20 Make New Promise Javascript
In JavaScript, we can create a new Promise with new Promise(), which takes in a function as an argument: (resolve, reject) => {}. In this function, resolve and reject are callback functions that are provided by default in JavaScript. Let's take a closer look at the code above. When we run the onMyBirthday function, after 2000ms: A JavaScript Promise object contains both the producing code and calls to the consuming code: Promise Syntax let myPromise = new Promise(function(myResolve, myReject) {
 Promises In Javascript Lets Understand Them By Krishankant
Promises In Javascript Lets Understand Them By Krishankant
In general, there are 4 ways to create a new promise in JavaScript: Using the Promise constructor Using the static helpers Promise.resolve () and Promise.reject () Chaining with the then () function or catch () function

Make new promise javascript. function getData() { return new Promise(); } That seems very simple. But right now, our function doesn't do anything, at least not what we want it to do, that is, to get some data. The Promise constructor takes two arguments. The Promise.resolve() method returns a Promise object that is resolved with a given value. If the value is a promise, that promise is returned; if the value is a thenable (i.e. has a "then" method), the returned promise will "follow" that thenable, adopting its eventual state; otherwise the returned promise will be fulfilled with the value.. This function flattens nested layers of promise-like ... Use Promises over Callbacks, and How to Create a New Promise in Javascript. ... If you want to create a new promise, you would simply need to create a new instance of this class.
Promise.resolve () and Promise.reject () are shortcuts to manually create an already resolved or rejected promise respectively. This can be useful at times. Promise.all () and Promise.race () are two composition tools for running asynchronous operations in parallel. We can start operations in parallel and wait for them all to finish like this: An introduction to JavaScript Promises # A Promise is a JavaScript object (everything is an object in JS) that represents an asynchronous function. // Create a Promise object var sayHello = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) { // In 5 seconds, resolve the Promise. // Pass along "Hi, universe!" Creating a Promise. We create an instance of a promise by calling new on the Promise class, like so: TypeScript. Copy. var promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => { }); We pass to Promise an inner function that takes two arguments (resolve, reject).
The constructor syntax for a promise object is: let promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) { // executor (the producing code, "singer") }); The function passed to new Promise is called the executor. When new Promise is created, the executor runs automatically. const delay = ms => new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, ms)); See a snippet and comments for each of the options below. 1. With for. You can use a for loop, but you must make sure it doesn't create all promises synchronously. Instead you create an initial immediately resolving promise, and then chain new promises as the previous ones ... Also, create a new folder named src inside the typescript folder.. Simplify Async Callback Functions using Async/Await. Lets see how we can write a Promise and use it in async await.This method helps simplify the code inside functions like setTimeout.. Create a new file inside src folder called index.ts.We'll first write a function called start that takes a callback and calls it using the ...
Promise.all ([promises]) method takes an array of promises and returns a new promise. This promise will be fulfilled when and if all promises are fulfilled. Promise.race ([promises]) also takes an... how to write promise; create a new promise javascript; create a new promise using ono js; javascript create promise with simple return; using promise; understand promise in javascript; how does a promise work; js creating a new promise; Promise.new() create a promise javascript example; how to define promise in javascript; how to create new promise You can create a promise using the promise constructor like this: let promise = new Promise (function (resolve, reject) { // Make an asynchronous call and either resolve or reject }); In most cases, a promise may be used for an asynchronous operation. However, technically, you can resolve/reject on both synchronous and asynchronous operations.
Promise, in Javascript, is a concept which allows the callee function to send back a promise (sort of assurance) to the caller function that it would, for sure, send back a resolution, be it a success or a failure at a little later point of time. The caller believes the callee if a promise is sent back, and, proceeds ahead with the program ... Creating a new Promise A Promise object is created using the new keyword and its constructor. This constructor takes a function, called the "executor function", as its parameter. This function should take two functions as parameters. What is a promise? A JavaScript promise is an object that represents the completion or failure of an asynchronous task and its resulting value.¹. The end. I'm kidding of course. So, what does that definition even mean? First of all, many things in JavaScript are objects. You can create an object a few different ways.
