22 Not Equal Operator Javascript
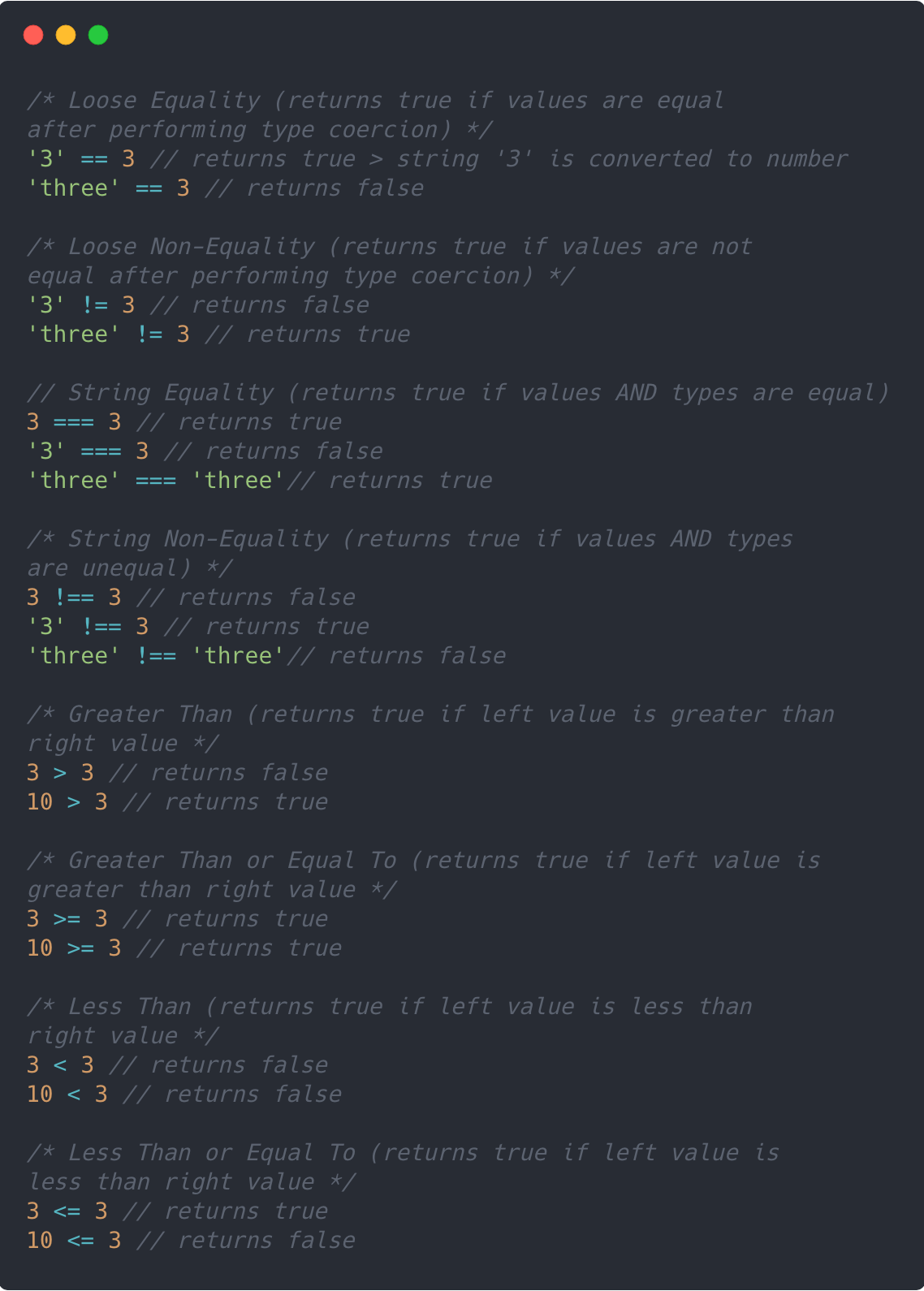
Not equal value or Not equal type is an comparison operator which is used to check whether the two operands are having not equal value or not equal type. The symbolic representation of Not equal value or Not equal type is !==. In this any one should be different either value or type. When comparing a string with a number, JavaScript will convert the string to a number when doing the comparison. An empty string converts to 0. A non-numeric string converts to NaN which is always false. When comparing two strings, "2" will be greater than "12", because (alphabetically) 1 is less than 2.
