29 What Is Promise In Javascript With Example
21/7/2021 · Promises are used to handle asynchronous operations in JavaScript. They are easy to manage when dealing with multiple asynchronous operations where callbacks can create callback hell leading to unmanageable code. Prior to promises events and callback functions were used but they had limited functionalities and created unmanageable code. Promises used in JavaScript for asynchronous programming. For asynchronous programming, JavaScript used callbacks but there is a problem using the callback which is callback hell or Pyramid of Doom. Using the ES6 Promise will simply avoid all the problems associated with the callback.
What Is Promise Try And Why Does It Matter Joepie91 S
With ES2015, JavaScript finally introduced the Promise: an object that may or may not contain some value at some point in the future. Promises offer a powerful and legible syntax for writing asynchronous code in JavaScript. This post assumes a basic understanding of Promises and how they work.

What is promise in javascript with example. In JavaScript promise is the same as a promise we make in real life. When we make a promise in real life, it is assured that we are going to do keep in the future. As promises can only be made for the future. A promise has 2 general outputs: it will either be kept when the time comes, or it won't. A Promise is an object representing the eventual completion or failure of an asynchronous operation. Essentially, a promise is a returned object you attach callbacks to, instead of passing callbacks into a function. The example given below shows a function add_positivenos_async () which adds two numbers asynchronously. The promise is resolved if positive values are passed. The promise is rejected if negative values are passed.
Well organized and easy to understand Web building tutorials with lots of examples of how to use HTML, CSS, JavaScript, SQL, Python, PHP, Bootstrap, Java, XML and more. ... "async and await make promises easier to write" async makes a function return a Promise. await makes a function wait for a Promise. A promise in JavaScript is similar to a promise in real life. When we make a promise in real life, it is a guarantee that we are going to do something in the future. Because promises can only be made for the future. A promise has 2 possible outcomes: it will either be kept when the time comes, or it won't. Promise Object Properties. A JavaScript Promise object can be: Pending; Fulfilled; Rejected; The Promise object supports two properties: state and result. While a Promise object is "pending" (working), the result is undefined. When a Promise object is "fulfilled", the result is a value. When a Promise object is "rejected", the result is an error object.
A promise is a method that eventually produces a value. It can be considered as the asynchronous counterpart of a getter function. Its essence can be explained as: promise.then (function (value) { // Do something with the 'value' }); The Promise.all() method takes an iterable of promises as an input, and returns a single Promise that resolves to an array of the results of the input promises. This returned promise will resolve when all of the input's promises have resolved, or if the input iterable contains no promises. It rejects immediately upon any of the input promises rejecting or non-promises throwing an error, and ... ES6 came with many new features, but one of the best features was the official introduction of Promises. Promises allow you to write clean non-callback-centr...
Promise Chaining in JavaScript. The methods of the Promise object such as promise.then (), promise.catch () and promise.finally () are used to connect further actions with a promise that becomes settled. These methods also return a separate newly generated promise object. Therefore, we can call the promise's instance method on the returned ... wait — promise example on CodePen Our wait (3000) call will wait 3000ms (3 seconds), and then log 'Hello!'. All spec-compatible promises define a.then () method which you use to pass handlers which... Promises are an important concept that is essential for a JavaScript developer to understand. If this concept is clear, the developer can utilize promises in a variety of ways in their day-to-day ...
In JavaScript, a promise is just like a promise that you make in real life to show that you are committed to doing something. For example, I promise to get good marks in mathematics, and then this Promise has two outcomes, either it will be fulfilled (or resolved) or not fulfilled (or be rejected). 31/3/2021 · A promise is a special JavaScript object that links the “producing code” and the “consuming code” together. In terms of our analogy: this is the “subscription list”. The “producing code” takes whatever time it needs to produce the promised result, and the “promise” makes that result available to all of the subscribed code when it’s ready. A Promise in JavaScript is a object representing a value which may be available in the future. For example, when asking the JavaScript runtime to make a request to Twitter, it might give you a Promise of the HTTP response instead of giving you the response immediately. We can use this promise object to get the response later.
