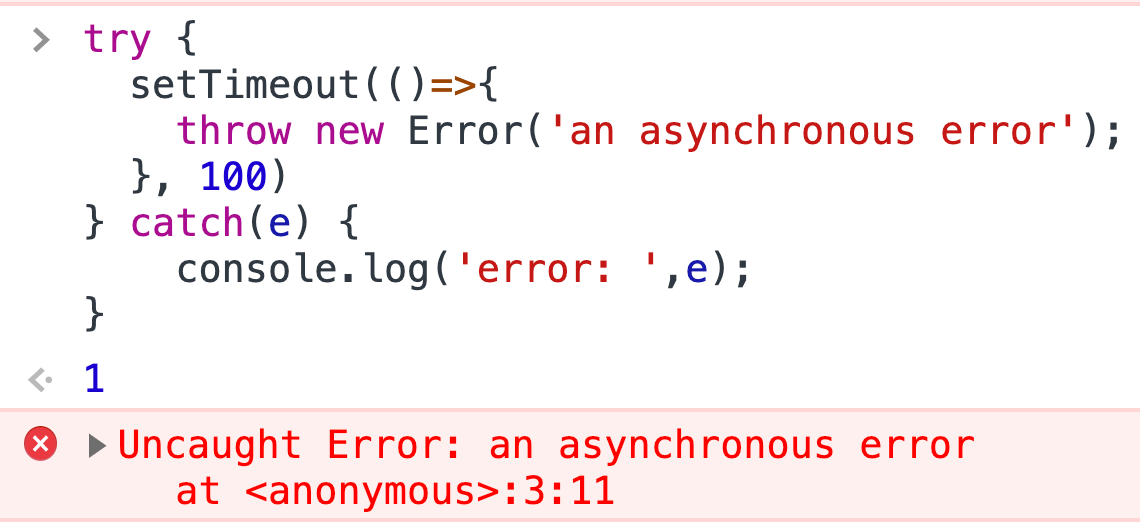
Javascript try catch syntax. Dec 30, 2020 - You put your code in the try block, and immediately if there is an error, JavaScript gives the catch statement control and it just does whatever you say. In this case, it alerts you to the error. All JavaScript errors are actually objects that contain two properties: the name (for example, Error, syntaxError... To access the data, you have to parse it (using the function JSON.parse()). Poorly formatted data can generate errors which can be problematic. This is where a try…catch statement comes in handy. Here is a simple implementation of a function which uses a try…catch statement to handle any possible errors in a JSON data string. A SyntaxError is thrown when the JavaScript engine encounters tokens or token order that does not conform to the syntax of the language when parsing code. But if there's a syntax error, how could the program even run in the first place? ... It's runtime errors that can be caught with try-catch, not ...
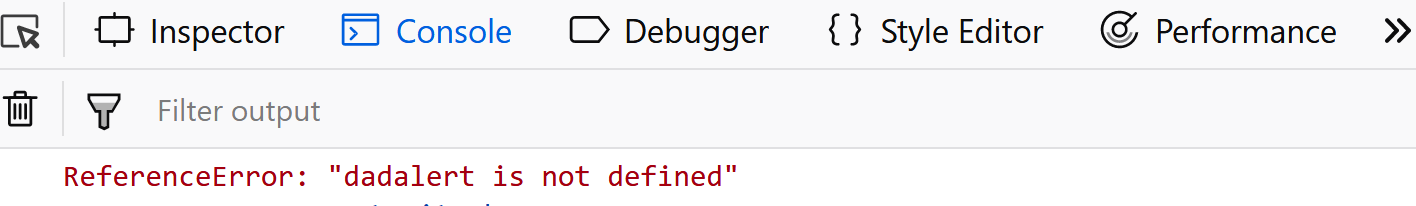
try { // statements } catch (error) { // statements The try block contains one or more statements enclosed by brackets. The catch block also contains one or more statements enclosed by brackets that specify what to do if an exception is thrown in the try block. JavaScript catches adddlert as an error, and executes the catch code to handle it. JavaScript try and catch The try statement allows you to define a block of code to be tested for errors while it is being executed. The catch statement allows you to define a block of code to be executed, if an error occurs in the try block. Here I'm using a nested try/catch statement to try and determine in IE which version of the ActiveX Object it supports that's needed to initialize an Ajax request. Using object detection won't work here, since the issue isn't whether the browser supports ActiveXObject here, but which version. Overview of try/catch/finally
The syntax for try/catch is: try { // Code } catch (varName) { // Optional // If exception thrown in try block, // execute this block } finally { // Optional // Execute this block after // try or after catch clause // (i.e. this is *always* called) } varName is available to the scope of the catch block only. Handle Javascript errors easy without the tears and the headache. Make your code looks sweet and efficient. ... "Try / Catch" statements are everywhere… and sometimes they are even nested or chained. ... Now you can use that sequential like syntax to handle errors in addition to your traditional try/catch blocks. Caveat: you can nest try... catch statements!catch and finally clauses are, in theory, both optional - though you need at least one of them. However, if you don't have a catch, any errors will be thrown up to the next catching scope (either the catch higher up, or the window if that doesn't exist). So… good rule of thumb, always have the ...