 Javascript Comparison Operators
Javascript Comparison Operators
Each bit in the operand is inverted in the result. The truth table for the NOT operation is: Bitwise NOTing any number x yields - (x + 1). For example, ~-5 yields 4. Note that due to using 32-bit representation for numbers both ~-1 and ~4294967295 (2^32 - 1) results in 0.

Not equal operator javascript. This is the strict not equal operator and only returns a value of true if both the operands are not equal and/or not of the same type. The following examples return a Boolean true: a !== b a !== "2" 4 !== '4' Bit operators work on 32 bits numbers. Any numeric operand in the operation is converted into a 32 bit number. The result is converted back to a JavaScript number. The examples above uses 4 bits unsigned examples. But JavaScript uses 32-bit signed numbers. Because of this, in JavaScript, ~ 5 will not return 10. It will return -6. The strict inequality operator (!==) is the logical opposite of the strict equality operator. It means "Strictly Not Equal" and returns true where strict equality would return false and vice versa. Strict inequality will not convert data types. For example 1 !== '1' will return true since 1 is an integer and '1' is a character and ...
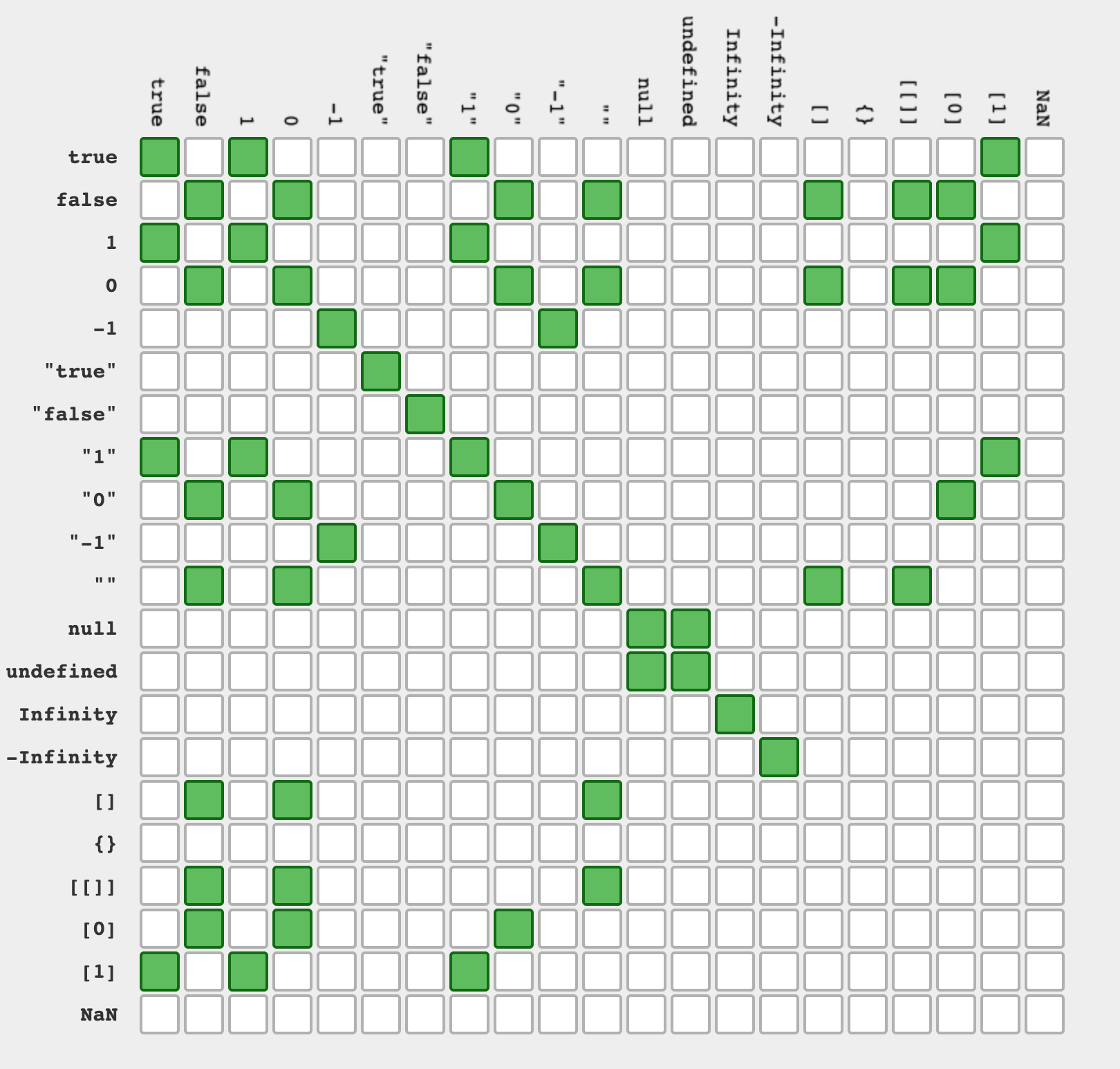
The logical NOT (!) operator (logical complement, negation) takes truth to falsity and vice versa. It is typically used with Boolean (logical) values. When used with non-Boolean values, it returns false if its single operand can be converted to true; otherwise, returns true. Greater than or equal operator. Note: => is not an operator, but the notation for Arrow functions. Since we used the === operator on this occasion, and because this operator does not do any type conversion, we see that the string value "3" and the number 3 are not the same after all. When in doubt, a relatively safe choice is simply to use the identity operator (===) as a matter of habit.
not equal to in js. react native conditional rendering. react propthpes or. return <Text> using if condition react native. ternary operator react. Use the conditional operator in the checkEqual function to check if two numbers are equal or not. The function should return either "Equal" or "Not Equal". Although not the most common use of a logical operator in JavaScript, ... NOT operator is the only logical operator that will always ... so the ! of !true (i.e.,false)will also equal true and so ... The strict inequality operator checks whether its operands are not equal. It is the negation of the strict equality operator so the following two lines will always give the same result: x !== y !(x === y) For details of the comparison algorithm, see the page for the strict equality operator.