Software Requirements and Conventions Used What is a "promise"? In Javascript, a promise is an object returned as the result of an asynchronous, non blocking operation, such, for example, the one performed by the fetch Promise, in Javascript, is a concept which allows the callee function to send back a promise (sort of assurance) to the caller function that it would, for sure, send back a resolution, be it a success or a failure at a little later point of time. The caller believes the callee if a promise is sent back, and, proceeds ahead with the program ... Introduction. Javascript Promises can be challenging to understand. Therefore, I would like to write down the way I understand promises. Understanding Promises. A Promise in short: "Imagine you are a kid.Your mom promises you that she'll get you a new phone next week.". You don't know if you will get that phone until next week. Your mom can really buy you a brand new phone, or she ...
In the above example, add() is a function and it is passed to function display() as a callback. Promise: A promise is an object which is used to handle the asynchronous result of an operation. The promise constructor takes one argument, a callback function with two parameters, resolve and reject. A promise is an object that may produce a single value some time in the future : either a resolved value, or a reason that it's not resolved (e.g., a network error occurred).... Promises are eager, meaning that a promise will start doing whatever task you give it as soon as the promise constructor is invoked. Where can I use promises? Here the first .then shows 1 and returns new Promise(…) in the line (*).After one second it resolves, and the result (the argument of resolve, here it's result * 2) is passed on to handler of the second .then.That handler is in the line (**), it shows 2 and does the same thing.. So the output is the same as in the previous example: 1 → 2 → 4, but now with 1 second delay between alert ...
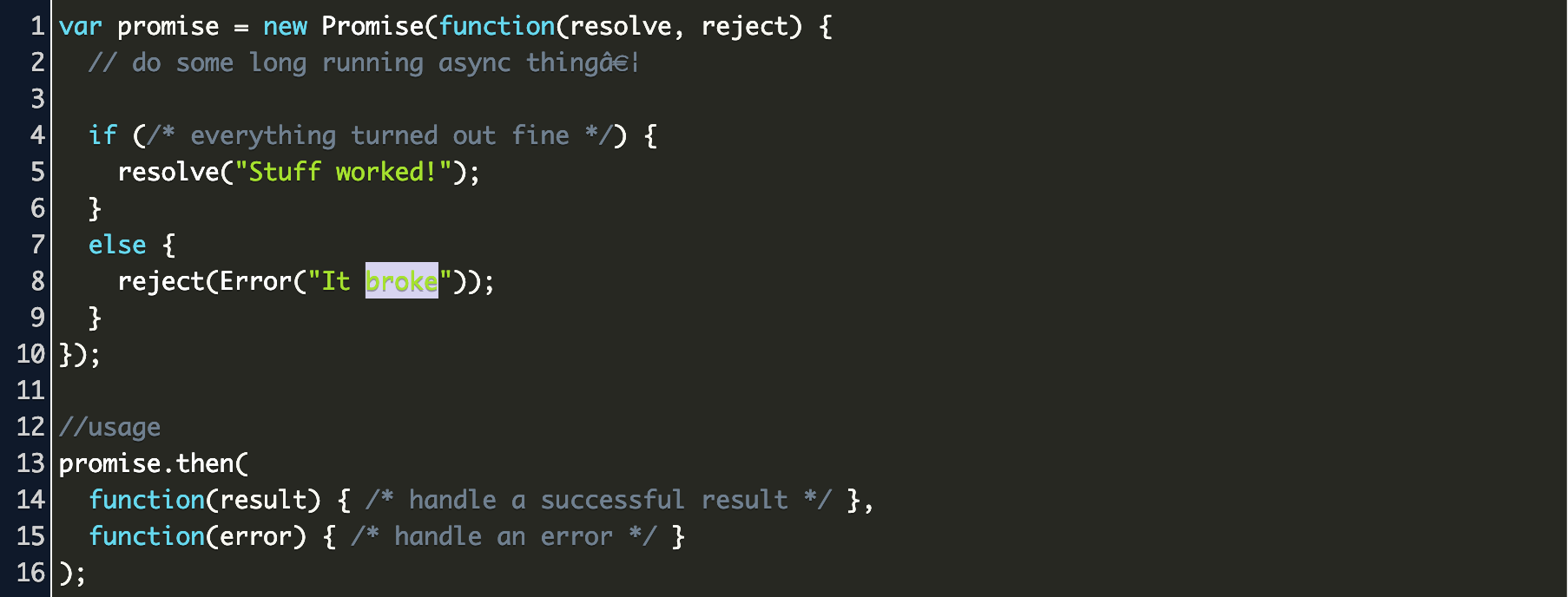
15/1/2020 · JavaScript is single threaded, meaning that two bits of script cannot run at the same time; they have to run one after another. A Promise is an object that represents the eventual completion (or failure) of an asynchronous operation, and its resulting value. var promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) { // do thing, then… This small example shows the mechanism of a Promise. The testPromise () method is called each time the <button> is clicked. It creates a promise that will be fulfilled, using WindowOrWorkerGlobalScope.setTimeout, to the promise count (number starting from 1) every 1-3 seconds, at random. The Promise () constructor is used to create the promise. Promise in Javascript is very much just like an everyday promise you make with your friend, parent or your spouse but there is a difference…. Instead of being highly optimistic that the other ...