First, the code in try {...} is executed. If not come to errors in the script, then catch (err) is ignored: the execution arrives at the finish of try and goes on, skipping catch. If an error occurs, try execution is stopped and jumps to the catch block. Syntax of JavaScript try catch and finally try { // test code goes here }catch (err) { // if test code throws error // catch it and display the error }finally { // put additional code // which does not depends on the test code // or display a message simply } 25/1/2021 · But there’s a syntax construct try...catch that allows us to “catch” errors so the script can, instead of dying, do something more reasonable. The “try…catch” syntax. The try...catch construct has two main blocks: try, and then catch:
JavaScript try…catch A try…catch is a commonly used statement in various programming languages. Basically, it is used to handle the error-prone part of the code. It initially tests the code for all possible errors it may contain, then it implements actions to tackle those errors (if occur). Jun 07, 2019 - catch: The block that follows this statement will see if the code following the try statement gave an error, and decides what to do with it · With these statements, in JavaScript, you can also add a throw or a finally clause. Let’s see what role they play. Explain try and catch statements in JavaScript with examples. Javascript Web Development Object Oriented Programming. The try statement allows us execute a block of code and test for errors. Those errors are then caught and handle by the catch statement. Following is the code for try and catch statement in JavaScript −.
The latest versions of JavaScript added exception handling capabilities. JavaScript implements the try...catch...finally construct as well as the throw operator to handle exceptions. You can catch programmer-generated and runtime exceptions, but you cannot catch JavaScript syntax errors. try { (((((((((} catch (e) { console.log ("The engine does not understand this code, it is invalid"); } In the example above, you can see unmatched curly braces. Generally, the engine of JavaScript first reads the code and then runs it. The errors, occurring in the reading phase are known as "parse-time" errors. The contents of a catch statement will run if your try statement cannot execute successfully. A finally statement executes immediately after either the try or catch statements. » MORE: JavaScript Trim: A Step-By-Step Guide
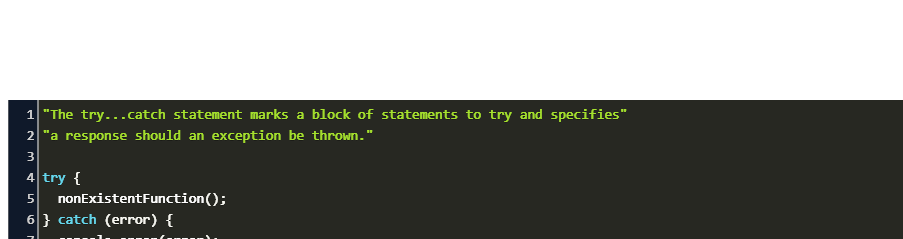
Apr 28, 2021 - The try...catch..finally statement specifies a block of code to try along with a response should an error occur. The try statement contains one or more try blocks, and ends with at least one catch and/or a finally clause. Mar 12, 2010 - Obviously javascript interprets this as syntax error because it thinks its javascript throwing a SyntaxError. So what I would like to do it to catch this error and perform the adjustment method if this occurs. I've already tried with try catch but it doesn't work since it keeps returning the ... The try statement consists of a try -block, which contains one or more statements. {} must always be used, even for single statements. At least one catch -block, or a finally -block, must be present. This gives us three forms for the try statement:
The try/catch/finally statement handles some or all of the errors that may occur in a block of code, while still running code. Errors can be coding errors made by the programmer, errors due to wrong input, and other unforeseeable things. The try statement allows you to define a block of code to be tested for errors while it is being executed. JavaScript try and catch Statement In JavaScript, you must write such code, which, if generates an error/exception at runtime, is inside the try block, so that the exception/error can be handled gracefully. Immediately, after the try block, there should be a catch block that specifies the exception type you want to catch. try { // code may cause error } catch (error) { // code to handle error } Code language: JavaScript (javascript) In this statement, you place the code that may cause errors in the try block and the code that handles the error in the catch block. If an error occurs, JavaScript terminates the code execution and jumps to the catch block.