Example of JavaScript Not equal (!=) operator The following function first evaluates if the condition (num != 55) evaluates to true. If it does, it returns the statement between the curly braces ("Not equal"). If it doesn't, it returns the next return statement outside them ("Equal"). Not equal (!==) Not equal is an comparison operator which is used to check the value of two operands are equal or not. If the value of two operands are not equal it returns true. The symbolic representation of Not equal operator in JavaScript is !=. Example 3: Strict Equal to Operator const a = 2; // strict equal operator console.log(a === 2); // true console.log(a === '2'); // false === evaluates totrue if the operands are equal and of the same type. Here 2 and '2' are the same numbers but the data type is different. And === also checks for the data type while comparing.
Before getting into equality operators its important that you understand data types in javascript. Javascript is a loosely typed and dynamic language. The variable is dynamically associated with a… For example, in the Equal operator we can write same value in different types gives the same result, like we declared var a = 5 and we are assigning a == 5 or a == "5" to the opertor gives the same result, but in Equal value and Equal type operator it is not possible. The symbolic representation of equal value and equal type is ===. JavaScript also inherits and extends the same concept and provides two variants of operators for comparing whether two operands are equal or not. In this article, we will discuss the Equality operator in JavaScript as well as the Inequality operator along with their differences.
=== (Triple equals) is a strict equality comparison operator in JavaScript, which returns false for the values which are not of a similar type. This operator performs type casting for equality. If we compare 2 with "2" using ===, then it will return a false value. Logical Operators. The logical operators used in Javascript are listed below: is true if both a and b are true. is true if either a or b is true. Logical NOT ( ! ) is true if a is not true. The following conditions are true : The following conditions are false : AND OR NOT Equal logical operators Logical operators are mostly consist of AND OR NOT and its combinations. We will discuss more on this with examples for better understanding. We will use if condition to check and then document.write to print the result. Here is the code. AND is also written as && OR is written as || NOT is written as ! NOT EQAL TO !=
7/7/2017 · The strict not equal operator (!==) will only return a Boolean True if both the operands are not equal in value and are not of the same type. The strict equal operator (===) will only return a… Operator Description Example == Equal to: returns true if the operands are equal: x == y!= Not equal to: returns true if the operands are not equal: x != y === Strict equal to: true if the operands are equal and of the same type: x === y!== Strict not equal to: true if the operands are equal but of different type or not equal at all: x !== y > Greater than: true if left operand is greater than ... What is equal to (===) Operator in JavaScript? Triple equals(===) is a strict equality comparison operator in JavaScript, that returns false for the values which are not of a similar type. It performs type casting for equality. Uses of equal to (=) Operator in JavaScript. These are the following important uses of = in JavaScript: It assigns the ...