How can the Promise class help us? First off, everyone uses it because it is now the standard way to deal with asynchronous code... so we have to use it. Following the standard is always the best thing to do. Now that we know that, here is a simple example of how to use a promise.
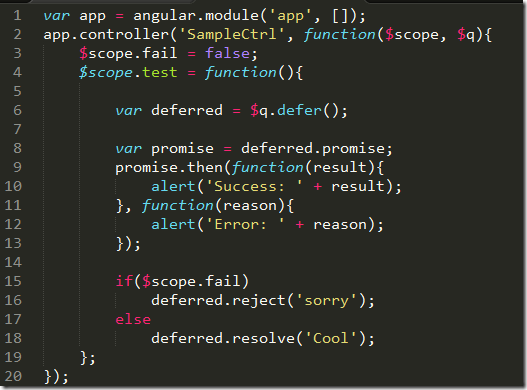 Angularjs Part 11 Promises Los Techies
Angularjs Part 11 Promises Los Techies
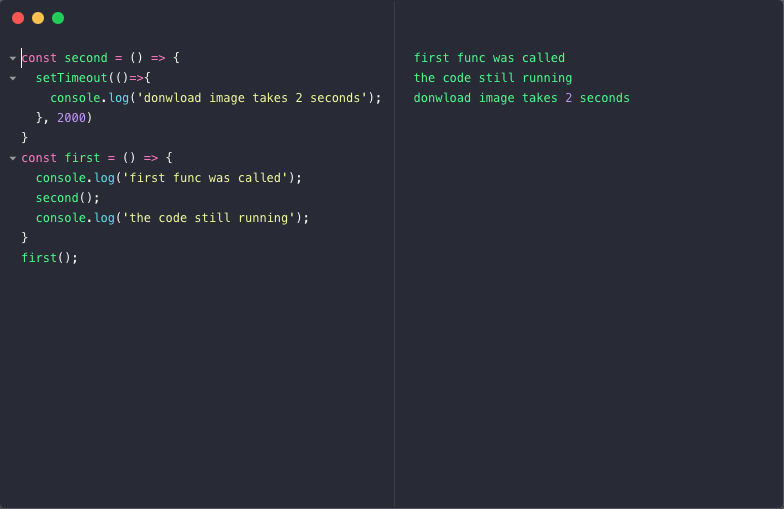 Callback Hell Promises And Async Await
Callback Hell Promises And Async Await