this might seem a silly question but I am a newbie in this topic. I am working on promises on node js. And I want to pass parameter to a promise function. However I could not figure it out. someMo... Promises in JavaScript represent processes that are already happening, which can be chained with callback functions. If you are looking to lazily evaluate an expression, consider the arrow function with no arguments: f = () => expression to create the lazily-evaluated expression, and f () to evaluate. how to make promise in javascript; new Promise javascript; return new Promise((resolve, reject) => creating a promise in javascript; js promise example; do you need promises for object creation; what is promises in java script; what is promise resolve and reject; how to create promise object in javascript; how promises resolve reject fufilled works
On the other hand, fulfilled is one of 3 states a promise can be in, and once a promise transitions to fulfilled, JavaScript executes any onFulfilled callbacks you passed to the then() function. With the Promise Constructor. When you create a promise using new, you call the Promise constructor. Promise.all takes an array of promises (it technically can be any iterable, but is usually an array) and returns a new promise.. The new promise resolves when all listed promises are resolved, and the array of their results becomes its result. For instance, the Promise.all below settles after 3 seconds, and then its result is an array [1, 2, 3]: A great example of chaining promises is the Fetch API, which we can use to get a resource and queue a chain of promises to execute when the resource is fetched. The Fetch API is a promise-based mechanism, and calling fetch() is equivalent to defining our own promise using new Promise(). Example of chaining promises
How to make a Promise out of a Callback function in JavaScript Back-end developers run into challenges all the time while building applications or testing code. As a developer who is fairly new and getting acquainted with those challenges, I have never run into a challenge or inconvenience more frequently — or more memorable — than with ... Then, all your logic flow is using promises and you won't see the new Promise(...) boilerplate in the regular flow of your code. Further, you can generally avoid manually promisifying these days. If you're using node.js, then util.promisify() can be used to create a promisified version of any async function following the node.js calling convention. Here the first .then shows 1 and returns new Promise(…) in the line (*).After one second it resolves, and the result (the argument of resolve, here it's result * 2) is passed on to handler of the second .then.That handler is in the line (**), it shows 2 and does the same thing.. So the output is the same as in the previous example: 1 → 2 → 4, but now with 1 second delay between alert ...