If your method doesn't return promises that are rejected with specific enough errors, you can do that yourself by re-throwing something more appropriate in a .catch() handler: try { const createdUser = await this.User.create(userInfo).catch(err => { throw new CreationError(err.message, {code: "USER_CREATE"}); }); … JavaScript try catch Statement. The try statement defines a block of code that you want to try to execute, and use the catch statement to define a block of code that will execute if an exception to the normal running of the code occurs in the block of code defined by the try statement.. The following are the key points to be noted while using try catch statement. A Computer Science portal for geeks. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions.
Find additional: JavaScript Articles A try catch in any programming language is a block in which code can execute in a way where an exception can safely occur in a way that won't result in the application's abnormal termination. The try catch statement marks a block of statements to try and specifies a response should an exception be thrown. We can declare try block with a catch or finally and nested try block in JavaScript without any complaints from JavaScript Engine. Apr 12, 2019 - Every modern programming language has the ability to handle and throw exceptions, and JavaScript is no exception. In this column, I discuss why, how, and when you should make use of JavaScript’s try catch statement as well as throwing your own custom errors.
Error Handling in JavaScript using Try...Catch Block Statements 1 week ago - You can use a catch block to handle ... in the try block. ... The catch block specifies an identifier (catchID in the preceding syntax) that holds the value specified by the throw statement. You can use this identifier to get information about the exception that was thrown. JavaScript creates this ... Learn how to properly handle errors in your JavaScript apps using the try/catch/finally construct as well as the throw statement.
Basic Syntax and Definition. The try-catch statement was introduced in ECMA-262, 3rd Edition as a way to handle exceptions, and its syntax is the same as in the Java programming language. Here is how a basic try-catch statement looks: The catch() method returns a Promise and deals with rejected cases only. It behaves the same as calling Promise.prototype.then(undefined, onRejected) (in fact, calling obj.catch(onRejected) internally calls obj.then(undefined, onRejected)). This means that you have to provide an onRejected function even if you want to fall back to an undefined result value - for example obj.catch(() => {}).
 Javascript Error And Exceptional Handling With Examples
Javascript Error And Exceptional Handling With Examples
 Google Apps Script Exception Handling
Google Apps Script Exception Handling
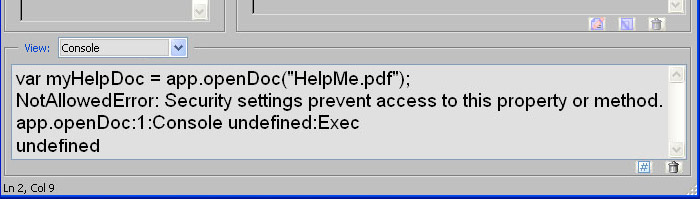 Exception Handling In Acrobat Javascript
Exception Handling In Acrobat Javascript
5 7 Exception Handling Try Catch And Finally
Returning Value From Method Having Try Catch Finally Blocks
 Javascript Errors Amp Exceptions Handling Ppt Download
Javascript Errors Amp Exceptions Handling Ppt Download
 Javascript Errors Throw And Try To Catch Geeksforgeeks
Javascript Errors Throw And Try To Catch Geeksforgeeks
 Javascript Error Handling Ten Years Ago At The Beginning Of