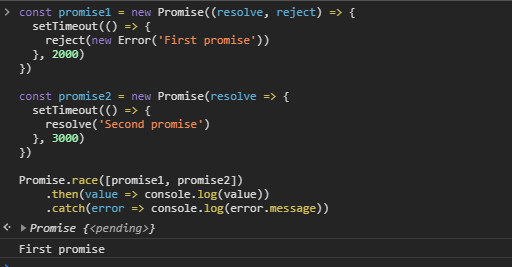 Dealing With Multiple Promises In Javascript By Edvinas
Dealing With Multiple Promises In Javascript By Edvinas
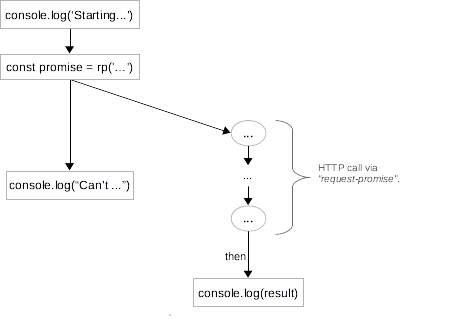 Await And Async Explained With Diagrams And Examples
Await And Async Explained With Diagrams And Examples
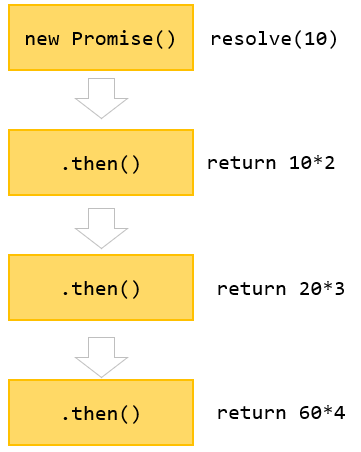 Promise Chaining In Javascript
Promise Chaining In Javascript
Github Stevekane Promise It Wont Hurt A Workshopper Module