Introduction. Promises offer a better way to handle asynchronous code in JavaScript. Promises have been around for a while in the form of libraries, such as: The promise libraries listed above and promises that are part of the ES2015 JavaScript specification (also referred to as ES6) are all Promises/A+ compatible. Promise.all () The Promise.all () method takes an iterable of promises as an input, and returns a single Promise that resolves to an array of the results of the input promises. This returned promise will resolve when all of the input's promises have resolved, or if the input iterable contains no promises. A promise in JavaScript is similar to a promise in real life. When we make a promise in real life, it is a guarantee that we are going to do something in the future. Because promises can only be made for the future. A promise has 2 possible outcomes: it will either be kept when the time comes, or it won't.
 Adding A Promise To Sequence If Condition Is Met Stack Overflow
Adding A Promise To Sequence If Condition Is Met Stack Overflow
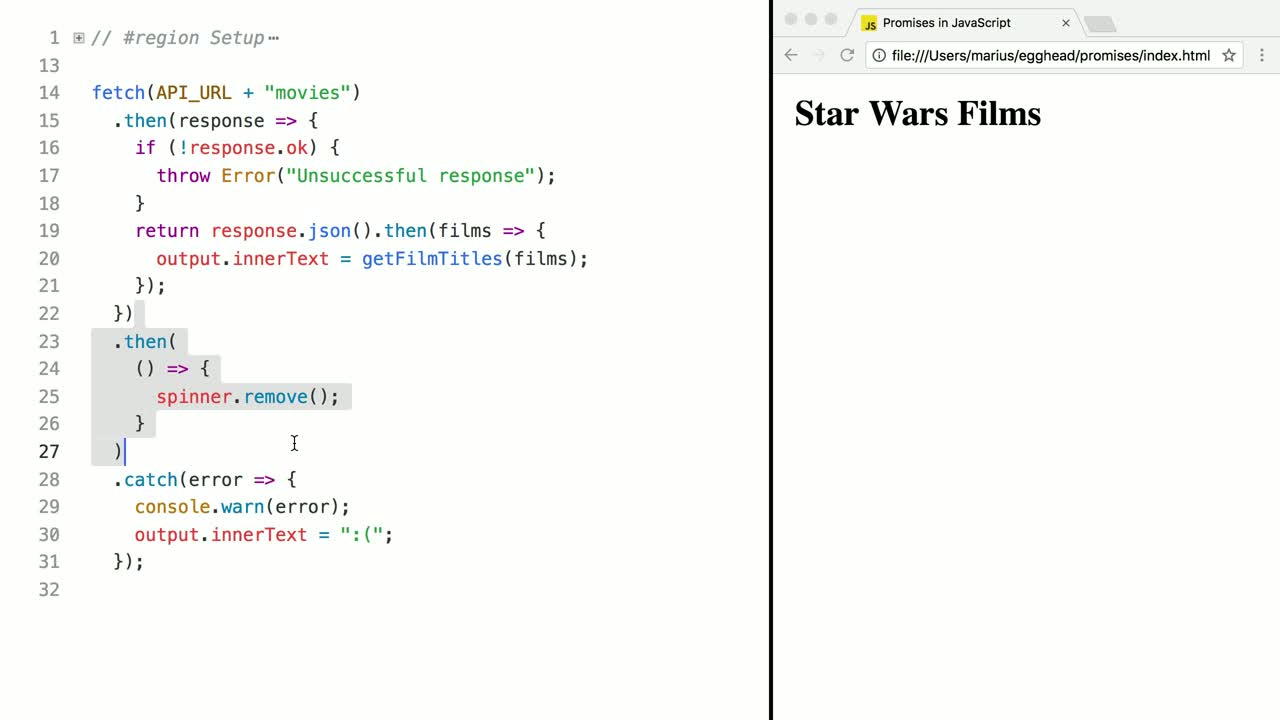 Execute Cleanup Logic In A Javascript Promise Chain With Promise Prototype Finally
Execute Cleanup Logic In A Javascript Promise Chain With Promise Prototype Finally
 The Javascript Promise Tutorial Adrian Mejia Blog
The Javascript Promise Tutorial Adrian Mejia Blog
 Keep Your Promises In Typescript Using Async Await By Gilad
Keep Your Promises In Typescript Using Async Await By Gilad
 How To Make Promise All Of Multiple Parallel Child Promises
How To Make Promise All Of Multiple Parallel Child Promises
 Async Await Vs Promises A Guide And Cheat Sheet By Kait
Async Await Vs Promises A Guide And Cheat Sheet By Kait
 Use Promises Over Callbacks And How To Create A New Promise
Use Promises Over Callbacks And How To Create A New Promise
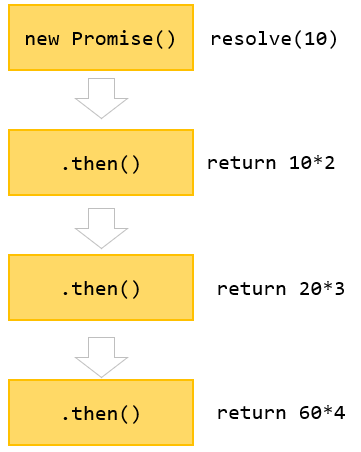 Promise Chaining In Javascript
Promise Chaining In Javascript
What Is A Promise In Javascript
 How To Create A New Promise In Javascript Bonsaiilabs
How To Create A New Promise In Javascript Bonsaiilabs
 How To Make Promise Resolve To Trigger In The Else Statement
How To Make Promise Resolve To Trigger In The Else Statement
Promises In Js How Many Times Have You Done A Callback By
 Javascript Promise And Promise Chaining
Javascript Promise And Promise Chaining
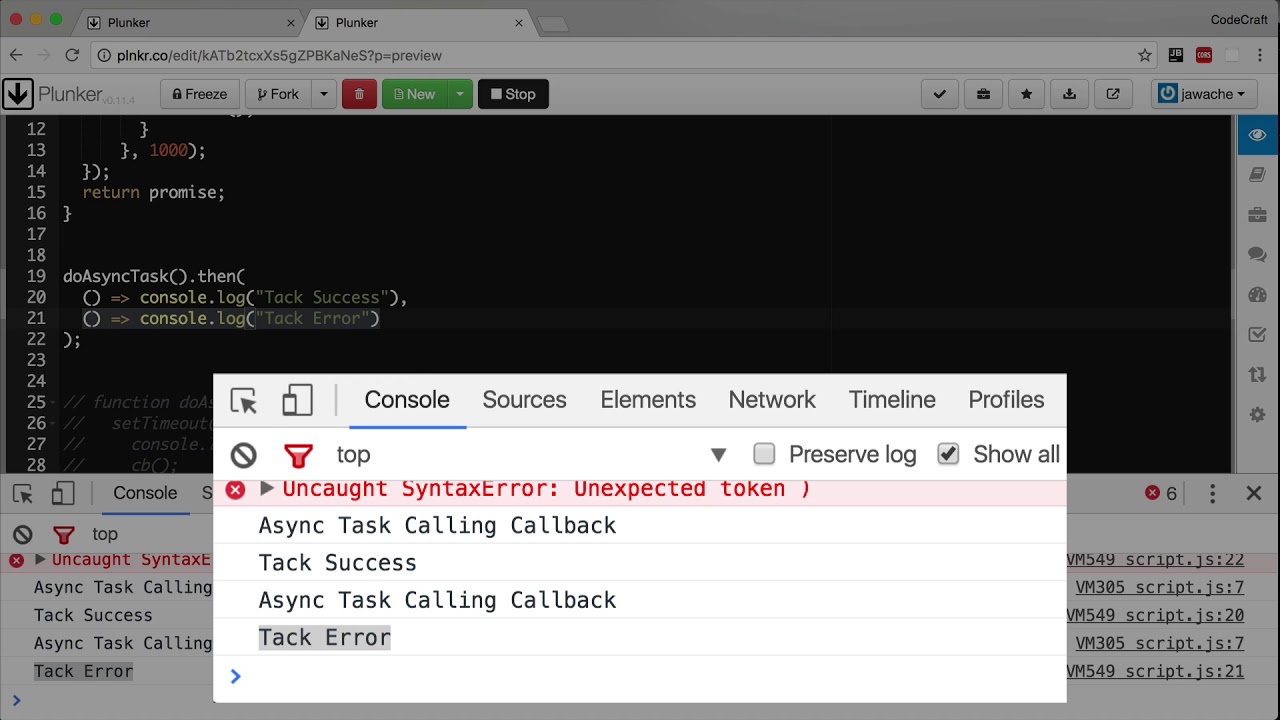


0 Response to "20 Make New Promise Javascript"
Post a Comment