JavaScript not equal to operator. Following this is the not equal to operator, which can evaluate if a comparison is not correct. 5!= 5; // false 8!= 5; // true '8'!= 5; // true 'String'!= 'string'; // true 'string'!= 'string'; // false JavaScript strict operators. Then we have these two as strict versions, which should be preferred over the ... "not equal to operator javascript" Code Answer's. javascript does not equal . javascript by A// on Jun 03 2020 Comment . 4. javascript not equal . javascript by 2 Programmers 1 Bug on Mar 13 2020 Donate Comment . 4 not equal to in js . javascript by ... When you need to convert a truthy or falsey value to a real boolean value the not operator (!) is your friend. The JavaScript Not Operator (!) Lets revisit the previous example and change it so the if statement evaluates to true: if (!0) { //this will execute }
JavaScript if not means simply if the value of two operands are not equal it returns true. You have to use not equal in if/else statement. How to representation not equal in JS? Here is symbol representation of not equal !=. !!foo applies the unary not operator twice and is used to cast to boolean type similar to the use of unary plus +foo to cast to number and concatenating an empty string ''+foo to cast to string. Instead of these hacks, you can also use the constructor functions corresponding to the primitive types (without using new) to explicitly cast values, ie In most cases, if the two operands are not of the same type, JavaScript attempts to convert them to an appropriate type for the comparison. This behavior generally results in comparing the operands numerically.
 Week 4 Workin It Out With Javascript By Zac Heisey Medium
Week 4 Workin It Out With Javascript By Zac Heisey Medium
 How To Use Does Not Equal In Google Sheets Comparison Operators
How To Use Does Not Equal In Google Sheets Comparison Operators
 Introduction To Javascript 5 If Statements Mvcode
Introduction To Javascript 5 If Statements Mvcode
 Using A Does Not Equal Operator In Excel Deskbright
Using A Does Not Equal Operator In Excel Deskbright
 Which Equals Operator Vs Should Be Used In
Which Equals Operator Vs Should Be Used In
 Comparison With The Inequality Operator Fyi Error In
Comparison With The Inequality Operator Fyi Error In
 Equality Operators In Javascript Vs Code Wala
Equality Operators In Javascript Vs Code Wala
Abdlulwahab Php Comparison Operators
 Lua Not Equal How Not Equal Operator Works In Lua
Lua Not Equal How Not Equal Operator Works In Lua
 Javascript Vs Comparison Operator Geeksforgeeks
Javascript Vs Comparison Operator Geeksforgeeks
 Javascript Triple Equals Sign Vs Double Equals Sign
Javascript Triple Equals Sign Vs Double Equals Sign
Comparison Operators Fields Of Study Abstract Principal Terms
 Vba Comparison Operators Not Equal Less Than Or Equal To
Vba Comparison Operators Not Equal Less Than Or Equal To
 Not Equal Sign How To Type The Does Not Equal Symbol
Not Equal Sign How To Type The Does Not Equal Symbol
 Which Equals Operator Vs Should Be Used In
Which Equals Operator Vs Should Be Used In
 Should I Use Or Equality Comparison Operator In
Should I Use Or Equality Comparison Operator In
 These Are Some Of The Most Important Logical Operators In
These Are Some Of The Most Important Logical Operators In
Not Equal Comparison Operator In Javascript
 Enabling Intellij S Fancy Not Equal To Operator Stack
Enabling Intellij S Fancy Not Equal To Operator Stack
 Which Equals Operator Vs Should Be Used In
Which Equals Operator Vs Should Be Used In
 Sql Comparison Operators Equal Not Equal Less Than Grater
Sql Comparison Operators Equal Not Equal Less Than Grater
0 Response to "22 Not Equal Operator Javascript"
Post a Comment