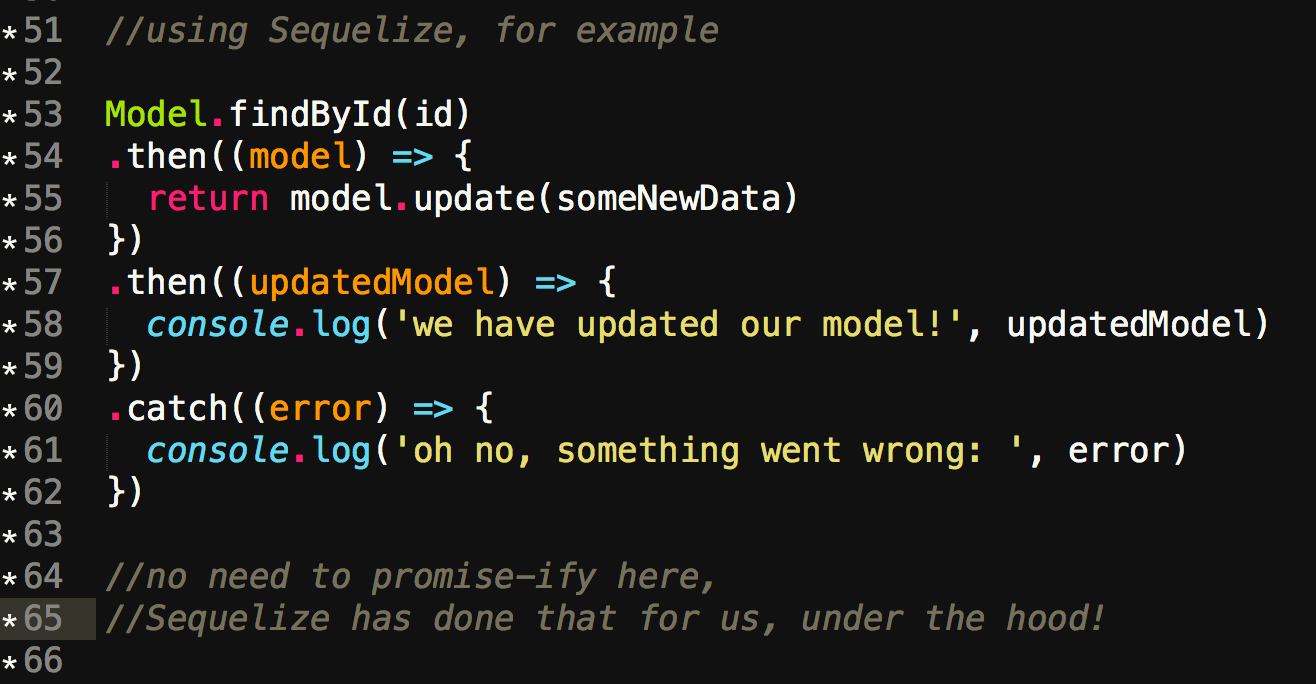 Javascript Promises In Sixteen Minutes By Leigh Steiner
Javascript Promises In Sixteen Minutes By Leigh Steiner
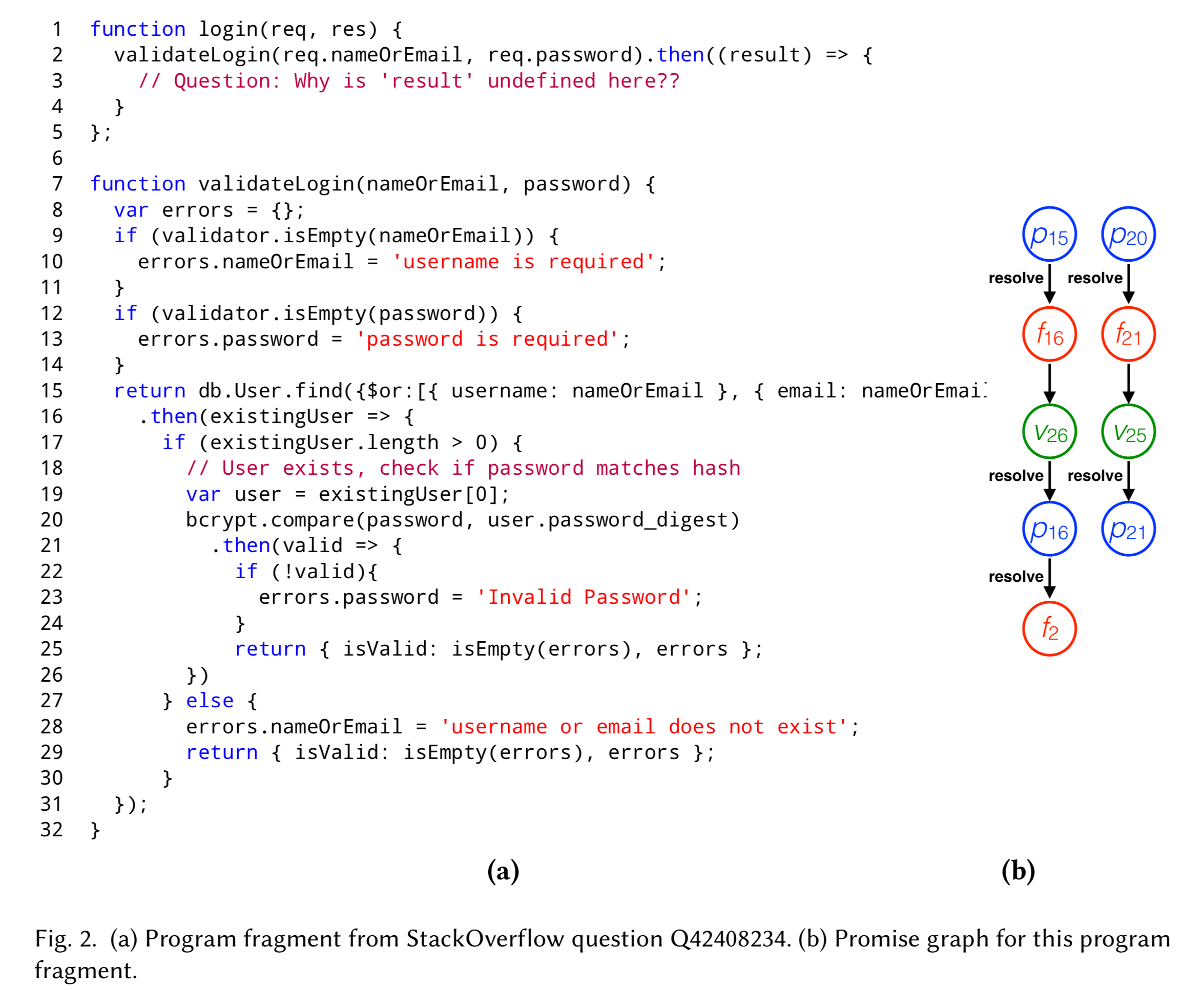 A Model For Reasoning About Javascript Promises The Morning
A Model For Reasoning About Javascript Promises The Morning
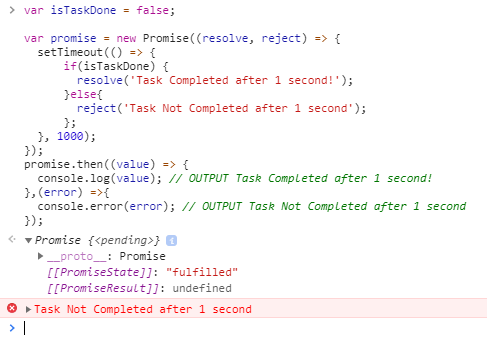 Angular 12 Javascript Promise Example Freaky Jolly
Angular 12 Javascript Promise Example Freaky Jolly
 Overview Of Promises In Javascript
Overview Of Promises In Javascript