Javascript Error Handling Ten Years Ago At The Beginning Of
 Php Exceptions Try Catch For Error Handling All Pro Web
Php Exceptions Try Catch For Error Handling All Pro Web
 What Exceptions Cannot Be Caught By Try Catch By Bytefish
What Exceptions Cannot Be Caught By Try Catch By Bytefish
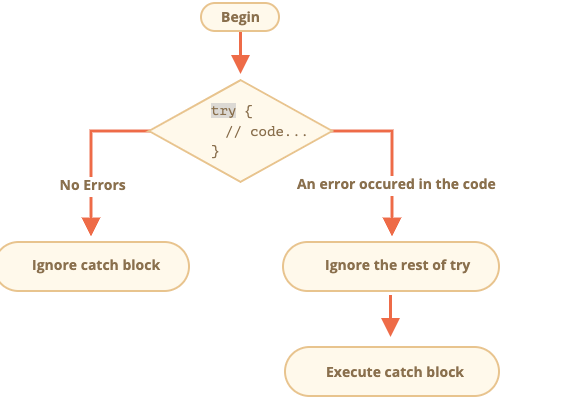 Js Error Handling No Matter How Great We Are At By
Js Error Handling No Matter How Great We Are At By
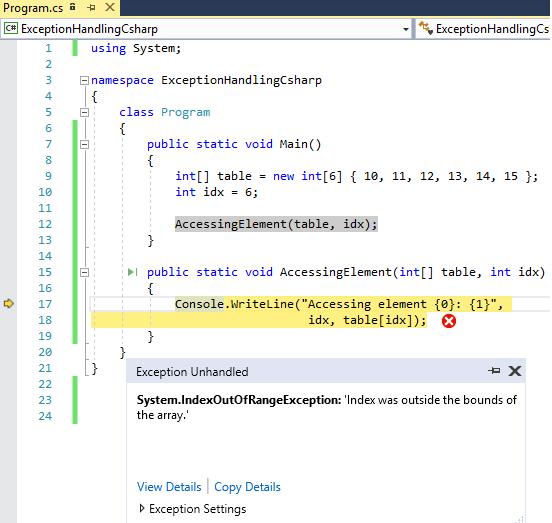 C Exception Handling In C With Try Catch Finally Block
C Exception Handling In C With Try Catch Finally Block
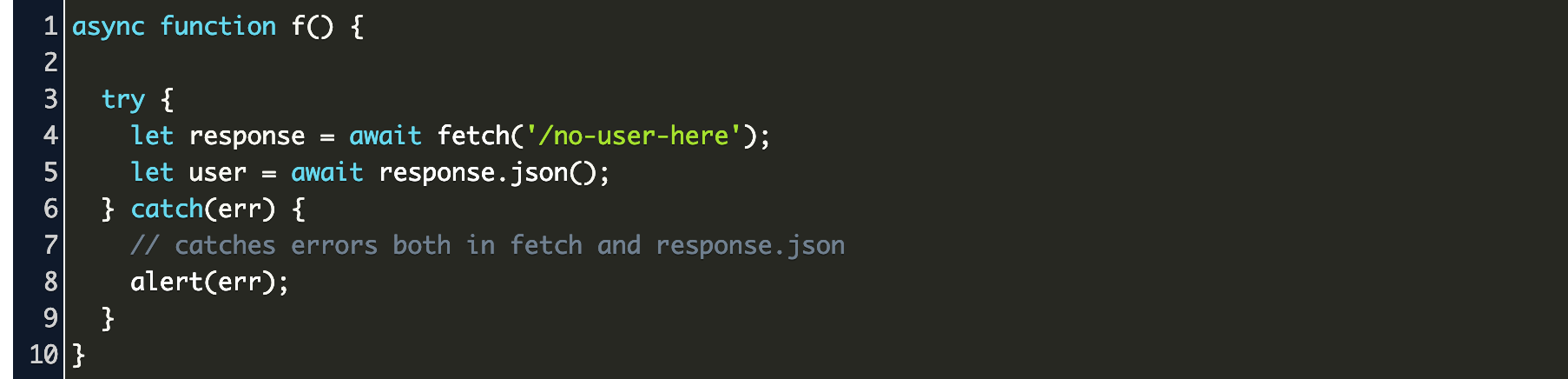 Multiple Api Calls Javascript Try Catch And Async Await Code
Multiple Api Calls Javascript Try Catch And Async Await Code
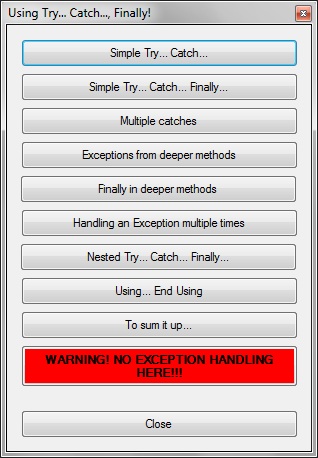 Using Try Catch Finally Codeproject
Using Try Catch Finally Codeproject
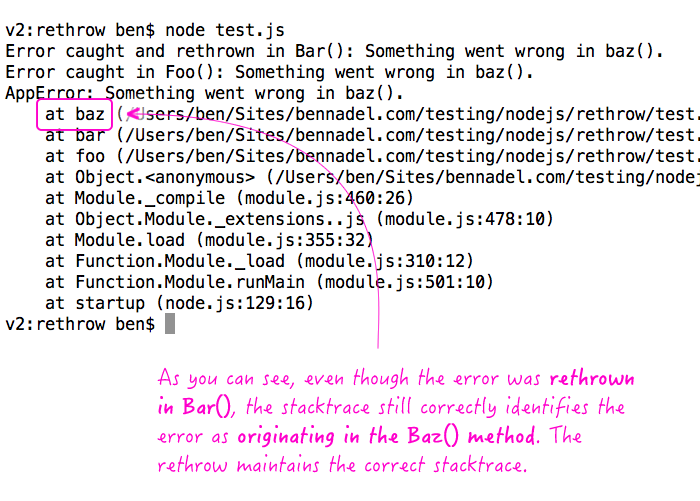 Rethrowing Errors In Javascript And Node Js
Rethrowing Errors In Javascript And Node Js
 Finally In Promises Amp Try Catch Dev Community
Finally In Promises Amp Try Catch Dev Community
Error Handling Try Catch Semantic Portal Learn Smart
 Error Handling With Async Await In Js By Ian Segers Itnext
Error Handling With Async Await In Js By Ian Segers Itnext
 Php Exceptions Try Catch For Error Handling
Php Exceptions Try Catch For Error Handling
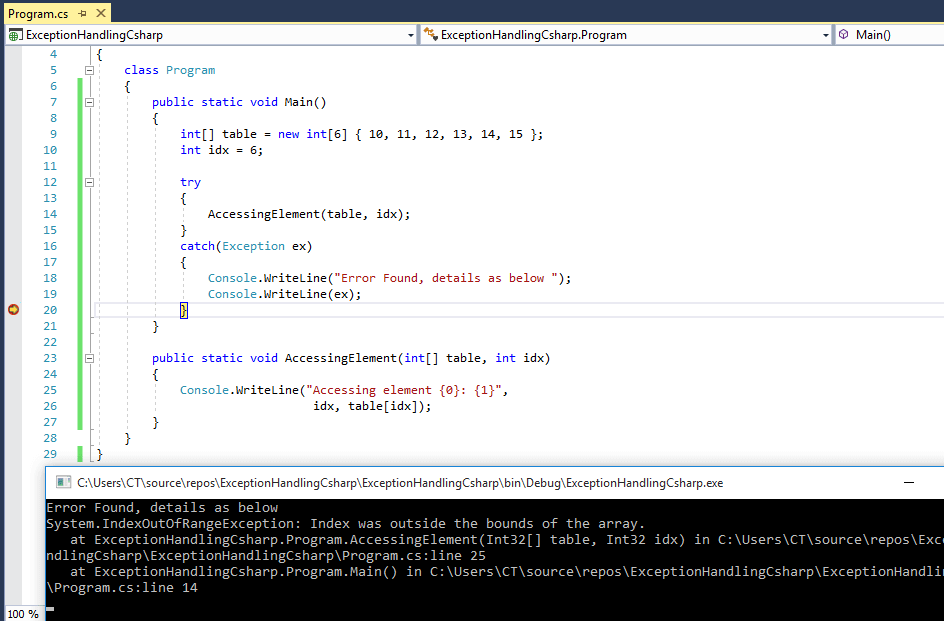 C Exception Handling In C With Try Catch Finally Block
C Exception Handling In C With Try Catch Finally Block
 What Exceptions Cannot Be Caught By Try Catch By Bytefish
What Exceptions Cannot Be Caught By Try Catch By Bytefish
0 Response to "22 Javascript Try Catch Syntax"
Post a Comment