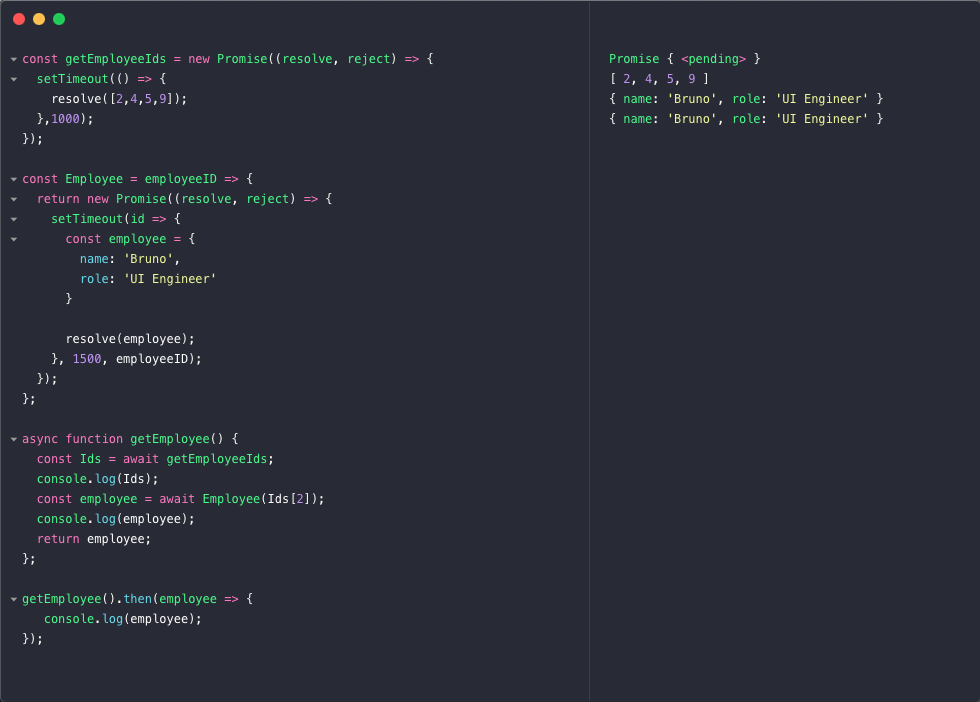 Callback Hell Promises And Async Await
Callback Hell Promises And Async Await
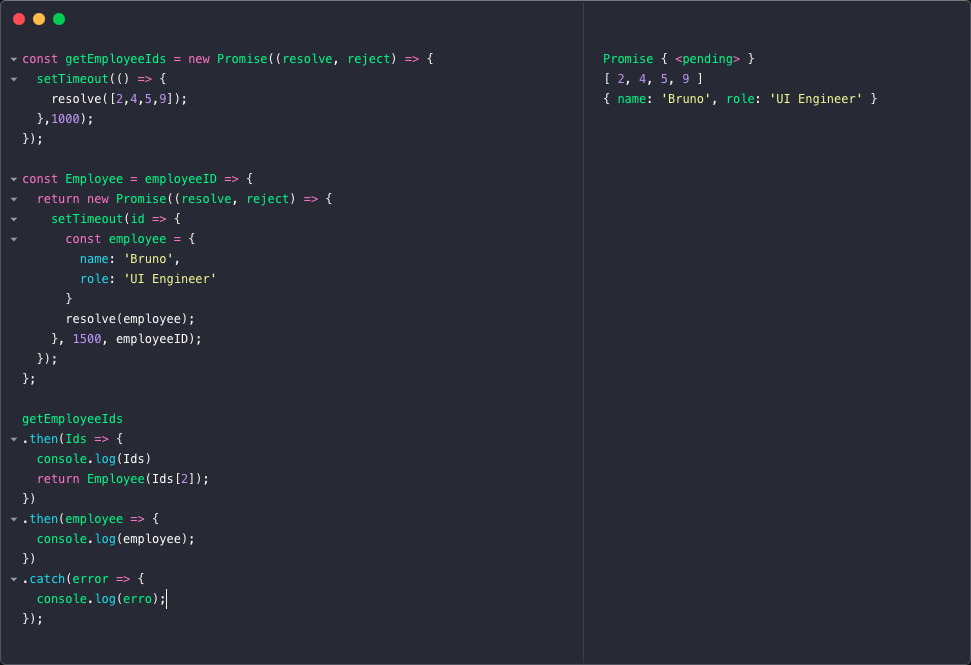 Callback Hell Promises And Async Await
Callback Hell Promises And Async Await
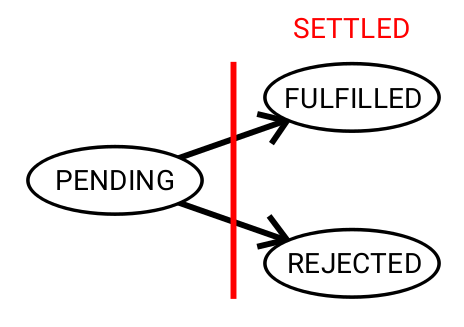 The Promise Then Function In Javascript Mastering Js
The Promise Then Function In Javascript Mastering Js
 Understanding Javascript Promises Digitalocean
Understanding Javascript Promises Digitalocean
Javascript Promises Tutorial How To Use Them Ictshore Com
 Read The Body Of A Fetch Promise Stack Overflow
Read The Body Of A Fetch Promise Stack Overflow
What Is A Promise In Javascript
 A Quick Introduction To Promises And Async Await With
A Quick Introduction To Promises And Async Await With
 Should I Use Promises Or Async Await Hacker Noon
Should I Use Promises Or Async Await Hacker Noon
 Javascript Promise And Promise Chaining
Javascript Promise And Promise Chaining
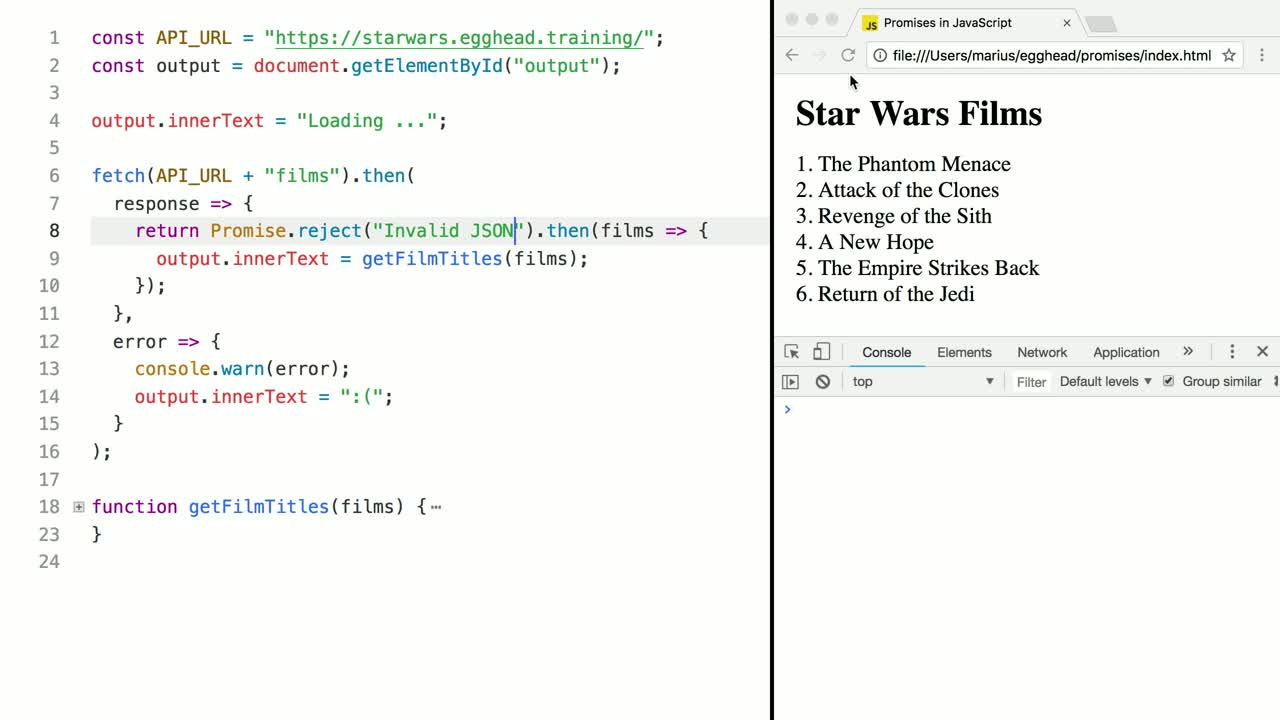 Javascript Promises In Depth Egghead Io
Javascript Promises In Depth Egghead Io
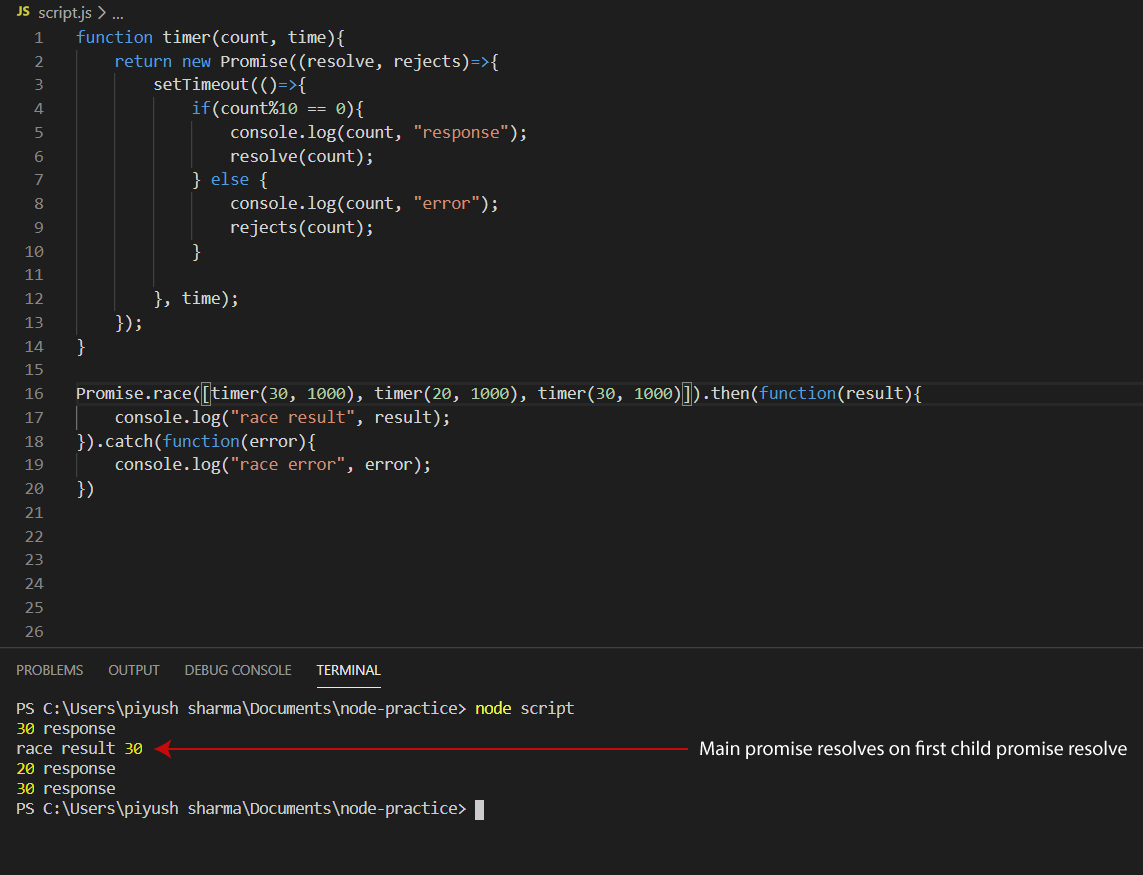 Javascript Promises In 5 Concepts By Piyush Sharma Codeburst
Javascript Promises In 5 Concepts By Piyush Sharma Codeburst
 Cleaning Up Asynchronous Javascript With Async Await Keywords
Cleaning Up Asynchronous Javascript With Async Await Keywords
 Understanding Promises In Javascript By Sukhjinder Arora
Understanding Promises In Javascript By Sukhjinder Arora


0 Response to "29 What Is Promise In Javascript With Example"
Post a Comment